标签:padding temp clu 目录 asc add char class algorithm
前言:
说起来小学的时候老师讲冒泡排序,算是学的第一个排序算法(然并卵),不过我是不会写
然后某一天突然写出了这么个鬼
(那时候还是用pascal)
1 for i:=1 to n do 2 for j:=i+1 to n do 3 if (a[i]>a[j]) then 4 begin 5 tmp:=a[i]; 6 a[i]:=a[j]; 7 a[j]:=tmp; 8 end;
好像应该是最简单的排序,不知道是选择还是冒泡,反正O(n2)是跑不了的,大概唯一的优点就是码起来快吧。。。实测小于10,000的数据差不多可以放心用,可AC明明的随机数(排序入门题,3000的数据吧,无优化)
快排:
快排是真的强!!
快排的基本思路:对于一个区间(1,n)的待排数据,取其目前位于中间的数为轴,对于轴左边的分区(partition)和右边的分区逐个进行比较,(假设要排成升序好了)就把右边比轴小的扔左边去,把左边比轴大的扔到右分区
这样以后知道左右分区选取的数都选完了以后,进入两边没排好的分区重复上述操作,最后就排好了。
对于pascal选手来说,大家只说没有stl很苦逼,不过在Pascal安装目录下 /demo/text/ 中有 qsort.pp 伟大的快排入门
OI选手该记的sth:时间复杂度最好O(n log n) 平均O(n log n) 最差 O(n2)
1 var 2 data:array[0..100000]of longint; 3 table,n:longint; 4 5 procedure qsort(l,r:longint); 6 var 7 axis,i,j,temp:longint; 8 begin 9 i:=l; 10 j:=r; 11 axis:=data[(l+r)div 2]; 12 repeat 13 while data[i]<axis do 14 inc(i); 15 while data[j]>axis do 16 dec(j); 17 if i<=j then 18 begin 19 temp:=data[i]; 20 data[i]:=data[j]; 21 data[j]:=temp; 22 inc(i); 23 dec(j); 24 end; 25 until i>j; 26 if l<j then 27 qsort(l,j); 28 if i<r then 29 qsort(i,r); 30 end; 31 32 begin 33 readln(n); 34 for table:=1 to n do 35 read(data[table]); 36 qsort(1,n); 37 for table:=1 to n-1 do 38 write(data[table],‘ ‘); 39 writeln(data[n]); 40 end.
用c++以后随意改写了一下:
1 #include <cstdio> 2 3 using namespace std; 4 5 int n,a[100000]; 6 7 void qsort(int l,int r){ 8 int mid = a[(l + r) >> 1]; 9 int i = l,j = r; 10 do{ 11 while(a[i]<mid){ 12 i++; 13 } 14 while(a[j]>mid){ 15 j--; 16 } 17 if (i<=j){ 18 a[0] = a[i]; 19 a[i] = a[j]; 20 a[j] = a[0]; 21 i++; 22 j--; 23 } 24 }while(i<=j); 25 if (i<r){ 26 qsort(i,r); 27 } 28 if (l<j){ 29 qsort(l,j); 30 } 31 } 32 33 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]){ 34 scanf("%d",&n); 35 for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){ 36 scanf("%d",&a[i]); 37 } 38 qsort(1,n); 39 for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i){ 40 printf("%d ", a[i]); 41 } 42 printf("%d\n", a[n]); 43 return 0; 44 }
对于这个code,可能有点意思的是do-while 毕竟平时用的不多,搞得我不得不阅读一下语法说明 真是涨姿势了
之后嘛 作为新cpp选手,stl一定要搞一下的
经机房的苦力老师简单介绍一下以后,写了这么个东西(雾):
1 #include <algorithm> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 int n,a[100000]; 7 8 bool cmp(int a,int b){ 9 return a<b; 10 } 11 12 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]){ 13 scanf("%d",&n); 14 for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){ 15 scanf("%d",&a[i]); 16 } 17 sort(a+1,a+n,cmp); 18 for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i){ 19 printf("%d ", a[i]); 20 } 21 printf("%d\n", a[n]); 22 return 0; 23 }
然而。。。
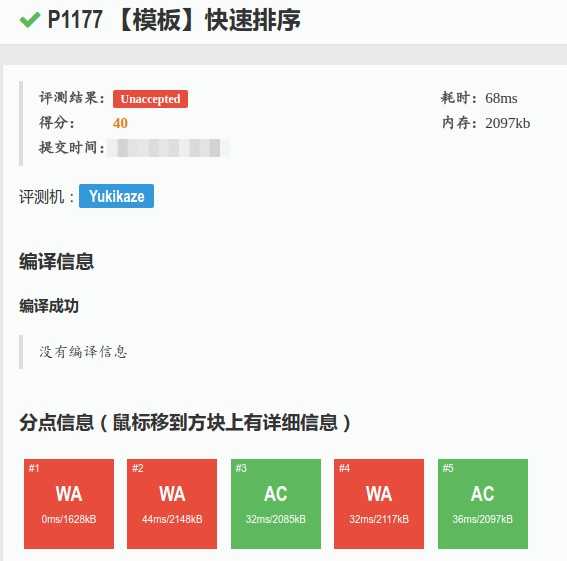
我:***
那么哪里错了呢?
显然sort写错了QAQ
1 #include <algorithm> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 int n,a[100000]; 7 8 bool cmp(int a,int b){ 9 return a<b; 10 } 11 12 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]){ 13 scanf("%d",&n); 14 for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){ 15 scanf("%d",&a[i]); 16 } 17 sort(a+1,a+n+1,cmp); 18 for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i){ 19 printf("%d ", a[i]); 20 } 21 printf("%d\n", a[n]); 22 return 0; 23 }
标红的才是正解
归纳一下,如果待排数组是a,数据是a[0]到a[n-1],则写作sort(a,a+n,cmp);如果是a[1]到a[n],就是sort(a+1,a+n+1,cmp);
(好像sort默认升序?那就不用写cmp)
新姿势:
include一下functional以后,sort的算子可以使用以下内容:equal_to<Type>、not_equal_to<Type>、greater<Type>、greater_equal<Type>、less<Type>、less_equal<Type>
怎么用顾名思义,再不会google去。。。
比方说降序排序,写作sort(a+1,a+n+1,greater<int>());就好
总之 stl 的 sort应该是普遍情况下最好的排序算法了,据说是快排接插入排序。
标签:padding temp clu 目录 asc add char class algorithm
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/mojibake/p/7745037.html