标签:base png 应用 struct mat mda strftime 三种方式 需要
最近在做一个项目:CMDB(Configuration Management Database)资产采集,由于当中涉及一个classmethod(类方法)方法,发现不会。
还有一个staticmethod(静态方法)方法一直不熟悉,所以从网上查阅的资料,加强理解,遂整理如下:
@classmethod:类方法( 只在类中运行而不在实例中运行的方法)
class C:
@classmethod
def f(cls,arg1,arg2,...):
举例来说明吧。
看下面定义的一个时间类:
class Date_test(object):
day=0
month=0
year=0
def __init__(self,year=0,month=0,day=0):
self.day=day
self.month=month
self.year=year
def out_date(self):
print("year:%s;month:%s;day:%s"%(self.year,self.month,self.day))
t=Date_test(2016,8,1)
t.out_date()
运行结果:
year:2016;month:8;day:1
符合期望。
如果用户输入的是“2016-8-1”的格式,那么就需要调用Date_test类前做一下处理:
string_date=‘2016-8-1‘ year,month,day=map(int,string_date.split(‘-‘)) s=Date_test(year,month,day)
先把‘2016-8-1’分解成year,month,day三个变量,然后转成int,再调用Date_test(year,month,day)函数。也很符合期望。
那我可不可以把这个字符串处理的函数放到Date_test类当中呢?
那么@classmethod就开始出场了。
class Date_test(object):
day=0
month=0
year=0
def __init__(self,year=0,month=0,day=0):
self.day=day
self.month=month
self.year=year
@classmethod
def get_date(cls,string_date):
#这里第一个参数是cls,表示调用当前的类名
year,month,day=map(int,string_date.split(‘-‘))
date1=cls(year,month,day)
#返回的是一个初始化后的类
return date1
def out_date(self):
print("year:%s;month:%s;day:%s"%(self.year,self.month,self.day))
#调用
obj=Date_test.get_date(‘2016-8-1‘)
obj.out_date()
运行结果:
year:2016;month:8;day:1
是不是瞬间很清晰了呢?!
下面接着看staticmethod的用法,以及两者的区别
@classmethod也不需要self参数,但第一个参数需要是表示自身类的cls参数。
应用场景:编写类时需要采用很多不同的方式来创建实例,而我们只有一个__init__函数,此时静态方法就派上用场了
下面上代码:
import time
class Date(object):
def __init__(self,year,month,day):
self.year=year
self.month=month
self.day=day
@staticmethod
def now():
t=time.localtime()
return Date(t.tm_year, t.tm_mon, t.tm_mday)
@staticmethod
def tomorrow():
t=time.localtime(time.time()+86400)
return Date(t.tm_year,t.tm_mon,t.tm_mday)
a=Date(2017,9,29)
b=Date.now()
c=Date.tomorrow()
print(‘__init__方法:‘,a.year,a.month,a.day)
print(‘staticmethod方法,当前时间:%s-%s-%s‘%(b.year,b.month,b.day))
print(‘staticmethod方法,明日时间:%s-%s-%s‘%(c.year,c.month,c.day))
运行结果:
staticmethod方法,当前时间:2017-9-29
staticmethod方法,明日时间:2017-9-30
tips:
Python中表示时间有三种方式:1)时间戳 2)格式化的时间字符串 3)元组(struct_time)
元组(struct_time)方式:struct_time元组共有9个元素,返回struct_time的函数主要有gmtime(),localtime(),strptime()。下面列出这种方式元组中的几个元素:
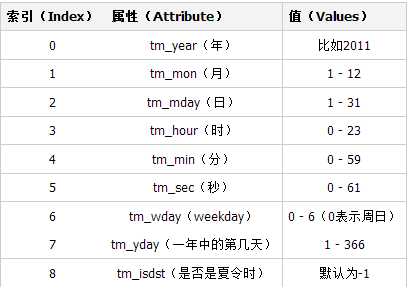
常用时间函数:
(1)time.localtime([secs]):将一个时间戳转换为当前时区的struct_time。secs参数未提供,则以当前时间为准。
(2)time.gmtime([secs]):和localtime()方法类似,gmtime()方法是将一个时间戳转换为UTC时区(0时区)的struct_time。
(3)time.strptime(string[, format]):把一个格式化时间字符串转化为struct_time。实际上它和strftime()是逆操作。
随性整理,查漏补缺,待补充。
话说最近CMDB项目中遇到的问题整理:类方法:classmethod、staticmethod
标签:base png 应用 struct mat mda strftime 三种方式 需要
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/metianzing/p/7613035.html