标签:str pad 技术 contain argument abc python2.x while 添加
print >> sys.stdout的形式就是print的一种默认输出格式,等于print "%VALUE%"
看下面的代码的英文注释,是print的默认帮助信息
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
# coding=utf-8import sys, oslist1Display = [‘1‘, ‘2‘, ‘3‘]list2Display = [‘abc‘, ‘def‘, ‘rfs‘]while list2Display != []: # Prints the values to a stream, or to sys.stdout by default. # Optional keyword arguments: # file: a file-like object (stream); defaults to the current sys.stdout. # sep: string inserted between values, default a space. # end: string appended after the last value, default a newline. # print 可以将值输出到指定的输出流(可以是文件句柄),若不指定, # 则输出到stdout(标准输出) # 一般我们使用的时候不加输出定向符“>>”到输出的file对象,本代码中对象是stdout # 下面的print在stdout对象中每次输出两个值 print >> sys.stdout, list2Display.pop(), list1Display.pop()os.system( "pause" ) |
上文中只演示了python2.x中的用法,2.x中的print无法指定end符号为其他值,默认会输出一个"\n",也就是用一次必定换到下一行,到了3.x中print成为了一个真正意义上的函数,后来就可以任意指定end符号的值,你可以输出一次后末尾添加上任意你想要的值,而不是强制换行。
因此在2.x中若想实现输出不换行,只能直接调用stdout对象的write方法了,下面也是一个实例,因为stdout没有end这个符号这一说,输出不会换行,因此如果你想同一样输出多次,在需要输出的字符串对象里面加上"\r",就可以回到行首了。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
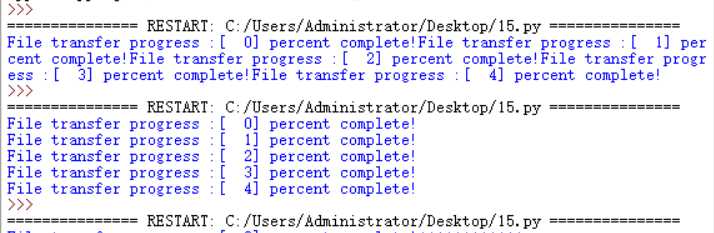
# coding=utf-8import sys, osimport timefor i in range(5): time.sleep( .5 ) sys.stdout.write( "File transfer progress :[%3d] percent complete!\r" % i ) sys.stdout.flush() |
体会一下,将上面的"\r"拿掉试试看,是不是不换行而直接输出了?明白了么。很长一段时间内python都会停留在2.x的时代。
运行结果的区别如下:
-----------------------------------------------------------------
网络摘抄笔记,若涉及版本,请联系本博主删除。
python 中sys.stdout.write 和 print >> sys.stdout的区别
标签:str pad 技术 contain argument abc python2.x while 添加
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/suosuoshu/p/7607584.html