标签:ble run conf ssi ready getname bug ini sources
首先看例子,这例子摘抄自开涛的跟我学spring3。
@Test public void testPlatformTransactionManager() { DefaultTransactionDefinition def = new DefaultTransactionDefinition(); def.setIsolationLevel(TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED); def.setPropagationBehavior(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED); TransactionStatus status = txManager.getTransaction(def); try { jdbcTemplate.update(INSERT_SQL, "test"); txManager.commit(status); } catch (RuntimeException e) { txManager.rollback(status); } } |
重要的代码在上面高亮处。
在执行jdbcTemplate.update的时候使用的是datasource.getConection获取连接。
实际上,
但是,Spring是如何保证,txManager中的conn就是jdbcTemplate中的conn的呢。从这点出发,开始看源代码。
因为是执行的jdbc操作,这里的txManager是DataSourceTransactionManager。我们来看代码:
getTransaction方法在DataSourceTransactionManager的超类中,也就是AbstractPlatformTransactionManager,我们来看方法:
public final TransactionStatus getTransaction(TransactionDefinition definition) throws TransactionException { Object transaction = doGetTransaction();
// Cache debug flag to avoid repeated checks. boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled();
if (definition == null) { // Use defaults if no transaction definition given. definition = new DefaultTransactionDefinition(); }
if (isExistingTransaction(transaction)) { // Existing transaction found -> check propagation behavior to find out how to behave. return handleExistingTransaction(definition, transaction, debugEnabled); }
// Check definition settings for new transaction. if (definition.getTimeout() < TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT) { throw new InvalidTimeoutException("Invalid transaction timeout", definition.getTimeout()); }
// No existing transaction found -> check propagation behavior to find out how to proceed. if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_MANDATORY) { throw new IllegalTransactionStateException( "No existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation ‘mandatory‘"); } else if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED || definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW || definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED) { SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources = suspend(null); if (debugEnabled) { logger.debug("Creating new transaction with name [" + definition.getName() + "]: " + definition); } try { boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER); DefaultTransactionStatus status = newTransactionStatus( definition, transaction, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources); doBegin(transaction, definition); prepareSynchronization(status, definition); return status; } catch (RuntimeException ex) { resume(null, suspendedResources); throw ex; } catch (Error err) { resume(null, suspendedResources); throw err; } } else { // Create "empty" transaction: no actual transaction, but potentially synchronization. boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() == SYNCHRONIZATION_ALWAYS); return prepareTransactionStatus(definition, null, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null); } } |
先看第一句,
Object transaction = doGetTransaction();
方法在AbstractPlatformTransactionManager中,方法为:
protected abstract Object doGetTransaction() throws TransactionException;
这是典型的模板方法设计模式,AbstractPlatformTransactionManager作为抽象类,定义了getTransaction方法,并且设置为final,然后方法内部调用的部分方法是protected abstract的,交给子类去实现。
我们来看在DataSourceTransactionManager类中的doGetTransaction方法的定义:
@Override protected Object doGetTransaction() { DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = new DataSourceTransactionObject(); txObject.setSavepointAllowed(isNestedTransactionAllowed()); ConnectionHolder conHolder = (ConnectionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(this.dataSource); txObject.setConnectionHolder(conHolder, false); return txObject; } |
注意这里,是new了一个DataSourceTransactionObject对象,重要的是高亮的两句。txObject中有一个ConnectionHolder对象,这么说来,在这一步的时候有可能已经在事务对象(DataSourceTransactionObject)中,保存了一个ConnectionHolder对象,顾名思义,ConnectionHolder中必然有Connection。如果是这样,我们只要确定,在执行jdbc操作的时候使用的Connection和这个ConnectionHolder中的是同一个就可以了。我们先看ConnectionHolder的结构。
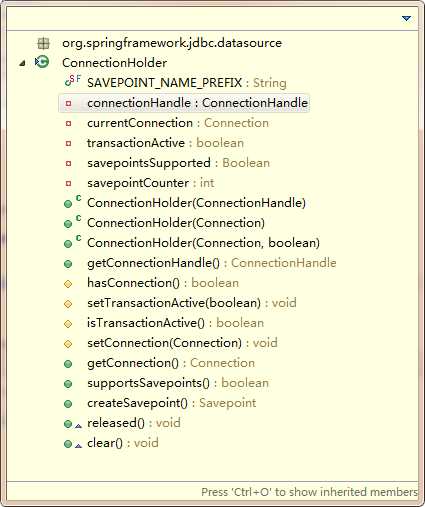
确实如我们所想。
我们再看TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(this.dataSource);代码如何获取ConnectionHolder的。
TransactionSynchronizationManager这个名字,应该是支持多线程并发读取的。我们看代码。
public static Object getResource(Object key) { Object actualKey = TransactionSynchronizationUtils.unwrapResourceIfNecessary(key); Object value = doGetResource(actualKey); if (value != null && logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Retrieved value [" + value + "] for key [" + actualKey + "] bound to thread [" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "]"); } return value; } |
看Object value = doGetResource(actualKey);代码:
private static Object doGetResource(Object actualKey) { Map<Object, Object> map = resources.get(); if (map == null) { return null; } Object value = map.get(actualKey); // Transparently remove ResourceHolder that was marked as void... if (value instanceof ResourceHolder && ((ResourceHolder) value).isVoid()) { map.remove(actualKey); // Remove entire ThreadLocal if empty... if (map.isEmpty()) { resources.remove(); } value = null; } return value; } |
高亮代码,看起来就是从一个map中获取了返回的结果,获取的时候使用的key是上一个方法传入的datasource。
看看这个map是什么。
private static final ThreadLocal<Map<Object, Object>> resources = new NamedThreadLocal<Map<Object, Object>>("Transactional resources"); |
看来是ThreadLocal对象。
那么这个对象是在什么时候初始化的呢。
经过查看是在这个方法:
public static void bindResource(Object key, Object value) throws IllegalStateException { |
那么那个地方调了这个方法呢?
经过查看,又回到了DataSourceTransactionManager类:
@Override protected void doResume(Object transaction, Object suspendedResources) { ConnectionHolder conHolder = (ConnectionHolder) suspendedResources; TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(this.dataSource, conHolder); } |
但是这个是在事务执行完毕的时候执行的,所以如果我们是第一次在当前线程执行事务,那么回到最初的代码:
public final TransactionStatus getTransaction(TransactionDefinition definition) throws TransactionException { Object transaction = doGetTransaction();
// Cache debug flag to avoid repeated checks. boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled();
if (definition == null) { // Use defaults if no transaction definition given. definition = new DefaultTransactionDefinition(); }
if (isExistingTransaction(transaction)) { // Existing transaction found -> check propagation behavior to find out how to behave. return handleExistingTransaction(definition, transaction, debugEnabled); }
// Check definition settings for new transaction. if (definition.getTimeout() < TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT) { throw new InvalidTimeoutException("Invalid transaction timeout", definition.getTimeout()); }
// No existing transaction found -> check propagation behavior to find out how to proceed. if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_MANDATORY) { throw new IllegalTransactionStateException( "No existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation ‘mandatory‘"); } else if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED || definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW || definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED) { SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources = suspend(null); if (debugEnabled) { logger.debug("Creating new transaction with name [" + definition.getName() + "]: " + definition); } try { boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER); DefaultTransactionStatus status = newTransactionStatus( definition, transaction, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources); doBegin(transaction, definition); prepareSynchronization(status, definition); return status; } catch (RuntimeException ex) { resume(null, suspendedResources); throw ex; } catch (Error err) { resume(null, suspendedResources); throw err; } } else { // Create "empty" transaction: no actual transaction, but potentially synchronization. boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() == SYNCHRONIZATION_ALWAYS); return prepareTransactionStatus(definition, null, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null); } } |
Object transaction = doGetTransaction();
这里的transaction中应该是没有connection的。
继续往下看:
if (isExistingTransaction(transaction)) { // Existing transaction found -> check propagation behavior to find out how to behave. return handleExistingTransaction(definition, transaction, debugEnabled); } |
其中,isExistingTransaction:
@Override protected boolean isExistingTransaction(Object transaction) { DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) transaction; return (txObject.getConnectionHolder() != null && txObject.getConnectionHolder().isTransactionActive()); } |
这是是判断txObject种有没有ConnectionHolder,也就是当前线程是否已经执行过事务。
我们忽略有的情况,主要看没有的情况,也就是说当前线程第一次处理事务的情况。
继续看最初的代码,主要看这段:
else if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED || definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW || definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED) { SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources = suspend(null); if (debugEnabled) { logger.debug("Creating new transaction with name [" + definition.getName() + "]: " + definition); } try { boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER);
definition, transaction, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources); DefaultTransactionStatus status = newTransactionStatus( doBegin(transaction, definition); prepareSynchronization(status, definition); return status; } catch (RuntimeException ex) { resume(null, suspendedResources); throw ex; } catch (Error err) { resume(null, suspendedResources); throw err; } } |
看doBegin(transaction, definition);
@Override protected void doBegin(Object transaction, TransactionDefinition definition) { DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) transaction; Connection con = null;
try { if (txObject.getConnectionHolder() == null || txObject.getConnectionHolder().isSynchronizedWithTransaction()) { Connection newCon = this.dataSource.getConnection(); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Acquired Connection [" + newCon + "] for JDBC transaction"); } txObject.setConnectionHolder(new ConnectionHolder(newCon), true); }
txObject.getConnectionHolder().setSynchronizedWithTransaction(true); con = txObject.getConnectionHolder().getConnection();
Integer previousIsolationLevel = DataSourceUtils.prepareConnectionForTransaction(con, definition); txObject.setPreviousIsolationLevel(previousIsolationLevel);
// Switch to manual commit if necessary. This is very expensive in some JDBC drivers, // so we don‘t want to do it unnecessarily (for example if we‘ve explicitly // configured the connection pool to set it already). if (con.getAutoCommit()) { txObject.setMustRestoreAutoCommit(true); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Switching JDBC Connection [" + con + "] to manual commit"); } con.setAutoCommit(false); } txObject.getConnectionHolder().setTransactionActive(true);
int timeout = determineTimeout(definition); if (timeout != TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT) { txObject.getConnectionHolder().setTimeoutInSeconds(timeout); }
// Bind the session holder to the thread. if (txObject.isNewConnectionHolder()) { TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(getDataSource(), txObject.getConnectionHolder()); } }
catch (Throwable ex) { if (txObject.isNewConnectionHolder()) { DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, this.dataSource); txObject.setConnectionHolder(null, false); } throw new CannotCreateTransactionException("Could not open JDBC Connection for transaction", ex); } } |
这里新建了一个Connection,并且将这个Connection绑定到了TransactionSynchronizationManager中,也就是上面的:
private static final ThreadLocal<Map<Object, Object>> resources = new NamedThreadLocal<Map<Object, Object>>("Transactional resources"); |
至此,我们只需要确定,我们使用datasource.getConction()的时候,也是从TransactionSynchronizationManager获取的就好。
标签:ble run conf ssi ready getname bug ini sources
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/xiaolang8762400/p/7407283.html