标签:images uppercase 宽度 oct amount init else pen 形参
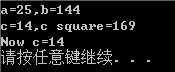
#include<iostream> using namespace std; inline double square(double x) {//inline表示内联函数 return x*x; } void main() { double a, b, c = 13.0; a = square(5.0); b = square(4.5+7.5); cout << "a=" << a << ",b=" << b << endl; cout << "c=" << c << ",c square=" << square(c++) << endl; cout << "Now c=" <<c<< endl; system("pause"); }

引用变量的主要用途是作为函数的形参:引用变量做参数,函数将使用原始数据。
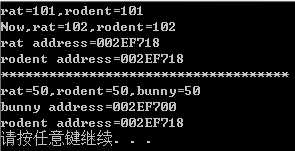
#include<iostream> using namespace std; void main() { int rat = 101; int &rodent = rat;//将rodent的类型声明为int&,即指向int变量的引用 cout << "rat=" <<rat<< ",rodent=" <<rodent<< endl; rodent++; cout << "Now,rat=" << rat << ",rodent=" << rodent << endl; cout << "rat address=" << &rat << endl; cout << "rodent address=" <<&rodent<< endl; cout << "************************************" << endl; int bunny = 50; rodent = bunny; cout << "rat=" << rat << ",rodent=" << rodent<<",bunny="<<bunny << endl; cout << "bunny address=" << &bunny << endl; cout << "rodent address=" << &rodent << endl; system("pause"); }
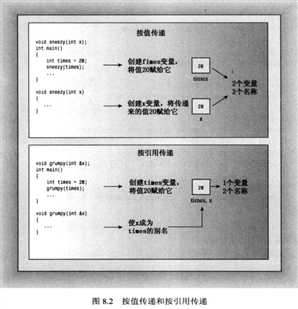
如果实参与引用参数不匹配,仅当参数为const引用时,C++将生成临时变量。


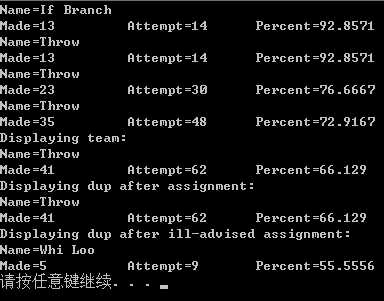
#include<iostream> #include<string> using namespace std; struct free_throw { string name; int made; int attempt; float percent; }; void display(const free_throw &ft) { cout << "Name=" << ft.name << endl; cout << "Made=" << ft.made << "\t\t"; cout << "Attempt=" << ft.attempt<< "\t"; cout << "Percent=" << ft.percent<<endl; } void set(free_throw &ft) { if (ft.attempt != 0) ft.percent = 100.0f*float(ft.made) / float(ft.attempt); else ft.percent = 0; } free_throw & accumulate(free_throw &target,const free_throw &source) { target.attempt += source.attempt; target.made += source.made; set(target); return target; } void main() { free_throw one = { "If Branch",13,14 }; free_throw two = { "Andor Knott",10,16 }; free_throw three = { "Min Max",7,9 }; free_throw four = { "Whi Loo",5,9 }; free_throw five = { "Long Long",6,14 }; free_throw team = { "Throw",0,0}; free_throw dup; set(one); display(one); accumulate(team, one); display(team); display(accumulate(team,two)); accumulate(accumulate(team, three), four); display(team); dup = accumulate(team, five);//返回的team赋给dup cout << "Displaying team:" << endl; display(team);//team经过48行代码,已经发生了变化 cout << "Displaying dup after assignment:" << endl; display(dup); set(four); accumulate(dup, five) = four;//four赋给dup cout << "Displaying dup after ill-advised assignment:" << endl; display(dup); system("pause"); }
string:标准库允许把字符串字面值和字符字面值转换为 string 对象,当把 string 对象和字符字面值以及字符串字面值混在一条语句中使用时,必须确保加法运算符( + )的两侧运算对象至少有一个是 string:
#include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; string version1(const string &s1, const string &s2) { string tmp; tmp = s2 + s1 + s2; return tmp;//返回main函数时,tmp不复存在,但tmp的内容被复制到临时存储单元 } string & version2(string &s1, const string &s2) {//有副作用,改变了s1的内容 s1 = s2 + s1 + s2; return s1; } string & version3(string &s1, const string &s2) {//坏设计 string tmp; tmp = s2 + s1 + s2; return tmp;//返回main函数时,tmp内存已被释放,程序不能引用已经释放的内存 } void main() { string input, copy, result; cout << "Enter a string:"; getline(cin, input);//用于字符串的输入 copy = input;//C++中,string可以直接赋值 cout << "Your string as entered:" << input << endl; result = version1(input, "***"); cout << "Your string enhanced:" << result << endl; cout << "Your original string:" << input << endl; result = version2(input, "###"); cout << "Your string enhanced:" << result << endl; cout << "Your original string:" << input << endl; cout << "Resetting original string." << endl; input = copy; result = version3(input, "@@@");//version3返回地址值时报错,因为该地址已释放 cout << "Your string enhanced:" << result << endl; cout << "Your original string:" << input << endl; system("pause"); }

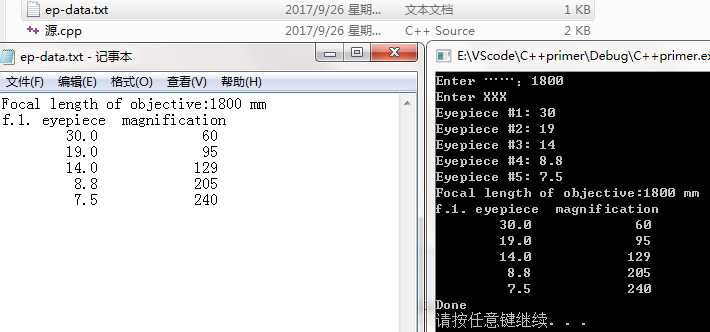
#include <iostream> #include <fstream> #include <cstdlib> using namespace std; const int LIMIT = 5; void file_it(ostream &os,double fo,const double fe[],int n) {//参数os可以指向ostream对象(如cout),也可以指向ofstream对象(如fout) ios_base::fmtflags initial;//ios_base::fmtflags是存储这种信息所需的数据类型名称 initial = os.setf(ios_base::fixed);//setf(ios_base::fixed)使用定点表示法 表示对象 os.precision(0);//指定显示多少位小数(假定处于定点模式下) os << "Focal length of objective:" << fo << " mm"<<endl; os.setf(ios::showpoint);//使用小数点 表示对象,即使小数部分为0 os.precision(1); os.width(12);//设置下一次输出操作使用的字段宽度,只在显示下一个值时有效 os << "f.1. eyepiece"; os.width(15); os << "magnification" << endl; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { os.width(12); os << fe[i]; os.width(15); os << int(fo / fe[i] + 0.5) << endl; } os.setf(initial);//返回调用它之前有效的所有格式化设置,即将对象回到传递给file_it()之前的状态 //当程序将cout传递给file_it()时,cout的设置将被修改,然后被恢复;fout同样如此 } void main() { ofstream fout; const char *fn = "ep-data.txt"; fout.open(fn); if (!fout.is_open()) { cout << "Can‘t open "<< fn <<".Bye."<< endl; exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } double objective; cout << "Enter ……:"; cin >> objective; double eps[LIMIT]; cout << "Enter XXX" << endl; for (int i = 0; i < LIMIT; i++) { cout << "Eyepiece #" << i + 1 << ": "; cin >> eps[i]; } file_it(fout, objective, eps, LIMIT);//将数据写入文件ep-data.txt file_it(cout, objective, eps, LIMIT);//将同样的信息以相同的格式显示到屏幕上 cout << "Done" << endl; system("pause"); }
以下是一些常见的控制函数的:
dec 置基数为10 相当于"%d"
hex 置基数为16 相当于"%X"
oct 置基数为8 相当于"%o"
setfill(c) 设填充字符为c
setprecision(n) 设显示小数精度为n位
setw(n) 设域宽为n个字符
setioflags(ios::fixed) 固定的浮点显示
setioflags(ios::scientific) 指数表示
setiosflags(ios::left) 左对齐
setiosflags(ios::right) 右对齐
setiosflags(ios::skipws 忽略前导空白
setiosflags(ios::uppercase) 16进制数大写输出
setiosflags(ios::lowercase) 16进制小写输出
setiosflags(ios::showpoint) 强制显示小数点
setiosflags(ios::showpos) 强制显示符号
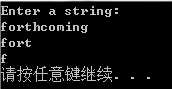
#include <iostream> using namespace std; const int Size = 80; char *left(const char *str, int n = 1);//默认n为1 void main() { char sample[Size]; cout << "Enter a string:\n"; cin.get(sample, Size); char *p = left(sample, 4);//调用此方法后要记得delete cout << p << endl; delete[] p; p = left(sample); cout << p << endl; delete[] p; system("pause"); } char *left(const char *str, int n) {//内部使用了new未delete,所以在main函数调用此方法后一定要记得delete if (n < 0) n = 0; char *p = new char[n + 1];//new和delete成对出现 int i; for (i = 0; i < n&&str[i]; i++) p[i] = str[i]; while (i <= n) p[i++] = ‘\0‘; return p; }
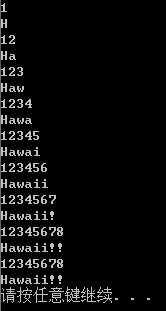
#include <iostream> using namespace std; char *left(const char *str, int n) {//内部使用了new未delete,所以在main函数调用此方法后一定要记得delete if (n < 0) n = 0; char *p = new char[n + 1];//new和delete成对出现 int i; for (i = 0; i < n&&str[i]; i++) p[i] = str[i]; while (i <= n) p[i++] = ‘\0‘; return p; } unsigned long left(unsigned long num, unsigned ct) { if (ct == 0 || num == 0) return 0; unsigned digit = 1; unsigned long n = num; while (n /= 10) digit++; if (digit > ct) { ct = digit - ct; while (ct--) num /= 10; return num; } else return num; } void main() { char *trip = "Hawaii!!"; unsigned long n = 12345678; int i; char * temp; for (i = 1; i < 10; i++) { cout << left(n, i) << endl; temp = left(trip, i); cout << temp << endl; delete[] temp; } system("pause"); }
#include <iostream> using namespace std; template <typename T> //函数模板 void swap2(T &a, T &b) { //引用 不能用swap函数名,用户自己定义的swap()函数与STL库定义的函数重载冲突 T temp; temp = a; a = b; b = temp; } template <typename T> void swap2(T a[], T b[],int n) { T temp; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { temp = a[i]; a[i] = b[i]; b[i] = temp; } } const int Size = 5; template <class Te>//模板的另一种表示方式 void show(Te a[]) { for (int i = 0; i < Size; i++) { cout << a[i] << "\t"; } cout << endl; } void main() { int i = 10, j = 20; cout << "i=" << i << ",j=" << j << endl; swap2(i, j); cout << "Now,i=" << i << ",j=" << j << endl; double x[Size] = { 1,2,3,4,5 }; double y[] = {6,7,8,9,10}; show(x); show(y); swap2(x, y ,Size); cout << "Now" << endl; show(x); show(y); system("pause"); }

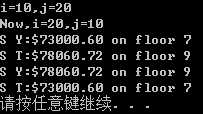
#include <iostream> using namespace std; //模板:交换a、b值 template <typename T> void Swap(T &a, T &b) { T temp = a; a = b; b = temp; } struct job { char name[40]; double salary; int floor; }; //显示具体化:交换结构体内部成员值 template <> void Swap<job>(job &j1, job &j2) {//引用 double t1; int t2; t1 = j1.salary; j1.salary = j2.salary; j2.salary = t1; t2 = j1.floor; j1.floor = j2.floor; j2.floor = t2; } void show(job &j) {//引用 cout << j.name << ":$"<<j.salary<<" on floor "<<j.floor<<endl; } void main() { cout.precision(2);//指定显示多少位小数(假定处于定点模式下):看有没有set ios::fixed,如果没有的话, 是代表2位有效数字, 不是3位小数 cout.setf(ios::fixed,ios::floatfield);//ios::fixed设置为定点输出格式,floatfield设置输出时按浮点格式,小数点后有6位数字 int i = 10, j = 20; cout << "i=" << i << ",j=" << j << endl; Swap(i, j); cout << "Now,i=" << i << ",j=" << j << endl; job sue = { "S Y",73000.60,7 }; job sid = { "S T",78060.72,9 }; show(sue); show(sid); Swap(sue, sid); show(sue); show(sid); system("pause"); }
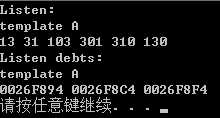
#include <iostream> using namespace std; template <typename T> void show(T arr[],int n) { cout << "template A" << endl; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cout << arr[i] << ‘ ‘; cout << endl; } template <typename T> void show(T * arr[], int n) {//指针数组:[]比*优先级高 cout << "template B" << endl; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cout << *arr[i] << ‘ ‘; cout << endl; } struct debt { char name[40]; double amount; }; void main() { int thing[6] = { 13,31,103,301,310,130 }; struct debt mr_E[3] = { { "I W",2400.0 }, { "U F",1300.0 }, { "I S",1800.0 } }; double *pd[3]; for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) pd[i] = &mr_E[i].amount; cout << "Listen:" << endl; show(thing, 6); cout << "Listen debts:" << endl; show(pd, 3); system("pause"); }
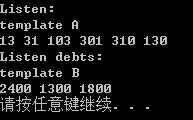
如果去掉 template B ,打印出来的将是地址
#include <iostream> using namespace std; //返回小值 template <typename T> T lesser(T a,T b) { return a < b ? a : b; } //先取绝对值,再返回绝对值中的小值 int lesser(int a, int b) { a = a < 0 ? -a : a; b = b < 0 ? -b : b; return a < b ? a : b; } void main() { int m = 20, n = -30; double x = 15.5, y = 25.9; cout << lesser(m, n) << endl;//调用函数 cout << lesser(x, y) << endl;//调用模板函数 cout << lesser<>(m, n) << endl;//<>表示调用模板函数 cout << lesser<int>(x,y)<<endl;//<int>表示 显示实例化,强转xy值 system("pause"); }


[C++ Primer Plus] 第8章、函数探幽(一)程序清单——内联、引用、格式化输入输出、模板、decltype
标签:images uppercase 宽度 oct amount init else pen 形参
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/little-monkey/p/7593281.html