标签:des style blog http color os io 使用 ar
用 pcap_next_ex() 函数代替 _5_ 中的 pcap_loop()函数;
pcap_loop()函数是基于回调的原理来进行数据捕获,这是一种精妙的方法,并且在某些场合中,它是一种很好的选择。 然而,处理回调有时候并不实用 -- 它会增加程序的复杂度,特别是在拥有多线程的C++程序中。
可以通过直接调用pcap_next_ex() 函数来获得一个数据包 -- 只有当编程人员使用了 pcap_next_ex() 函数才能收到数据包。
这个函数的参数和捕获回调函数的参数是一样的 -- 它包含一个网络适配器的描述符和两个可以初始化和返回给用户的指针 (一个指向 pcap_pkthdr 结构体,另一个指向数据报数据的缓冲)。
在下面的程序中,我们会再次用到上一讲中的有关回调方面的代码,只是我们将它放入了main()函数,之后调用 pcap_next_ex()函数。
int pcap_next_ex ( pcap_t * p, struct pcap_pkthdr ** pkt_header, const u_char ** pkt_data )
Read a packet from an interface or from an offline capture.
This function is used to retrieve the next available packet, bypassing the callback method traditionally provided by libpcap.
pcap_next_ex fills the pkt_header and pkt_data parameters (see pcap_handler()) with the pointers to the header and to the data of the next captured packet.
The return value can be:
typedef void(*) pcap_handler(u_char *user, const struct pcap_pkthdr *pkt_header, const u_char *pkt_data)
Prototype of the callback function that receives the packets.
When pcap_dispatch() or pcap_loop() are called by the user, the packets are passed to the application by means of this callback. user is a user-defined parameter that contains the state of the capture session, it corresponds to the user parameter of pcap_dispatch() and pcap_loop(). pkt_header is the header associated by the capture driver to the packet. It is NOT a protocol header. pkt_data points to the data of the packet, including the protocol headers.

1 #include "pcap.h" 2 #pragma comment(lib, "wpcap.lib") 3 #pragma comment(lib, "Packet.lib") 4 #pragma comment(lib, "wsock32.lib") 5 6 7 #include "pcap.h" 8 9 10 main() 11 { 12 pcap_if_t *alldevs; 13 pcap_if_t *d; 14 int inum; 15 int i=0; 16 pcap_t *adhandle; 17 int res; 18 char errbuf[PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE]; 19 struct tm *ltime; 20 char timestr[16]; 21 struct pcap_pkthdr *header; 22 const u_char *pkt_data; 23 time_t local_tv_sec; 24 25 26 /* 获取本机设备列表 */ 27 if (pcap_findalldevs_ex(PCAP_SRC_IF_STRING, NULL, &alldevs, errbuf) == -1) 28 { 29 fprintf(stderr,"Error in pcap_findalldevs: %s\n", errbuf); 30 exit(1); 31 } 32 33 /* 打印列表 */ 34 for(d=alldevs; d; d=d->next) 35 { 36 printf("%d. %s", ++i, d->name); 37 if (d->description) 38 printf(" (%s)\n", d->description); 39 else 40 printf(" (No description available)\n"); 41 } 42 43 if(i==0) 44 { 45 printf("\nNo interfaces found! Make sure WinPcap is installed.\n"); 46 return -1; 47 } 48 49 printf("Enter the interface number (1-%d):",i); 50 scanf("%d", &inum); 51 52 if(inum < 1 || inum > i) 53 { 54 printf("\nInterface number out of range.\n"); 55 /* 释放设备列表 */ 56 pcap_freealldevs(alldevs); 57 return -1; 58 } 59 60 /* 跳转到已选中的适配器 */ 61 for(d=alldevs, i=0; i< inum-1 ;d=d->next, i++); 62 63 /* 打开设备 */ 64 if ( (adhandle= pcap_open(d->name, // 设备名 65 65536, // 要捕捉的数据包的部分 66 // 65535保证能捕获到不同数据链路层上的每个数据包的全部内容 67 PCAP_OPENFLAG_PROMISCUOUS, // 混杂模式 68 1000, // 读取超时时间 69 NULL, // 远程机器验证 70 errbuf // 错误缓冲池 71 ) ) == NULL) 72 { 73 fprintf(stderr,"\nUnable to open the adapter. %s is not supported by WinPcap\n", d->name); 74 /* 释放设列表 */ 75 pcap_freealldevs(alldevs); 76 return -1; 77 } 78 79 printf("\nlistening on %s...\n", d->description); 80 81 /* 释放设备列表 */ 82 pcap_freealldevs(alldevs); 83 84 /* 获取数据包 */ 85 while((res = pcap_next_ex( adhandle, &header, &pkt_data)) >= 0){ 86 87 if(res == 0) 88 /* 超时时间到 */ 89 continue; 90 91 /* 将时间戳转换成可识别的格式 */ 92 local_tv_sec = header->ts.tv_sec; 93 ltime=localtime(&local_tv_sec); 94 strftime( timestr, sizeof timestr, "%H:%M:%S", ltime); 95 96 printf("%s,%.6d len:%d\n", timestr, header->ts.tv_usec, header->len); 97 } 98 99 if(res == -1){ 100 printf("Error reading the packets: %s\n", pcap_geterr(adhandle)); 101 return -1; 102 } 103 104 return 0; 105 }
·结果:
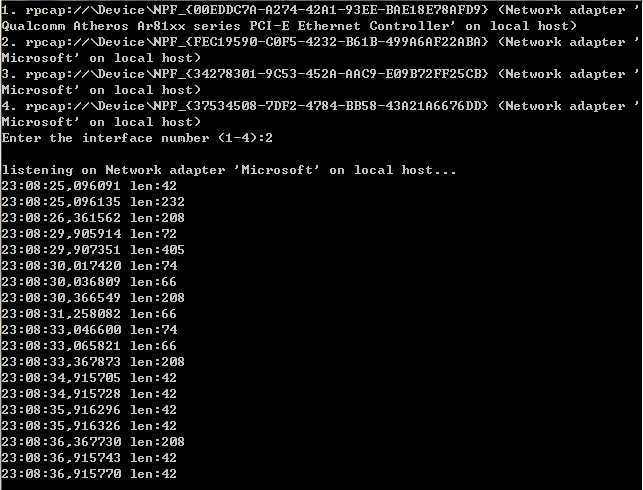
为什么我们要用 pcap_next_ex() 代替以前的 pcap_next()? 因为 pcap_next() 有一些不好的地方。首先,它效率低下,尽管它隐藏了回调的方式,但它依然依赖于函数 pcap_dispatch()。第二,它不能检测到文件末尾这个状态(EOF),因此,如果数据包是从文件读取来的,那么它就不那么有用了。
值得注意的是, pcap_next_ex() 在成功,超时,出错或EOF的情况下,会返回不同的值。
标签:des style blog http color os io 使用 ar
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/aze-003/p/3960020.html