标签:lis log span 没有 com 排列 end 目的 ges
Python 数据结构 主要有:list 列表,
1、list 列表
(1)基本方法
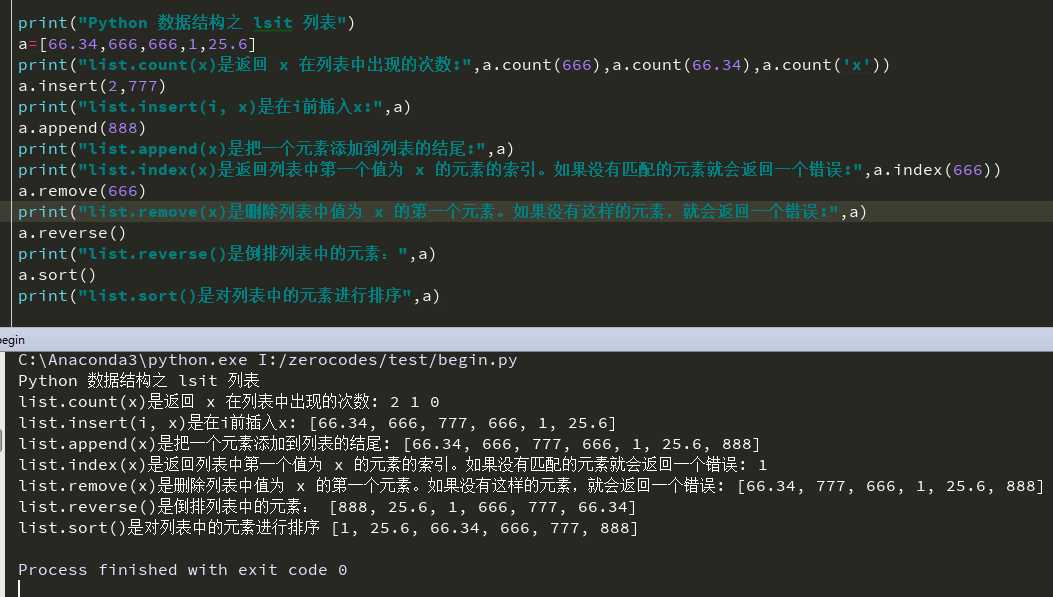
print("Python 数据结构之 lsit 列表")
a=[66.34,666,666,1,25.6]
print("list.count(x)是返回 x 在列表中出现的次数:",a.count(666),a.count(66.34),a.count(‘x‘))
a.insert(2,777)
print("list.insert(i, x)是在i前插入x:",a)
a.append(888)
print("list.append(x)是把一个元素添加到列表的结尾:",a)
print("list.index(x)是返回列表中第一个值为 x 的元素的索引。如果没有匹配的元素就会返回一个错误:",a.index(666))
a.remove(666)
print("list.remove(x)是删除列表中值为 x 的第一个元素。如果没有这样的元素,就会返回一个错误:",a)
a.reverse()
print("list.reverse()是倒排列表中的元素:",a)
a.sort()
print("list.sort()是对列表中的元素进行排序",a)
【注意】类似 insert, remove 或 sort 等修改列表的方法没有返回值。
结果为:
(2)list 列表可作为堆栈(后进先出)使用
用 append() 方法可以把一个元素添加到堆栈顶。
用不指定索引的 pop() 方法可以把一个元素从堆栈顶释放出来。
>>> stack=[2,3,4,5] >>> stack.append(6) >>> stack.append(7) >>> stack [2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7] >>> stack.pop() 7 >>> stack [2, 3, 4, 5, 6] >>> stack.pop() 6 >>> stack.pop() 5 >>> stack [2, 3, 4]
(3)list 列表可作为队列(先进先出)使用
可以把列表当做队列用,只是在队列里第一加入的元素,第一个取出来;但是拿列表用作这样的目的效率不高。在列表的最后添加或者弹出元素速度快,然而在列表里插入或者从头部弹出速度却不快(因为所有其他的元素都得一个一个地移动)。
>>> from collections import deque >>> queue=deque(["Zero","One","Two","Three"]) >>> queue.append("Four") # Four arrives >>> queue.append("Five") # Five arrives >>> queue deque([‘Zero‘, ‘One‘, ‘Two‘, ‘Three‘, ‘Four‘, ‘Five‘]) >>> queue.popleft() # The first to arrive now leaves ‘Zero‘ >>> queue.popleft() # The second to arrive now leaves ‘One‘ >>> queue # Remaining queue in order of arrival deque([‘Two‘, ‘Three‘, ‘Four‘, ‘Five‘])
标签:lis log span 没有 com 排列 end 目的 ges
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/shenxiaolin/p/7766890.html