标签:ext nbsp deb images done 接受 get strlen() +=
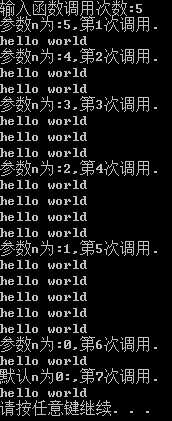
1.编写通常接受一个参数(字符串的地址),并打印该字符串的函数。不过,如果提供了第二个参数(int类型),且该参数不为0,则该函数打印字符串的次数将为该函数被调用的次数(注意,字符串的打印次数不等于第二个参数的值,而等于函数被调用的次数)。是的,这是一个非常可笑的函数,但它让读者能够使用本章介绍的一些技术。在一个简单的程序中使用该函数,以演示该函数是如何工作的。
#include <iostream> using namespace std; void show(const char * a, int b = 0);//默认b为0 void show(const char * a, int b) { static int uses = 0; int lim = ++uses; cout << ",第" << uses << "次调用.\n"; if (b == 0) lim = 1; for (int i = 0; i<lim; i++) cout << a<< endl; } void main() { int i; const char * p = "hello world"; cout << "输入函数调用次数:"; cin >> i; while (i >= 0) { cout << "参数n为:" << i; show(p, i); i--; } cout << "默认n为0:"; show(p); system("pause"); }
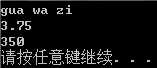
2、CandyBar结构饱含3个成员。第一个成员存储candy bar的品牌名称;第二个成员存储candy bar的重量(可能有小数);第三个成员存储candy bar的热量(整数)。请编写一个程序,它使用一个这样的函数,即将CandyBar的引用、char指针、double和int作为参数,并用最后3个值设置相应的结构成员。最后3个参数的默认值分别为"Millennium Munch"、2.85和350。另外,该程序还包含一个以CandyBar的引用为参数,并显示结构内容的函数。请尽可能使用const.
#include <iostream> using namespace std; struct CandyBar { char brand[50]; double weight; int energy; }; void fun(CandyBar &cb, char *p = "Mill Munch", double w = 2.85, int e = 350) { strcpy(cb.brand,p); //字符串拷贝,字符串不能直接使用赋值号 cb.weight = w; cb.energy = e; } void show(const CandyBar &cb) { cout << cb.brand << endl; cout << cb.weight<< endl; cout << cb.energy<< endl; } void main() { CandyBar haha; fun(haha, "gua wa zi", 3.75); show(haha); system("pause"); }
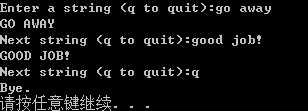
enter a string (q to quit) :go away
GO AWAY
next string (q to quit) : good grief !
GOOD GRIEF!
next string (q to quit) : q
bye.
#include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; void toBig(string &s) { int i = 0; while (s[i]) { s[i] = toupper(s[i]); i++; } } void main() { string str; cout << "Enter a string (q to quit):"; getline(cin, str); while (str != "q") { toBig(str); cout << str << endl; cout << "Next string (q to quit):"; getline(cin, str); } cout << "Bye." << endl; system("pause"); }

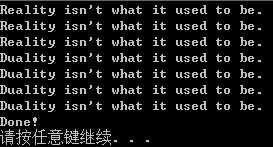
#include <iostream> #include <cstring> //for strlen(),strcpy() using namespace std; struct stringy { char *str; int ct; }; void set(stringy &s, const char *str); void show(const char *str, const int count = 1); void show(const stringy &s, const int count = 1); void main() { stringy beany; char testing[] = "Reality isn‘t what it used to be."; set(beany, testing); show(beany); show(beany, 2); testing[0] = ‘D‘; testing[1] = ‘u‘; show(testing); show(testing, 3); show("Done!"); system("pause"); } void set(stringy &s, const char *str) { int len = strlen(str); s.ct = len; s.str = new char(len + 1); //要留一个字符存放‘\0‘ 所以分配len + 1空间 strcpy(s.str, str); } void show(const char *str, const int count) { for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i) cout << str << endl; } void show(const stringy &s, const int count) { for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i) cout << s.str << endl; }
5、编写模板函数max5(),它将一个包含5个T类型元素的数组作为参数,并返回数组中最大的元素(由于长度固定,因此可以在循环中使用硬编码,而不必通过参数来传递)。在一个程序中使用该函数,将T替换为一个包含5个int值的数组和一个包含5个dowble值的数组,以测试该函数。
#include <iostream> using namespace std; template<typename T> T max5(T t[5]) { T m=t[0]; for (int i = 1; i < 5; i++) { if (t[i] > m) m = t[i]; } return m; } void main() { int n[] = { 1,8,10,6,3 }; double m[] = { 5.0,2.0,7.0,3.0,7.1 }; cout << max5(n) << endl; cout << max5(m) << endl; system("pause"); }

6、编写模板函数maxn(),它将由一个T类型元素组成的数组和一个表示数组元素数目的整数作为参数,并返回数组中最大的元素。在程序对它进行测试,该程序使用一个包含6个int元素的数组和一个包含4个double元素的数组来调用该函数。程序还包含一个具体化,它将char指针数组和数组中的指针数量作为参数,并返回最长的字符串的地址。如果有多个这样的字符串,则返回其中第一个字符串的地址。使用由5个字符串指针组成的数组来测试该具体化。
#include <iostream> #include <cstring> using namespace std; template<typename T> T maxn(T t[],int n) { T m=t[0]; for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) { if (t[i] > m) m = t[i]; } return m; } //模板具体化 template <> char * maxn<char *>(char *arr[], int n) { int len = strlen(arr[0]); char *p = arr[0]; for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) { if (strlen(arr[i]) > len) { p = arr[i]; len = strlen(arr[i]); } } return p; } void main() { int n[] = { 1,8,10,6,30,7 }; double m[] = { 5.0,2.0,7.2,3.0}; cout << maxn(n,6) << endl; cout << maxn(m,4) << endl; char *str[] = { "asd","asdf","asdfg","asdfgh","asdfop"}; cout << maxn(str, 5) << endl; system("pause"); }

7.修改程序清单8.14,使模板函数返回数组元素的总和,而不是显示数组的内容.程序thing的总和以及所有debt的总和.
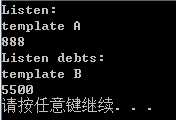
#include <iostream> using namespace std; template <typename T> T SumArray(T arr[], int n) { cout << "template A" << endl; T sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) sum+=arr[i]; return sum; } template <typename T> T SumArray(T * arr[], int n) {//指针数组:[]比*优先级高 cout << "template B" << endl; T sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) sum += *arr[i]; return sum; } struct debt { char name[40]; double amount; }; void main() { int thing[6] = { 13,31,103,301,310,130 }; struct debt mr_E[3] = { { "I W",2400.0 }, { "U F",1300.0 }, { "I S",1800.0 } }; double *pd[3]; for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) pd[i] = &mr_E[i].amount; cout << "Listen:" << endl; cout <<SumArray(thing, 6)<<endl; cout << "Listen debts:" << endl; cout << SumArray(pd, 3)<<endl; system("pause"); }
[C++ Primer Plus] 第8章、函数探幽(二)课后习题
标签:ext nbsp deb images done 接受 get strlen() +=
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/little-monkey/p/7625885.html