标签:getname 控制 实现 容器 point array jar包 tsig style
1、数学计算器
①数学计算器接口[MathCalculator]
public void add(int i,int j);
public int sub(int i,int j);
public int multi(int i,int j);
public void divide(int i,int j);
②提供简单实现:加减乘除运算[EasyImpl]
③在简单实现的基础上让每一个计算方法都能够打印日志[LoginImpl]
④缺陷
[1]手动添加日志繁琐,重复,容易出现代码混乱
[2]代码分散,统一修改不便
[3]对目标方法本来要实现的核心功能有干扰,使程序代码很臃肿,不易于开发维护
⑤使用动态代理实现
[1]创建一个类,让这个类能够提供一个目标对象的代理对象
[2]在代理对象中打印日志
(动态代理设计模式的原理:使用一个代理将对象包装起来,然后用该代理对象取代原始对象。任何对原始对象的调用都要通过代理。代理对象决定是否以及何时将方法调用转到原始对象上。)
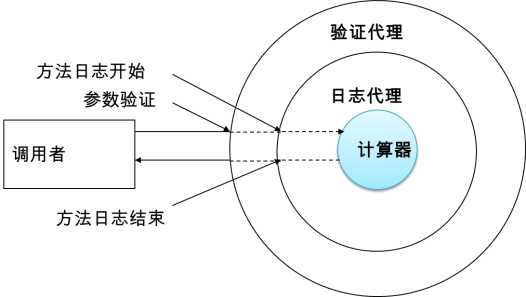
2、常规实现
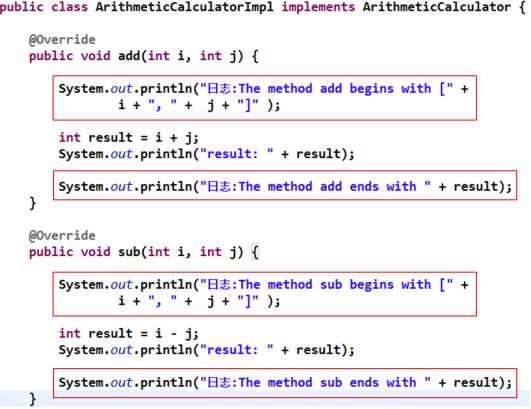
3 数学计算器的改进
在Spring中使用AOP实现日志功能
①Spring中可以使用注解或XML文件配置的方式实现AOP。
②导入jar包
com.springsource.net.sf.cglib -2.2.0.jar
com.springsource.org.aopalliance-1.0.0 .jar
com.springsource.org.aspectj.weaver-1.6.8 .RELEASE.jar
commons-logging-1.1.3. jar
spring-aop-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-aspects-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-beans-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-context-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-core-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-expression-4.0.0.RELEASE. jar
③开启基于注解的AOP功能
< aop:aspectj-autoproxy />
④声明一个切面类,并把这个切面类加入到IOC容器中
@Aspect//表示这是一个切面类
@Component//加入IOC容器
1 @Component 2 @Aspect 3 public class CaculatorAspect { 4 }
⑤在切面类中声明通知方法
[1]前置通知:@Before
[2]返回通知:@AfterReturning
[3]异常通知:@AfterThrowing
[4]后置通知:@After
[5]环绕通知:@Around :环绕通知是前面四个通知的集合体!

1 @Component//将本类对象加入到IOC容器中! 2 @Aspect//表示这是一个切面类 3 public class CaculatorAspect { 4 @Before(value="execution(public void com.neuedu.aop.CaculatorEasyImpl.*(int, int))") 5 public void showBeginLog(){ 6 System.out.println("AOP日志开始"); 7 } 8 @AfterThrowing(value="execution(public void com.neuedu.aop.CaculatorEasyImpl.*(int, int))") 9 public void showExceptionLog(){ 10 System.out.println("AOP方法异常"); 11 } 12 @AfterReturning(value="execution(public void com.neuedu.aop.CaculatorEasyImpl.*(int, int))") 13 public void showAfterLog(){ 14 System.out.println("AOP方法正常结束"); 15 } 16 @After(value="execution(public void com.neuedu.aop.CaculatorEasyImpl.*(int, int))") 17 public void showReturnLog(){ 18 System.out.println("AOP方法终止"); 19 } 20 }
⑥被代理的对象也需要加入IOC容器

1 @Component//将被代理对象加入到IOC容器中 2 public class CaculatorEasyImpl implements MathCaculate{ 3 //CaculatorEasyImpl继承接口,获取的bean是CaculatorEasyImpl的代理类 4 @Override 5 public void add(int i, int j) { 6 int result =i+j; 7 System.out.println("目标add方法执行了"); 8 } 9 10 @Override 11 public int sub(int i, int j) { 12 int result =i-j; 13 System.out.println("目标sub方法执行了"); 14 return result; 15 } 16 17 @Override 18 public int multi(int i, int j) { 19 int result =i*j; 20 System.out.println("目标multi方法执行了"); 21 return result; 22 } 23 24 @Override 25 public void divide(int i, int j) { 26 int result =i/j; 27 System.out.println("目标divide方法执行了"); 28 } 29 30 }
6.切入点表达式:
1.上述案例通过junit测试,会发现,我们调用目标类的四个方法只有add方法被加入了4个通知,如果想所有的方法都加上这些通知,可以
在切入点表达式处,将execution(public int com.neuedu.aop.target.MathCalculatorImpl.add(int, int)) 换成:
execution(public int com.neuedu.aop.target.MathCalculatorImpl.*(int, int))这样只要是有两个参数,且
参数类型为int的方法在执行的时候都会执行其相应的通知方法!
2.①切入点表达式的语法格式
execution([权限修饰符] [返回值类型] [简单类名/全类名] [方法名]([参数列表]))
1.任意参数,任意类型execution(public int com.neuedu.aop.target.MathCalculatorImpl.*(..))
2.任意返回值execution(* com.neuedu.aop.target.MathCalculatorImpl.*(int, int))
3.用@PointCut注解统一声明,然后在其它通知中引用该统一声明即可!

1 @Component 2 @Aspect 3 public class CaculatorAspect { 4 5 @Pointcut(value="execution(public * com.neuedu.aop.CaculatorEasyImpl.*(int, int))") 6 public void showLog(){ 7 8 } 9 10 @Before(value="showLog()") 11 public void showBeginLog(JoinPoint point){ 12 Object[] args = point.getArgs(); 13 Signature signature = point.getSignature(); 14 String name = signature.getName(); 15 List<Object> asList = Arrays.asList(args); 16 System.out.println("【日志】【方法开始】目标方法名为:"+name+",参数为:"+asList); 17 System.out.println("AOP日志开始"); 18 } 19 @AfterThrowing(value="showLog()",throwing="ex") 20 public void showExceptionLog(JoinPoint point,Exception ex){ 21 System.out.println("出异常了,异常信息为:"+ex.getMessage()); 22 System.out.println("AOP方法异常"); 23 } 24 @AfterReturning(value="showLog()",returning="result") 25 public void showAfterLog(JoinPoint point,Object result){ 26 System.out.println("目标方法的返回值为:"+result); 27 System.out.println("AOP方法正常结束"); 28 } 29 @After(value="showLog()") 30 public void showReturnLog(){ 31 System.out.println("AOP方法终止"); 32 } 33 34 }
需要注意的是:权限是不支持写通配符的,当然你可以写一个*表示所有权限所有返回值!
最详细的切入点表达式:
execution(public int com.neuedu.aop.target.MathCalculatorImpl.add(int, int))
最模糊的切入点表达式:
execution (* *.*(..))
7.统一声明切入点表达式
@Pointcut(value= "execution(public int com.atguigu.aop.target.EazyImpl.add(int,int))")
public void myPointCut(){}
8.通知方法的细节
①在通知中获取目标方法的方法名和参数列表
[1]在通知方法中声明一个JoinPoint类型的形参
[2]调用JoinPoint对象的getSignature()方法获取目标方法的签名
[3]调用JoinPoint对象的getArgs()方法获取目标方法的实际参数列表
②在返回通知中获取方法的返回值
[1]在@AfterReturning注解中添加returning属性
@AfterReturning (value="myPointCut()", returning= "result")
[2]在返回通知的通知方法中声明一个形参,形参名和returning属性的值一致
showReturnLog(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result)
③在异常通知中获取异常对象
[1]在@ AfterThrowing注解中添加throwing属性
@AfterThrowing (value="myPointCut()",throwing= "throwable" )
[2]在异常通知的通知方法中声明一个形参,形参名和throwing属性值一致
showExceptinLog(JoinPoint joinPoint, Throwable throwable)

1 @Pointcut(value="execution(public * com.neuedu.aop.CaculatorEasyImpl.*(int, int))") 2 public void showLog(){ 3 4 } 5 6 @Before(value="showLog()") 7 public void showBeginLog(JoinPoint point){ 8 Object[] args = point.getArgs(); 9 Signature signature = point.getSignature(); 10 String name = signature.getName(); 11 List<Object> asList = Arrays.asList(args); 12 System.out.println("【日志】【方法开始】目标方法名为:"+name+",参数为:"+asList); 13 System.out.println("AOP日志开始"); 14 } 15 @AfterThrowing(value="showLog()",throwing="ex") 16 public void showExceptionLog(JoinPoint point,Exception ex){ 17 System.out.println("出异常了,异常信息为:"+ex.getMessage()); 18 System.out.println("AOP方法异常"); 19 } 20 @AfterReturning(value="showLog()",returning="result") 21 public void showAfterLog(JoinPoint point,Object result){ 22 System.out.println("目标方法的返回值为:"+result); 23 System.out.println("AOP方法正常结束"); 24 } 25 @After(value="showLog()") 26 public void showReturnLog(){ 27 System.out.println("AOP方法终止"); 28 }
9.根据接口类型获取target对象时,实际上真正放在IOC容器中的对象是代理对象,而并不是目标对象本身!

1 @Test 2 public void test() { 3 ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); 4 MathCaculate bean = (MathCaculate) ioc.getBean("caculatorEasyImpl");//获取的bean对象为代理对象 5 System.out.println(bean.getClass()); 6 bean.add(10, 5); 7 System.out.println(); 8 bean.sub(10, 5); 9 System.out.println(); 10 bean.multi(10, 5); 11 System.out.println(); 12 bean.divide(10, 0); 13 }
代理对象与目标对象同用一个id(类名首字母小写),当父接口被多个类继承时,不可用类的形式获取bean对象
10.环绕通知:@Around
1.环绕通知需要在方法的参数中指定JoinPoint的子接口类型ProceedingJoinPoint为参数
@Around(value="pointCut()") public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint){ }
2.环绕通知会将其他4个通知能干的,自己都给干了!
环绕通知@Around(value = "")可控制是否执行连接点。
注意:@Around修饰的方法一定要将方法的返回值返回!本身相当于代理!

1 @Component 2 @Aspect 3 public class TestAspect { 4 5 @Around(value = "execution(public void com.neuedu.aop.CaculatorEasyImpl.*(..))") 6 public Object showLog(ProceedingJoinPoint point) { 7 //ProceedingJoinPoint point连接点 8 Object[] args = point.getArgs();//获取目标方法的参数 9 Object result=null; 10 Signature signature = point.getSignature();//标签名 11 List<Object> asList = Arrays.asList(args); 12 String name = signature.getName(); 13 14 try { 15 try { 16 //目标方法之前要执行的操作 17 System.out.println("【日志1】【方法开始】目标方法名为:"+name+",参数为:"+asList); 18 //调用目标方法 19 result = point.proceed(args);//得到目标方法的返回值 20 } finally { 21 //方法最终结束时执行的操作! 22 System.out.println("【日志1】【后置通知】目标方法名为:"+name+",返回值为:"+result); 23 } 24 //目标方法正常执行之后的操作 25 System.out.println("【日志1】【方法正常结束】目标方法名为:"+name+",返回值为:"+asList); 26 } catch (Throwable e) { 27 //目标方法抛出异常信息之后的操作 28 System.out.println("【日志1】【异常通知】异常信息为:"+e.getMessage()); 29 } 30 return result; 31 } 32 }
11.切面的优先级
[1]在同一个连接点上应用不止一个切面(即对于同一个代理对象,可以同时有多个切面共同对它进行代理)时,除非明确指定,否则它们的优先级是不确定的。
(先通过切面优先级判断先执行那个切面的开始方法,再根据优先级逐个执行开始方法,最后执行的切面执行完后置方法后,再逐次外推执行后置方法)
[2] 切面的优先级可以通过实现Ordered接口或利用@Order注解指定。
[3]实现Ordered接口,getOrder()方法的返回值越小,优先级越高。
[4]若使用@Order注解,序号出现在注解中@Order (value=50),值越小优先级越高!


12.注意:上面的AOP都是通过注解实现的,AOP实际上也可以通过xml配置的方式实现!
将前面切面类中的注解全部去掉,搭配下面代码配置实现AOP

1 <!-- 1.将需要加载到IOC容器中的bean配置好 --> 2 <bean id="logAspect" class="com.neuedu.aop.proxy.LogAspect"></bean> 3 <bean id="txAspect" class="com.neuedu.aop.target.TxAspect"></bean> 4 <bean id="calculator" class="com.neuedu.aop.target.MathCalculatorImpl"></bean> 5 6 <!-- 2.配置AOP,需要导入AOP名称空间 --> 7 <aop:config> 8 <!-- 声明切入点表达式 --> 9 <aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.neuedu.aop.target.MathCalculatorImpl.*(..))" id="myPointCut"/> 10 <!-- 配置日志切面类,引用前面的类 ,通过order属性控制优先级--> 11 <aop:aspect ref="logAspect" order="25"> 12 <!-- 通过method属性指定切面类的切面方法,通过pointcut-ref指定切入点表达式 --> 13 <aop:before method="showBeginLog" pointcut-ref="myPointCut"/> 14 <aop:after method="showAfterLog" pointcut-ref="myPointCut"/> 15 <aop:after-throwing method="showExceptionLog" pointcut-ref="myPointCut" throwing="ex"/> 16 <aop:after-returning method="showReturnLog" pointcut-ref="myPointCut" returning="result"/> 17 <aop:around method="around" pointcut-ref="myPointCut"/> 18 </aop:aspect> 19 20 <!-- 配置事务切面类,引用前面的类(环绕通知) --> 21 <aop:aspect ref="txAspect" order="20"> 22 <aop:around method="around" pointcut-ref="myPointCut"/> 23 </aop:aspect> 24 </aop:config>
需要知道的是:事务的管理是和AOP是有很大关系的,即声明式事务的底层是用事务实现的!
spring相关—AOP编程—数学计算器情景示例讲解(包含注解配置AOP与XML配置AOP)
标签:getname 控制 实现 容器 point array jar包 tsig style
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/kangxingyue-210/p/7449865.html