标签:存在 reader object 文件路径 tor 超过 读取 导致 seq
关于 I/O 的类可以分为四种:
在本篇博客中我们来看一下前两种 I/O,即字符流与字节流,首先两者的实现关系如下图所示
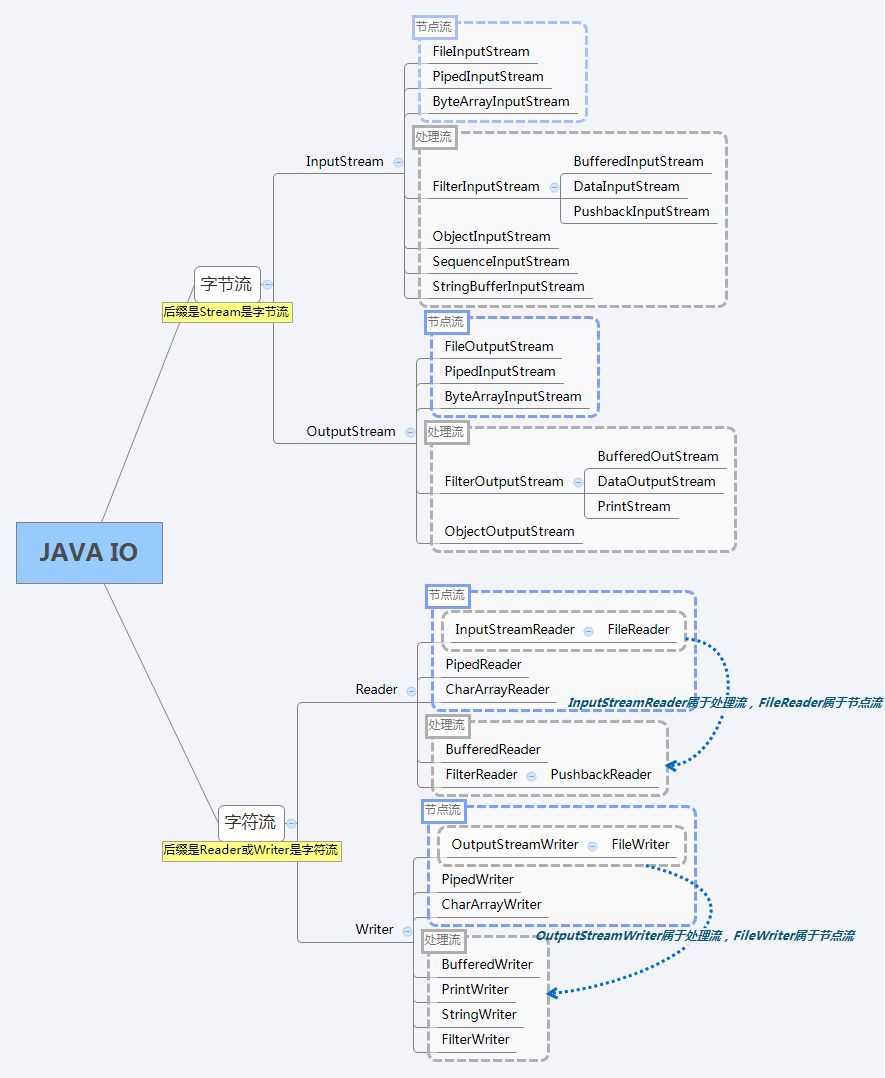
一、字节流
在字节流的类中,最顶层的是 Inputstream 抽象类和 OutputStream 抽象类,两者定义了一些关于字节数据读写的基本操作。他们的实现类有
1、InputStream类与OutputStream类及它们的子类
InputStream抽象类中的方法如下:
public abstract int read() // 抽象的读取方法 public int read(byte b[]) // 最多读取 b.length 长度的字节,并储存到数组 b 中,返回实际读取长度,利用 read() 实现 public int read(byte b[], int off, int len) // 同上,最多读取 len 个字节,从 off 开始保存 public long skip(long n) // 跳过n个字节 public int available() // 返回可以读取的字节数目,不受阻塞 public void close() // 关闭输入流,并释放与此流有关的所有资源,未实现,方法体为空 public synchronized void mark(int readlimit) // 标记当前位置,以便可以使用 reset() 方法复位到该标记的位置,未实现,方法体为空 public synchronized void reset() // 将当前位置复位到上次使用 mark() 方法标记的位置,未实现,调用抛出IO异常 public boolean markSupported() // 判断次输入流是否支持 mark() 和 reset() 方法
OutputStream抽象类中的方法如下:
public abstract void write(int b) // 抽象的写入方法 public void write(byte b[]) // 写入一个字节数组,利用 write(int b)实现 public void write(byte b[], int off, int len) // 同上 public void flush() // 未实现,方法体为空 public void close() // 未实现,方法体为空
1.1 ByteArrayInputStream类与ByteArrayOutputStream类
ByteArrayInputStream 与 ByteArrayOutputStream 并无直接关系,两者都可以单独使用。
在 ByteArrayOutputStream 中利用一个字节数组作为缓冲区记录写入的数据,我们可以通过 wirte() 方法向缓冲区写入数据。如果需要使用这些数据我们可以通过 toString() 、toByteArray() 从缓冲区中获取,也可以通过 writeTo() 将缓冲区数据其写入其它 OutputStream 类中,如下图


在 ByteArrayInputStream 中根据一个字节数组来构造自身,并将数组记录到缓冲区中,我们可以通过 read() 方法来获取。所以,我们可以利用 ByteArrayInputStream 来读取 ByteArrayOutputStream 写入的数据。


ByteArrayInputStream相关方法:
// 构造方法: public ByteArrayInputStream(bytebuf[]) public ByteArrayInputStream(bytebuf[],int offset, int length) // 该类中的属性: protected byte buf[] // 用来存储待读取字符的数组 protected int pos // 当前读取位置 protected int mark // 记录复位位置 protected int count // 待读取字符数组总长度 // 该类中的方法: public synchronized int read() // 读取1个字节,如果已经读完返回-1,不会阻塞 public synchronized int read(byteb[],int off,intlen) // 同上 public synchronized long skip(longn) public synchronized int available() public boolean markSupported() public void mark(intreadAheadLimit) public synchronized void reset() public void close()
ByteArrayOutputStream相关方法:
// 构造方法: public ByteArrayOutputStream() // 默认缓冲区32字节 public ByteArrayOutputStream(int size) // 指定缓冲区大小 // 该类中的属性: protected byte buf[] // 缓冲区,用来存储写入的字符的数组 protected int count // 缓冲区内容大小 private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8; // 缓冲区最大容量 // 该类中的方法: private void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) // 判断缓冲区是否需扩容 private void grow(int minCapacity) // 缓冲区扩容 private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) public synchronized void write(int b) public synchronized void write(byte b[], int off, int len) public synchronized void writeTo(OutputStream out) public synchronized void reset() public synchronized byte toByteArray()[] public synchronized int size() public synchronized String toString() public synchronized String toString(String charsetName) public synchronized String toString(int hibyte) // @Deprecated 已弃用 public void close() // 这个方法没有效果,方法体为空
1.2 FileInputStream类与FileOutputStream类
FileInputStream 与 FileOutputStream 并无直接关系,两者都可以单独使用,这点与 ByteArrayInputStream 和 ByteArrayOutputStream 类似。它们区别是前者操作的是文件,后者操作的是字符数组。
FileInputStream相关方法:
// 构造方法:(检查文件是否为空、是否可读、是否有效,然后调用native open0()打开文件) public FileInputStream(String name) throws FileNotFoundException public FileInputStream(File file) throws FileNotFoundException public FileInputStream(FileDescriptor fdObj) // 该类中的属性: private final FileDescriptor fd; private final String path; // 储存文件的路径 private File Channelchannel = null; private final Object closeLock = new Object(); private volatile boolean closed = false; // 该类中的方法: public int read() // 读取1个字节,如果已经读完返回-1,调用native read0()来实现,不会阻塞 public int read(byte b[]) // 读取到字节数组中,调用native readBytes()来实现,不会阻塞 public int read(byte b[],int off, int len) public native long skip(long n) // 跳过n个字节 public native int available() public void close() //关闭流,用closeLock变量作为锁在synchronized代码块中改变closed属性,之后调用native close0() public final FileDescriptor getFD() // 返回表示到文件系统中实际文件的连接的 FileDescriptor 对象。 public FileChannel getChannel() // 返回与此文件输入流有关的唯一FileChannel 对象 protected void finalize() // 确保在不再引用文件输入流时调用其close()方法
FileOutputStream相关方法:
// 构造方法:(检查文件是否为空、是否可写、是否有效,然后调用native open0()打开文件) public FileOutputStream(String name) // 根据文件路径与文件名称构造 public FileOutputStream(String name, boolean append) // 内容追加在文件后 public FileOutputStream(File file) public FileOutputStream(File file, boolean append) public FileOutputStream(FileDescriptor fdObj) // 该类中的属性: private final FileDescriptor fd; private final boolean append; // 写入文件的方式是否为追加 private FileChannel channel; private final String path; // 文件路径 private final Object closeLock = new Object(); // 锁 private volatile boolean closed = false; // 文件是否关闭 // 该类中的方法: public void write(int b) // 向文件中写入一个字节,调用native write()来实现 public void write(byte b[]) // 向文件中写入一个字节数组,调用native writeBytes()来实现 public void write(byte b[], int off, int len) // 同上 public void close() //关闭流,用closeLock变量作为锁在synchronized代码块中改变closed属性,之后调用native close0()
public final FileDescriptor getFD()
public FileChannel getChannel()
protected void finalize() //
1.3 ObjectInputStream类
注:该类所读写的对象必须实现Serializable接口
// 文件构造输入流: public ObjectInputStream(InputStreamin) throws IOException protected ObjectInputStream()throws IOException, SecurityException // 该类中的方法: public final Object readObject()
protected Object readObjectOverride()
public Object readUnshared()
public void defaultReadObject()
public ObjectInputStream.GetField readFields()
public void registerValidation(ObjectInputValidation obj, int prio)
protected Class<?> resolveClass(ObjectStreamClassdesc)
protected Class<?> resolveProxyClass(String[]interfaces)
protected Object resolveObject(Objectobj)
protected boolean enableResolveObject(boolean enable)
protected void readStreamHeader()
protected ObjectStreamClass readClassDescriptor() public int read()
public int read(byte[] buf, int off,int len)
public int available()
public void close()
public boolean readBoolean()
public byte readByte()
public int readUnsignedByte()
public char readChar()
public short readShort()
public int readUnsignedShort()
public int readInt()
public long readLong()
public float readFloat()
public double readDouble()
public void readFully(byte[] buf)
public void readFully(byte[] buf, int off,int len)
public int skipBytes(int len)public String readUTF()
// 该类中的内部类: private staticclass Caches public static abstract class GetField private class GetFieldImplextends GetField private static class ValidationList private staticclass PeekInputStream extends InputStream private class BlockDataInputStream extends InputStreamimplements DataInput private static class HandleTable
1.4 PipedInputStream类与PipedOutputStream类
PipedInputStream 和 PipedOutputStream 的实现原理类似于“生产者-消费者”原理,PipedOutputStream 是生产者,PipedInputStream 是消费者,在 PipedInputStream 中有一个 buffer 字节数组作为缓冲区,默认大小为1024,存放“生产者”生产出来的东西。还有两个变量 in 和 out,in 是用来记录“生产者”生产了多少,out 是用来记录“消费者”消费了多少,in 为-1表示消费完了,in==out 表示生产满了。当消费者没东西可消费的时候,也就是当 in 为-1的时候,消费者会一直等待,直到有东西可消费。
PipedInputStream相关方法:
// 构造方法: public PipedInputStream(PipedOutputStream src) throws IOException // 与输出管道建立完整管道,默认缓冲区1024字节 public PipedInputStream(PipedOutputStream src, int pipeSize) throws IOException // 同上,但缓冲区大小由pipeSize指定 public PipedInputStream() // 创建输入管道,使用前必须与输出管道建立完整管道,默认缓冲区1024字节 public PipedInputStream(int pipeSize) // 同上,但缓冲区大小由pipeSize指定 // 该类中的属性: boolean closedByWriter = false; volatile boolean closedByReader = false; boolean connected = false; // 是否已建立完整管道 Thread readSide; Thread writeSide; private static final int DEFAULT_PIPE_SIZE = 1024; // 缓冲区默认大小 protected static final int PIPE_SIZE = DEFAULT_PIPE_SIZE; protected byte buffer[]; // 缓冲区 protected int in = -1; // 表示从输出管道读出下一个字节后在缓冲区储存的位置,in==-1表示缓冲区为空,in==out表示缓冲区已满 protected int out = 0; // 表示从缓冲区读取下一个字节的位置 // 该类中的方法 private void initPipe(int pipeSize) // 初始化缓冲区 public void connect(PipedOutputStream src) // 与输出管道建立连接 protected synchronized void receive(int b) // 接收一个字节的数据,没有数据输入则阻塞 synchronized void receive(byte b[], int off, int len) // 接收大小为len的数据到数组,不足则阻塞 private void checkStateForReceive() // 判断是否建立连接,读写是否已关闭 private void awaitSpace()synchronized void receivedLast() // 通知所有等待的线程,最后一个字符已经接收 public synchronized int read() // 从缓冲区读取字节,返回读取的字节,如果缓冲区没有数据则会阻塞 public synchronized int read(byte b[], int off, int len) // 从缓冲区读取字节数组到b,返回读取字节数,如果缓冲区没有数据则阻塞 public synchronized int available()
public void close()
PipedOutputStream相关方法:
// 构造方法: public PipedOutputStream(PipedInputStream snk) public PipedOutputStream() // 该类中的属性: private PipedInputStream sink; // 该类所连接的输入流 // 该类中的方法: public synchronized void connect(PipedInputStream snk) // 与输入流建立连接,需要先获取到对象锁 public void write(int b) // 调用连接的输入流的receive方法,向其写入一个字节 public void write(byte b[], int off, int len) // 同上,写入一个字节数组 public synchronized void flush() // 唤醒所连接的输入流 public void close()
关于 PipedInputStream 和 PipedOutputStream 的几点要注意:
产生“死锁”的代码: 输出结果:

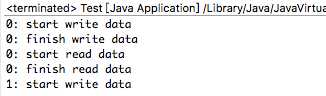
1.5 FilterInputStream类与FilterOutputStream类
FilterInputStream 与 FilterOutputStream 及子类是使用了装饰者设计模式。为什么要使用装饰者设计模式?如果我们觉得某几个类都缺少一些功能的时候,根据开闭原则,我们不去修改代码,那我们可以利用继承对功能进行扩展,但是如果几个类都需要扩展相同的功能,那么就必须分别对这个几个类扩展。如果使用装饰者设计模式,我们就可以解决这个问题。举个例子,当我们使用 ByteArrayInputStream 的时候只能读取到以 byte 为单位的数据,我们可以按需要把读取出来的字节进行转码,转成我们需要的数据,那么能不能直接读取字符,int等数据呢?答案是可以的,我们利用 DataInputStream 类对其进行装饰即可拥有 readInt() 这个方法。
FilterInputStream相关方法:
// 构造方法: protected FilterInputStream(InputStream in) // 该类中的属性: protected volatile InputStream in; // 需要装饰的对象 // 该类中的方法: public int read() public int read(byte b[]) public int read(byte b[], int off, int len) public long skip(long n) public int available() public void close() public synchronized void mark(int readlimit) public synchronized void reset() public boolean markSupported()
FilterOutputStream相关方法:
// 构造方法: public FilterOutputStream(OutputStream out) // 该类中的属性: protected OutputStream out; // 需要装饰的对象 // 该类中的方法: public void write(int b) public void write(byte b[]) public void write(byte b[], int off, int len) public void flush() public void close()
1.5.1 DataInputStream类与DataOutputStream类
DataInputStream 与 DataOutputStream 是装饰类,可以对继承了 InputStream 的类进行装饰,使其用于读取或写入指定类型内容的数据。
DataInputStream相关方法:
// 构造方法: public DataInputStream(InputStream in) // 传入一个需装饰的对象 // 该类中的属性: private byte bytearr[] = new byte[80]; private char chararr[] = new char[80]; private byte readBuffer[] = new byte[8]; // 在readLong()中使用,利用readFully()读取8个字节,然后 private char lineBuffer[]; // 该类中的方法: public final int read(byte b[]) // 调用被装饰对象的read()方法 public final int read(byte b[], int off, int len) // 同上 public final void readFully(byte b[]) // 读取数据到数组,直到存满,当流中数据不足时,readFully()会阻塞等待 public final void readFully(byte b[], int off, int len) // 同上 public final int skipBytes(int n) // 跳过n个字节 public final boolean readBoolean() public final byte readByte() public final int readUnsignedByte() public final short readShort() // 连续调用read()两次,然后将结果拼接后强转short类型,(short)((ch1<<8)+(ch2<<0)) public final int readUnsignedShort() // 同上,但不需要进行强转 public final char readChar() public final int readInt() public final long readLong() // 利用readFully()读取8个字节到readBuffer数组,然后拼接转换成long类型 public final float readFloat() // 使用Float.intBitsToFloat(readInt()) public final double readDouble() // 使用Double.longBitsToDouble(readLong()) public final String readLine() // 弃用的 public final String readUTF() public final static String readUTF(DataInput in) // 待研究
DataOutputStream相关方法:
// 构造方法: public DataOutputStream(OutputStream out) // 传入一个需装饰的对象 // 该类中的属性: protected int written; //写入到流的字节数 private byte[] bytearr = null; // 在writeUTF()使用 private byte writeBuffer[] = new byte[8]; // 该类中的方法: private void incCount(int value) // 记录写入到流的字节数 public synchronized void write(int b) public synchronized void write(byte b[], int off, int len) public void flush() // 让缓存中的数据传入到输入流中 public final void writeBoolean(boolean v) public final void writeByte(int v) public final void writeShort(int v) public final void writeChar(int v) public final void writeInt(int v) public final void writeLong(long v) public final void writeFloat(float v) // writeInt(Float.floatToIntBits(v)) public final void writeDouble(double v) // writeLong(Double.doubleToLongBits(v)); public final void writeBytes(String s) public final void writeChars(String s) public final void writeUTF(String str) static int writeUTF(String str, DataOutput out) public final int size()
1.5.2 BufferedInputStream类与BufferedOutputStream类
当我们在使用 FileInputStream 和 FileOutputStream 时,要用一个 byte 数组用来接收或写入数据,硬盘存取的速度远低于内存中的数据存取速度,为了减少对硬盘的存取,通常从文件中一次读入一定长度的数据,而写入时也是一次写入一定长度的数据,这可以增加文件存取的效率。
BufferedInputStream 有一个字节数组 buf 作为缓冲区,默认为8192字节。当使用 read() 方法读取数据时,实际上是先读取 buf 中的数据,当 buf 中的数据不足时,BufferedInputStream 会再从被装饰的 InputStream 对象的 read() 方法中读取数据填满 buf ,然后再从 buf 中读取所需大小的数据。如果一次读取的数据大小超过 buf 缓冲区的大小,则放弃缓冲直接调用被装饰对象的 read() 方法。
BufferedOutputStream 也有一个字节数组 buf 作为缓冲区,默认同样为8192字节。当使用 write() 方法写入数据时,实际上会先将数据写至 buf 中,当 buf 已满时,BufferedOutputStream 才会利用被装饰的 OutputStream 对象的 write() 方法写入数据。如果一次写入的数据大小超过 buf 缓冲区的大小,则放弃缓冲直接调用被装饰对象的 write() 方法。
BufferedInputStream相关方法:
// 构造方法: public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in) // 传入一个需装饰的对象 public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in, int size) // 该类中的属性: private static int DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE = 8192; private static int MAX_BUFFER_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8; protected volatile byte buf[]; // 缓冲区 /* AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater 位于Atomic包中,是一个基于反射的工具类,它能对指定类的指定的volatile引用字段进行原子更新(注意这个字段不能是private的)。通过静态方法newUpdater就能创建它的实例,三个参数分别是:包含该字段的对象的类、将被更新的对象的类、将被更新的字段的名称。 */ private static final AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater<BufferedInputStream, byte[]> bufUpdater = AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater.newUpdater (BufferedInputStream.class, byte[].class, "buf"); protected int count; // 缓冲区内容大小 protected int pos; // 缓冲区当前位置 protected int markpos = -1; protected int marklimit; // 该类中的方法: private InputStream getInIfOpen() // 检查流是否存在 private byte[] getBufIfOpen() // 检查缓冲区是否存在 private void fill() // public synchronized int read() private int read1(byte[] b, int off, int len) public synchronized int read(byte b[], int off, int len) public synchronized long skip(long n) public synchronized int available() public synchronized void mark(int readlimit) public synchronized void reset() public boolean markSupported() public void close()
BufferedOutputStream相关方法:
// 构造方法: public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out) // 传入一个需装饰的对象 public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out, int size) // 该类中的属性: protected byte buf[]; protected int count; // 缓冲区内数据大小 // 该类中的方法: private void flushBuffer() // 将缓冲区的数据写入流,调用了被装饰对象的write方法 public synchronized void write(int b) // 将数据写入缓冲,如果缓冲满了,调用flushBuffer()方法 public synchronized void write(byte b[], int off, int len) // 同上 public synchronized void flush()
1.5.3 PushbackInputStream类
对输入流进行装饰,可以将当前读取的字节数据推回到缓存区,一般用不到的。
// 构造方法: public PushbackInputStream(InputStream in, int size) // 传入一个需装饰的对象 public PushbackInputStream(InputStream in) // 该类中的属性: protected byte[] buf; protected int pos; // 该类中的方法: private void ensureOpen() public int read() public int read(byte[] b, int off, int len) public void unread(int b) public void unread(byte[] b, int off, int len) public void unread(byte[] b) public int available() public long skip(long n) public boolean markSupported() // 不支持mark功能 public synchronized void mark(int readlimit) public synchronized void reset() public synchronized void close()
1.5.4 LineNumberInputStream类
对输入流进行装饰,可以获取输入流的行数或设置行数,已过时。已经被LineNumberReader替代。
1.5.5 PrintStream类
对输出流进行装饰,
// 构造方法: private PrintStream(boolean autoFlush, OutputStream out) // 传入一个需装饰的对象 private PrintStream(boolean autoFlush, OutputStream out, Charset charset) private PrintStream(boolean autoFlush, Charset charset, OutputStream out) public PrintStream(OutputStream out) public PrintStream(OutputStream out, boolean autoFlush) public PrintStream(OutputStream out, boolean autoFlush, String encoding) public PrintStream(String fileName) public PrintStream(String fileName, String csn) public PrintStream(File file) public PrintStream(File file, String csn) // 该类中的属性: private final boolean autoFlush; private boolean trouble = false; private Formatter formatter; private BufferedWriter textOut; private OutputStreamWriter charOut; private boolean closing = false; // 该类中的方法: private static <T> T requireNonNull(T obj, String message) private static Charset toCharset(String csn) private void ensureOpen() public void flush() public void close() public boolean checkError() protected void setError() protected void clearError() public void write(int b) public void write(byte buf[], int off, int len) private void write(char buf[]) private void write(String s) private void newLine() public void print(boolean b) public void print(char c) public void print(int i) public void print(long l) public void print(float f) public void print(double d) public void print(char s[]) public void print(String s) public void print(Object obj) public void println() public void println(boolean x) public void println(char x) public void println(int x) public void println(long x) public void println(float x) public void println(double x) public void println(char x[]) public void println(String x) public void println(Object x) public PrintStream printf(String format, Object ... args) public PrintStream printf(Locale l, String format, Object ... args) public PrintStream format(String format, Object ... args) public PrintStream format(Locale l, String format, Object ... args) public PrintStream append(CharSequence csq) public PrintStream append(CharSequence csq, int start, int end) public PrintStream append(char c)
1.6 StringBufferInputStream类
已经不再适合将字符转化为字节,更优的选择是通过StringReader将字符转化为流。
1.7 SequenceInputStream类
// 构造方法: public SequenceInputStream(Enumeration<? extends InputStream> e) public SequenceInputStream(InputStream s1, InputStream s2) // 该类中的属性: Enumeration<? extends InputStream> e InputStream in; // 该类中的方法: final void nextStream() public int available() public int read() public int read(byte b[], int off, int len) public void close()
二、Reader类与Writer类
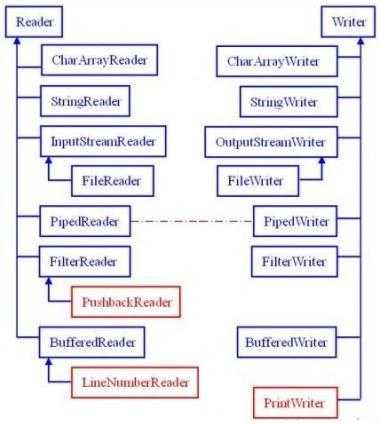
2、Reader类与Writer类及它们的子类
Reader抽象类中的方法如下:
// 构造方法 protected Reader() protected Reader(Object lock) // 该类中的属性 protected Object lock; private static final int maxSkipBufferSize = 8192; private char skipBuffer[] = null; // 该类中的方法 public int read(java.nio.CharBuffer target) public int read() public int read(char cbuf[]) abstract public int read(char cbuf[], int off, int len) public long skip(long n) public boolean ready() public boolean markSupported() public void mark(int readAheadLimit) public void reset() abstract public void close()
Writer抽象类中的方法如下:
// 构造方法 protected Writer() protected Writer(Object lock) // 该类中的属性 private char[] writeBuffer; private static final int WRITE_BUFFER_SIZE = 1024; protected Object lock; // 该类中的方法 public void write(int c) public void write(char cbuf[]) abstract public void write(char cbuf[], int off, int len) public void write(String str) public void write(String str, int off, int len) public Writer append(CharSequence csq) public Writer append(CharSequence csq, int start, int end) public Writer append(char c) abstract public void flush() abstract public void close()
2.1 CharArrayReader类与CharArrayWriter类
CharArrayReader 与 CharArrayWriter,并无直接关系,两者都可以单独使用。
CharArrayReader相关方法:
// 构造方法 public CharArrayReader(char buf[]) public CharArrayReader(char buf[], int offset, int length) // 该类中的属性 protected char buf[]; // 缓冲区 protected int pos; // 缓冲区使用位置 protected int markedPos = 0; protected int count; // 该类中的方法 private void ensureOpen() // 如果流关闭,则抛出IO异常 public int read() // 读一个字符,返回,若流中数据已读完则返回-1 public int read(char b[], int off, int len) public long skip(long n) public boolean ready() // 判断是否已经可以从流中读数据 public boolean markSupported() public void mark(int readAheadLimit) public void reset() public void close()
CharArrayWriter相关方法:
// 构造方法 public CharArrayWriter() // 缓冲区默认32 public CharArrayWriter(int initialSize) // 该类中的属性 protected char buf[]; // 缓冲区 protected int count; // 该类中的方法 public void write(int c) public void write(char c[], int off, int len) public void write(String str, int off, int len) public void writeTo(Writer out) // 将缓冲区的内容写入到另一个字符流 public CharArrayWriter append(CharSequence csq) // public CharArrayWriter append(CharSequence csq, int start, int end) // public CharArrayWriter append(char c) // public void reset() public char toCharArray()[] public int size() public String toString() public void flush() public void close()
2.2 StringReader类与StringWriter类
与CharArrayReader 与 CharArrayWriter 相似
StringReader相关方法:
// 构造方法 public StringReader(String s)// 该类中的属性 private String str; private int length; private int next = 0; private int mark = 0; // 该类中的方法 private void ensureOpen() public int read() public int read(char cbuf[], int off, int len) public long skip(long ns) public boolean ready() public boolean markSupported() public void mark(int readAheadLimit) public void reset() public void close()
StringWriter相关方法(就是把StringBuffer封装了一下):
// 构造方法 public StringWriter() public StringWriter(int initialSize) // 该类中的属性 private StringBuffer buf; // 该类中的方法 public void write(int c) public void write(char cbuf[], int off, int len) public void write(String str) public void write(String str, int off, int len) public StringWriter append(CharSequence csq) public StringWriter append(CharSequence csq, int start, int end) public StringWriter append(char c) public String toString() public StringBuffer getBuffer() public void flush() public void close()
2.3 PipedReader类与PipedWriter类
PipedReader 与 PipedWriter 的使用和 PipedInputStream 与 PipedOutputStream 十分相似,原理也相同。
PipedReader相关方法:
// 构造方法 public PipedReader(PipedWriter src) public PipedReader(PipedWriter src, int pipeSize) public PipedReader() public PipedReader(int pipeSize) // 该类中的属性 boolean closedByWriter = false; boolean closedByReader = false; boolean connected = false; Thread readSide; Thread writeSide; private static final int DEFAULT_PIPE_SIZE = 1024; char buffer[]; int in = -1; int out = 0; // 该类中的方法 private void initPipe(int pipeSize) public void connect(PipedWriter src) synchronized void receive(int c) synchronized void receive(char c[], int off, int len) synchronized void receivedLast() public synchronized int read() public synchronized int read(char cbuf[], int off, int len) public synchronized boolean ready() public void close()
PipedWriter相关方法:
// 构造方法 public PipedWriter(PipedReader snk) public PipedWriter() // 该类中的属性 private PipedReader sink; private boolean closed = false; // 该类中的方法 public synchronized void connect(PipedReader snk) public void write(int c) public void write(char cbuf[], int off, int len) public synchronized void flush() public void close()
2.4 InputStreamReader类与OutputStreamWriter类
InputStreamReader 与 OutputStreamWriter 使用的是适配器模式,作为字节流与字符流两个不兼容的类(接口)之间的桥梁。以 InputStreamReader 为例,InputStreamReader 继承了 Reader 抽象类,利用 InputStream 对象(这个对象是由构造方法传来的)的方法,对 Reader 抽象类的方法进行实现(实现的时候是利用 StreamDecoder 进行转码),从而使字节流转换成字符流。
InputStreamReader相关方法:
// 构造方法 public InputStreamReader(InputStream in) public InputStreamReader(InputStream in, String charsetName) public InputStreamReader(InputStream in, Charset cs) public InputStreamReader(InputStream in, CharsetDecoder dec) // 该类中的属性 private final StreamDecoder sd; // 该类中的方法 public String getEncoding() public int read() public int read(char cbuf[], int offset, int length) public boolean ready() public void close()
OutputStreamWriter相关方法:
// 构造方法 public OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out, String charsetName) public OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out) public OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out, Charset cs) public OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out, CharsetEncoder enc) // 该类中的属性 private final StreamEncoder se; // 该类中的方法 public String getEncoding() void flushBuffer() public void write(int c) public void write(char cbuf[], int off, int len) public void write(String str, int off, int len) public void flush() public void close()
2.4.1 FileReader类和FileWriter类
两者都是在构造方法中创建对应的 FileInputStream 或 FileOutputStream对象,然后将调用父构造方法将其传入。
public FileReader(String fileName) public FileReader(File file) public FileReader(FileDescriptor fd)
public FileWriter(String fileName) public FileWriter(String fileName, boolean append) public FileWriter(File file) public FileWriter(File file, boolean append) public FileWriter(FileDescriptor fd)
2.5 FilterReader类和FilterWriter类
FilterReader相关方法:
// 构造方法 protected FilterReader(Reader in) // 该类中的属性 protected Reader in; // 需要装饰的对象 // 该类中的方法 public int read() public int read(char cbuf[], int off, int len) public long skip(long n) public boolean ready() public boolean markSupported() public void mark(int readAheadLimit) public void reset() public void close()
FilterWriter相关方法:
// 构造方法 protected FilterWriter(Writer out) // 该类中的属性 protected Writer out; // 需要装饰的对象 // 该类中的方法 public void write(int c) public void write(char cbuf[], int off, int len) public void write(String str, int off, int len) public void flush() public void close()
2.5.1 PushbackReader类
// 构造方法 public PushbackReader(Reader in, int size) public PushbackReader(Reader in) // 该类中的属性 private char[] buf; private int pos; // 该类中的方法 private void ensureOpen() public int read() public int read(char cbuf[], int off, int len) public void unread(int c) public void unread(char cbuf[], int off, int len) public void unread(char cbuf[]) public boolean ready() public void mark(int readAheadLimit) public void reset() public boolean markSupported() public void close() public long skip(long n)
标签:存在 reader object 文件路径 tor 超过 读取 导致 seq
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/tengyunhao/p/7278126.html