标签:控制 control red stat div 访问 通过 type get
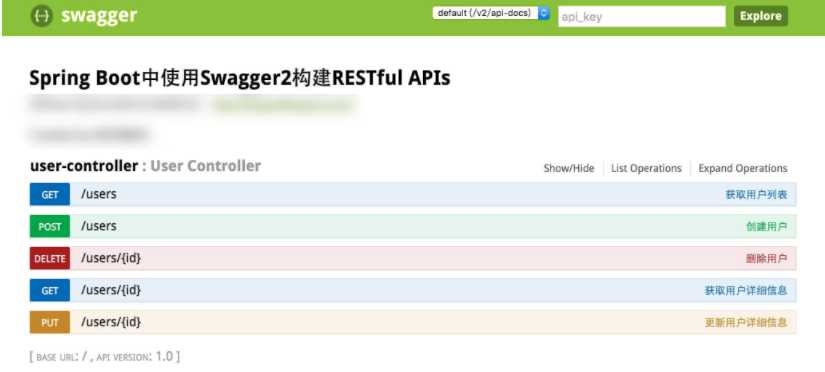
效果如下图所示:
添加Swagger2依赖
在pom.xml中加入Swagger2的依赖
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.springfox/springfox-swagger2 --> <dependency> <groupId>io.springfox</groupId> <artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId> <version>2.7.0</version> </dependency> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.springfox/springfox-swagger-ui --> <dependency> <groupId>io.springfox</groupId> <artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId> <version>2.7.0</version> </dependency>
创建Swagger2配置类
在Application.java同级创建Swagger2的配置类Swagger2。
@Configuration @EnableSwagger2 public class Swagger2 { @Bean public Docket createRestApi() { return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2) .apiInfo(apiInfo()) .select() .apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.didispace.web")) .paths(PathSelectors.any()) .build(); } private ApiInfo apiInfo() { return new ApiInfoBuilder() .title("Spring Boot中使用Swagger2构建RESTful APIs") .description("更多Spring Boot相关文章请关注:http://easonjim.com/") .termsOfServiceUrl("http://easonjim.com/") .contact("EasonJim") .version("1.0") .build(); } }
如上代码所示,通过@Configuration注解,让Spring来加载该类配置。再通过@EnableSwagger2注解来启用Swagger2。
再通过createRestApi函数创建Docket的Bean之后,apiInfo()用来创建该Api的基本信息(这些基本信息会展现在文档页面中)。select()函数返回一个ApiSelectorBuilder实例用来控制哪些接口暴露给Swagger来展现,本例采用指定扫描的包路径来定义,Swagger会扫描该包下所有Controller定义的API,并产生文档内容(除了被@ApiIgnore指定的请求)。
添加文档内容
在完成了上述配置后,其实已经可以生产文档内容,但是这样的文档主要针对请求本身,而描述主要来源于函数等命名产生,对用户并不友好,我们通常需要自己增加一些说明来丰富文档内容。如下所示,我们通过@ApiOperation注解来给API增加说明、通过@ApiImplicitParams、@ApiImplicitParam注解来给参数增加说明。
@RestController @RequestMapping(value="/users") // 通过这里配置使下面的映射都在/users下,可去除 public class UserController { static Map<Long, User> users = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap<Long, User>()); @ApiOperation(value="获取用户列表", notes="") @RequestMapping(value={""}, method=RequestMethod.GET) public List<User> getUserList() { List<User> r = new ArrayList<User>(users.values()); return r; } @ApiOperation(value="创建用户", notes="根据User对象创建用户") @ApiImplicitParam(name = "user", value = "用户详细实体user", required = true, dataType = "User") @RequestMapping(value="", method=RequestMethod.POST) public String postUser(@RequestBody User user) { users.put(user.getId(), user); return "success"; } @ApiOperation(value="获取用户详细信息", notes="根据url的id来获取用户详细信息") @ApiImplicitParam(name = "id", value = "用户ID", required = true, dataType = "Long") @RequestMapping(value="/{id}", method=RequestMethod.GET) public User getUser(@PathVariable Long id) { return users.get(id); } @ApiOperation(value="更新用户详细信息", notes="根据url的id来指定更新对象,并根据传过来的user信息来更新用户详细信息") @ApiImplicitParams({ @ApiImplicitParam(name = "id", value = "用户ID", required = true, dataType = "Long"), @ApiImplicitParam(name = "user", value = "用户详细实体user", required = true, dataType = "User") }) @RequestMapping(value="/{id}", method=RequestMethod.PUT) public String putUser(@PathVariable Long id, @RequestBody User user) { User u = users.get(id); u.setName(user.getName()); u.setAge(user.getAge()); users.put(id, u); return "success"; } @ApiOperation(value="删除用户", notes="根据url的id来指定删除对象") @ApiImplicitParam(name = "id", value = "用户ID", required = true, dataType = "Long") @RequestMapping(value="/{id}", method=RequestMethod.DELETE) public String deleteUser(@PathVariable Long id) { users.remove(id); return "success"; } }
完成上述代码添加上,启动Spring Boot程序,访问:http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html
。就能看到前文所展示的RESTful API的页面。我们可以再点开具体的API请求,以POST类型的/users请求为例,可找到上述代码中我们配置的Notes信息以及参数user的描述信息,如下图所示。
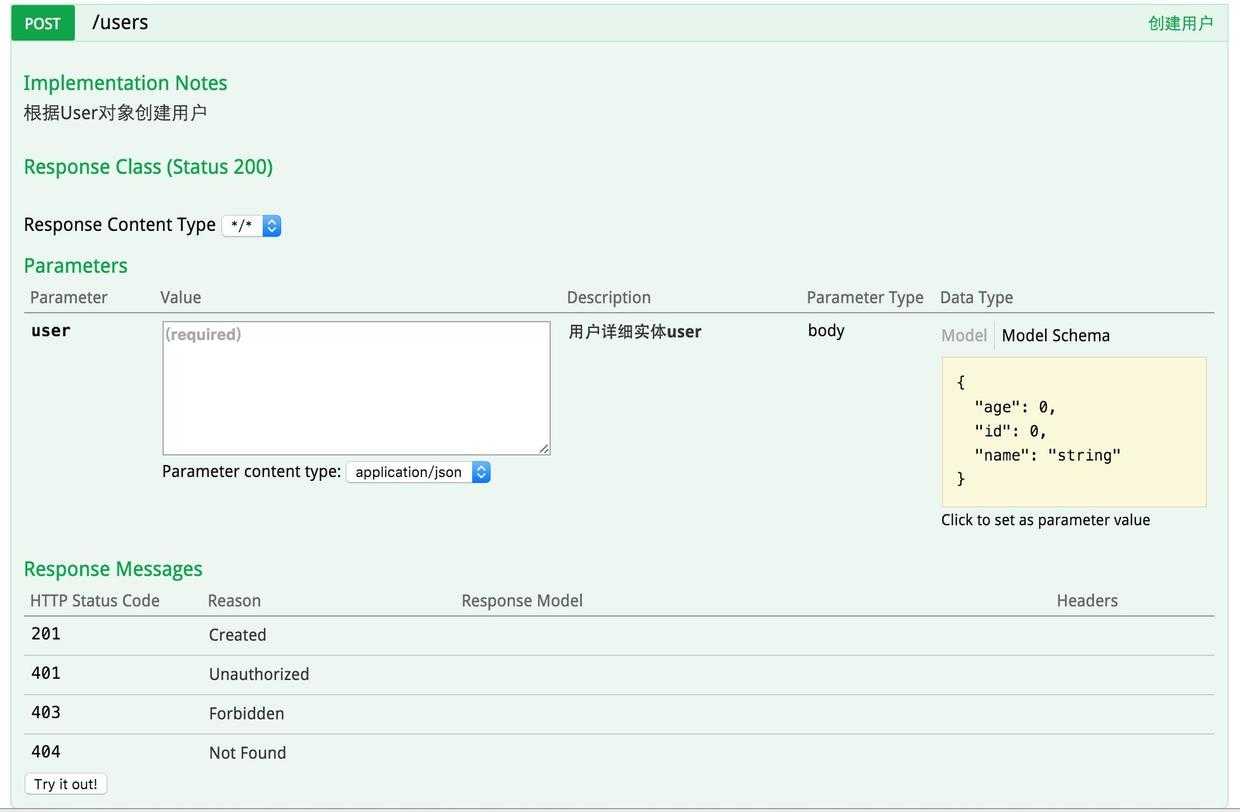
在上图请求的页面中,我们看到user的Value是个输入框?是的,Swagger除了查看接口功能外,还提供了调试测试功能,我们可以点击上图中右侧的Model Schema(黄色区域:它指明了User的数据结构),此时Value中就有了user对象的模板,我们只需要稍适修改,点击下方“Try it out!”按钮,即可完成了一次请求调用!
Maven示例:
https://github.com/easonjim/5_java_example/tree/master/springboottest/springboottest2
参考:
http://www.jianshu.com/p/8033ef83a8ed(以上内容转自此篇文章)
Spring Boot中使用Swagger2生成RESTful API文档(转)
标签:控制 control red stat div 访问 通过 type get
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/EasonJim/p/7518394.html