标签:targe 系统 als blog world base 业务 image mys
Spring Framework 是 IOC (Inversion of Control 控制反转)原则的实践。 IoC is also known as dependency injection (DI 依赖注入)。
org.springframework.beans 和 org.springframework.context 两个包实现了Ioc 容器。 BeanFactory接口的子接口 ApplicationContext 定义了容器的基本功能。如果是web app 使用的是 WebApplicationContext 。
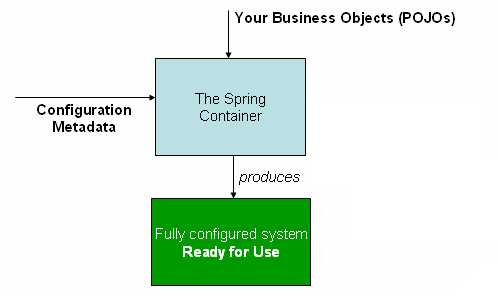
这个容器的作用正如上图, 把定义在配置文件中的 POJO的关系解析并实例化,应用业务系统。
POJO: Plain Old Java Object 。
spring配置文件有以下三种形式:
build.gradle
apply plugin: ‘java‘ apply plugin: ‘idea‘ // mainClassName 是 application的一个属性,否则会报错 apply plugin: ‘application‘ mainClassName = ‘xmlConfig.HelloWorld‘ sourceCompatibility = 1.8 targetCompatibility = 1.8 repositories { mavenCentral() } dependencies { compile "joda-time:joda-time:2.2" compile ‘org.springframework:spring-context:5.0.0.RELEASE‘ } // 该项目生成的jar包的名字和版本,如 gs-gradle-0.1.0.jar jar { baseName = ‘gs-gradle‘ version = ‘0.1.0‘ }
在src/main/resources目录下创建 helloWorld.xml,这个文件名字随意
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="helloWorld" name="helloWorld2" class="xmlConfig.HelloWorld"/> </beans>
HelloWorld.java
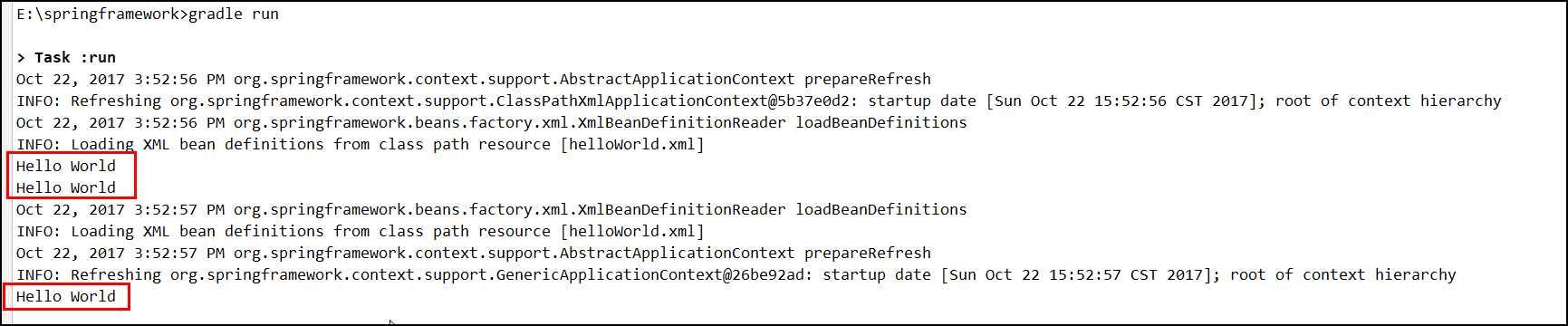
package xmlConfig; import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.GenericApplicationContext; /** * Created by sheting on 10/22/2017 */ public class HelloWorld { public void sayHello() { System.out.println("Hello World"); } public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("helloWorld.xml"); HelloWorld helloWorld2 = context.getBean("helloWorld2", HelloWorld.class); helloWorld2.sayHello(); HelloWorld helloWorld = context.getBean("helloWorld", HelloWorld.class); helloWorld.sayHello(); GenericApplicationContext context2 = new GenericApplicationContext(); new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(context2).loadBeanDefinitions("helloWorld.xml"); context2.refresh(); HelloWorld context2Bean = context2.getBean("helloWorld", HelloWorld.class); context2Bean.sayHello(); } }
运行结果:
gradle.build
apply plugin: ‘java‘ apply plugin: ‘idea‘ // mainClassName 是 application的一个属性,否则会报错 apply plugin: ‘application‘ mainClassName = ‘annotationConfig.Test‘ sourceCompatibility = 1.8 targetCompatibility = 1.8 repositories { mavenCentral() } dependencies { compile "joda-time:joda-time:2.2" compile ‘org.springframework:spring-context:5.0.0.RELEASE‘ } // 该项目生成的jar包的名字和版本,如 gs-gradle-0.1.0.jar jar { baseName = ‘gs-gradle‘ version = ‘0.1.0‘ }
HelloWorld.java
package annotationConfig; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /** * Created by sheting on 10/22/2017 */ /** * 如果属性名称是value,value可以省略。 * 如果不指定value,默认值是类名首先字母变为小写。 * @Component(value="beanId") 就是把当前类实例化。相当于<bean id="beanId"> */ @Component public class HelloWorld { public void sayHello() { System.out.println("Hello World"); } }
Test.java
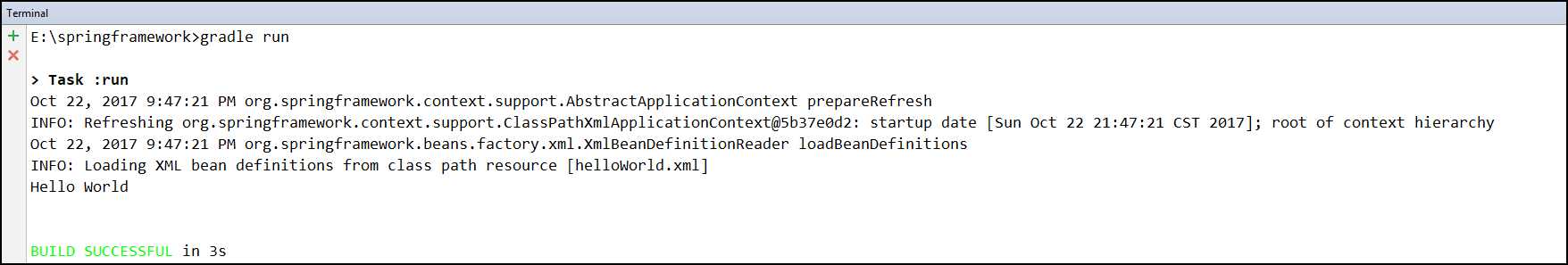
package annotationConfig; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; /** * Created by sheting on 10/22/2017 */ public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("helloWorld.xml"); HelloWorld helloWorld = context.getBean("helloWorld", HelloWorld.class); helloWorld.sayHello(); } }
helloWorld.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- 开启注解扫描 --> <context:component-scan base-package="annotationConfig"/> </beans>
运行结果:
gradle.build
apply plugin: ‘java‘ apply plugin: ‘idea‘ // mainClassName 是 application的一个属性,否则会报错 apply plugin: ‘application‘ mainClassName = ‘javaConfig.Test‘ sourceCompatibility = 1.8 targetCompatibility = 1.8 repositories { mavenCentral() } dependencies { compile "joda-time:joda-time:2.2" compile ‘org.springframework:spring-context:5.0.0.RELEASE‘ } // 该项目生成的jar包的名字和版本,如 gs-gradle-0.1.0.jar jar { baseName = ‘gs-gradle‘ version = ‘0.1.0‘ }
MyService.java
package javaConfig; /** * Created by sheting on 10/22/2017 */ public interface MyService { void sayHello(); }
MyServiceImpl.java
package javaConfig; /** * Created by sheting on 10/22/2017 */ public class MyServiceImpl implements MyService { public void sayHello() { System.out.println("Hello World"); } }
AppConfig.java
package javaConfig; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; /** * Created by sheting on 10/22/2017 * * 这个类和下面的配置类似 * <beans> * <bean id="myService" class="com.acme.services.MyServiceImpl"/> * </beans> * * Java配置是通过@Configuration和@Bean来实现的。 * @Configuartion 声明当前类是一个配置类,相当于一个spring配置的xml文件的<beans></beans>。 * @Bean 注解在方法上,声明当前方法的返回值为一个bean,bean的名称为方法名。 * @ComponentScan 自动扫描包名下所有的 @Service @Component @Repository @Controller的类,并注册为bean。 * */ @Configuration public class AppConfig { @Bean public MyService myService() { return new MyServiceImpl(); } }
Test.java
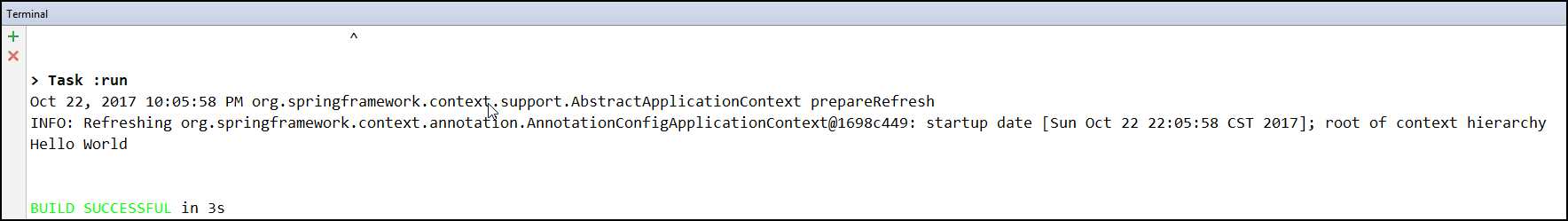
package javaConfig; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; /** * Created by sheting on 10/22/2017 */ public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { //加载配置 ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class); MyService myService = ctx.getBean(MyService.class); myService.sayHello(); } }
运行结果:
Spring Framework5.0 学习(3)—— spring配置文件的三种形式
标签:targe 系统 als blog world base 业务 image mys
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/zheting/p/7712269.html