标签:ast next put containe do it result 源码 实现 current
摘要:之前虽然对集合框架一些知识点作了总结,但是想想面试可能会问源码,于是又大致研究了一下集合框架的一些实现类的源码,在此整理一下。
一.集合框架
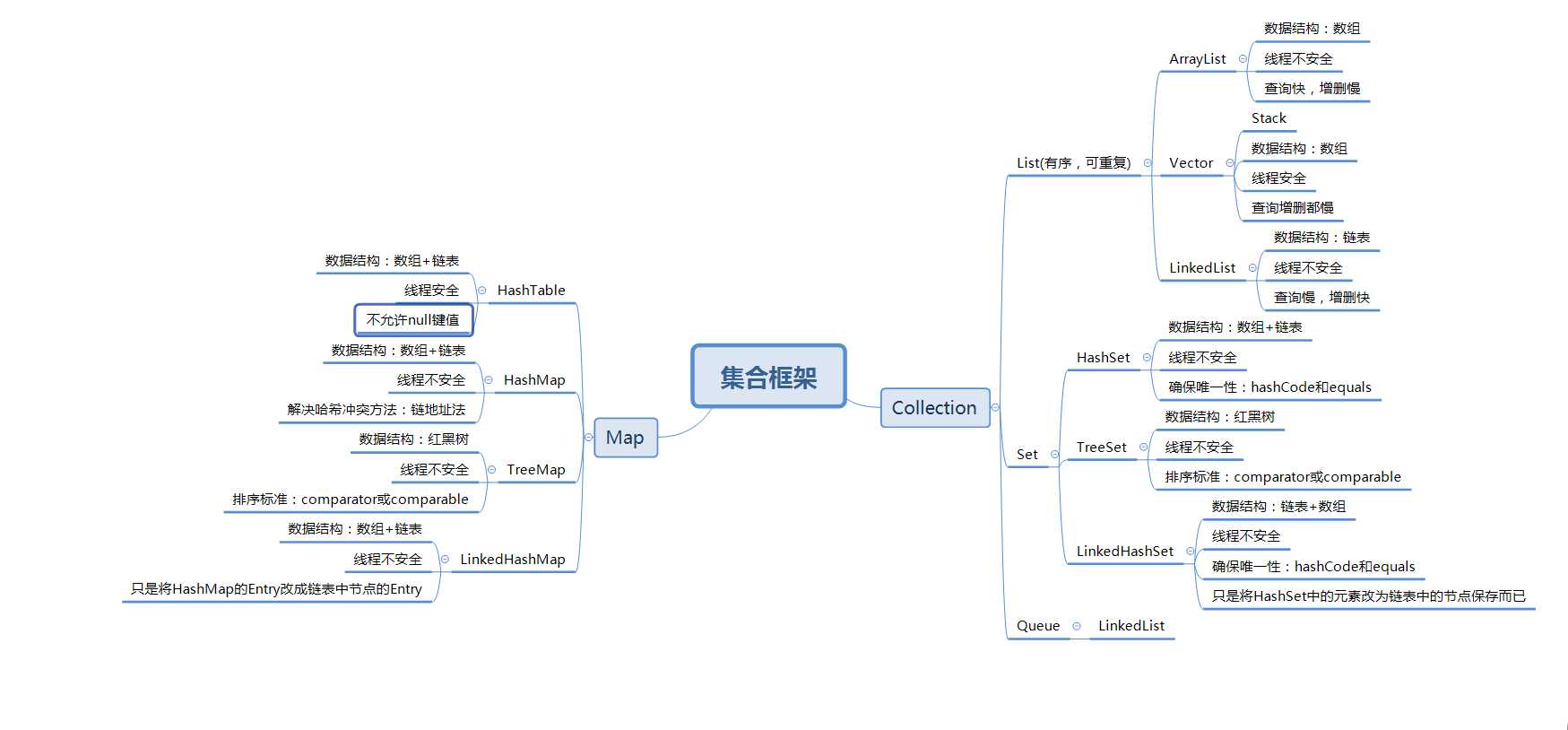
二.深究实现类
1.ArrayList源码实现
ArrayList内部维护了一个动态数组,如果没有显式的初始化的话,动态数组的默认容量是10,当数组容量已满时,每次将容量扩大至1.5倍加1。
ArrayList的remove、add、clear等方法的实现原理都是对内部的Object数组进行操作,需要注意的是,在add方法执行前,都会提前对数组的容量进行确认,如果已满,则先进行扩容,此处很简单,就不对源码进行解析了。
需要注意的是有一个方法trimToSize,这个方法的作用是去掉预留位置,在内存紧张时会用到。

/** * Returns the element at the specified position in this list. * * @param index index of the element to return * @return the element at the specified position in this list * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */ public E get(int index) { rangeCheck(index); return elementData(index); } /** * Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with * the specified element. * * @param index index of the element to replace * @param element element to be stored at the specified position * @return the element previously at the specified position * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */ public E set(int index, E element) { rangeCheck(index); E oldValue = elementData(index); elementData[index] = element; return oldValue; } /** * Appends the specified element to the end of this list. * * @param e element to be appended to this list * @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Collection#add}) */ public boolean add(E e) { ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! elementData[size++] = e; return true; } /** * Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this * list. Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and * any subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices). * * @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted * @param element element to be inserted * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */ public void add(int index, E element) { rangeCheckForAdd(index); ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, size - index); elementData[index] = element; size++; } /** * Removes the element at the specified position in this list. * Shifts any subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their * indices). * * @param index the index of the element to be removed * @return the element that was removed from the list * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */ public E remove(int index) { rangeCheck(index); modCount++; E oldValue = elementData(index); int numMoved = size - index - 1; if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved); elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work return oldValue; } /** * Removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this list, * if it is present. If the list does not contain the element, it is * unchanged. More formally, removes the element with the lowest index * <tt>i</tt> such that * <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt> * (if such an element exists). Returns <tt>true</tt> if this list * contained the specified element (or equivalently, if this list * changed as a result of the call). * * @param o element to be removed from this list, if present * @return <tt>true</tt> if this list contained the specified element */ public boolean remove(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) if (elementData[index] == null) { fastRemove(index); return true; } } else { for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) if (o.equals(elementData[index])) { fastRemove(index); return true; } } return false; }
2.Vector源码实现
Vector同ArrayList相同,也是内部维护了一个动态数组,数组默认长度是10,但是扩容方案与ArrayList有所不同,Vector扩容后的容量取决于扩容因子capacityIncremen和旧数组容量oldCapacity,法则如下:int newCapacity = (capacityIncrement > 0) ?(oldCapacity + capacityIncrement) : (oldCapacity * 2),注意:在计算出新数组尺寸后,还要与Vector类内部定义的最小值和最大值进行比较,如果超过上下限,那么新数组容量就等于上下限。另外,如果初始化时未传入扩容因子,那么扩容因子默认为0。
Vector的基本增删等操作的实现原理与ArrayList相同,都是简单的对数组进行操作。
Vector是线程安全的,实现的方式就是在基本操作的方法添加了synchronized关键字进行修饰,这样就确保了这个方法只能在同一时刻只能被一个线程访问,从而保证了多线程访问的安全性。
Vector内部也实现了迭代器,不过是用Enumeration来实现的。

public Enumeration<E> elements() { return new Enumeration<E>() { int count = 0; public boolean hasMoreElements() { return count < elementCount; } public E nextElement() { synchronized (Vector.this) { if (count < elementCount) { return elementData(count++); } } throw new NoSuchElementException("Vector Enumeration"); } }; }
3.LinkedList
LinkedList内部通过一个双向链表实现,每一个传入的对象都会转化为一个Node节点(Entry和Node都是通过一个内部类实现的),LinkedList的增删基本操作的实现就是通过对链表的节点地址赋值或置null来实现的,具体是link和unlink类似的方法。

private static class Node<E> { E item; Node<E> next; Node<E> prev; Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) { this.item = element; this.next = next; this.prev = prev; } } public boolean add(E e) { linkLast(e); return true; } public boolean remove(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (x.item == null) { unlink(x); return true; } } } else { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (o.equals(x.item)) { unlink(x); return true; } } } return false; }
4.HashSet
HashSet内部是通过HashMap底层来实现的,只不过是将HashMap的value全部赋值为一个常量Object对象,内部的增删等方法都是直接调用hashMap的方法,故在此不做赘述,等HashMap再深入分析。

private transient HashMap<E,Object> map; private static final Object PRESENT = new Object(); public boolean add(E e) { return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null; } public boolean remove(Object o) { return map.remove(o)==PRESENT; }
5.TreeSet
TreeSet内部是通过TreeMap底层来实现的,与HashSet相同,都是将value设定成一个常量。
6.HashMap
HashMap底层是通过数组加链表的数据结构实现的,为什么使用数据加链表的形式呢?这就引出了一个很重要的问题,就是哈希冲突的问题,我们都知道,对于hashXXX这种实现类,确保key唯一性的方法就是hashCode和equals方法,当往HashMap中存入元素时,会对key进行检测,判断是否已经存在相同的key,
标签:ast next put containe do it result 源码 实现 current
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/insistence/p/7476332.html