标签:value strong rac his header for may 间接 设计
转载:原文地址 http://www.cnblogs.com/android-blogs/p/5566212.html
一、Collection接口
从《Java集合:整体结构》一文中我们知道所有的List和Set都继承自Collection接口,该接口类提供了集合最基本的方法,虽然List接口和Set等都有一些自己独有的方法,但是基本的操作类似。我们先看下Collection接口提供的方法:
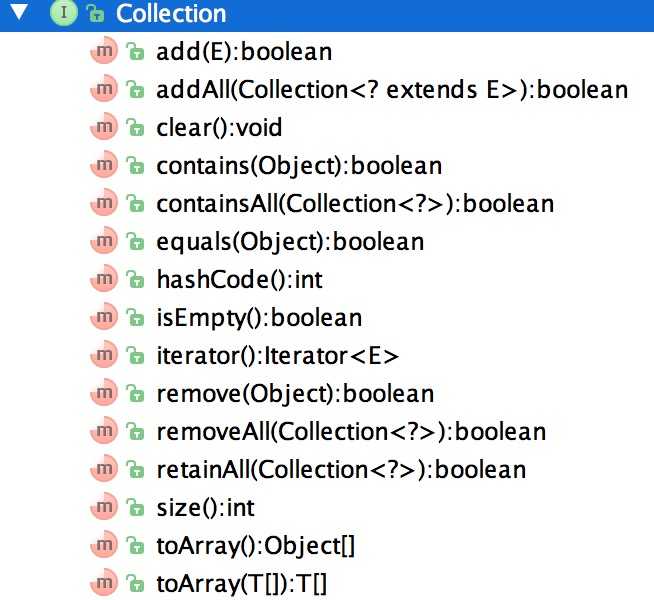
总体上可以将Collection的方法分为以下几大类:
1、增加(add/addAll)
2、删除(remove/removeAll/clear/retainAll)
3、查询(contain/containAll/iterator/size/isEmpty)
4、转数组(toArray/toArray(T[]))
直接实现该接口的类只有AbstractCollection类,该类也只是一个抽象类,提供了对集合类操作的一些基本实现。List和Set的具体实现类基本上都直接或间接的继承了该类。为了方便以后更清晰的理解这些类的实现,我们先看下AbstractCollection的实现。
二、AbstractCollection源码解析
1 package java.util; 2 3 public abstract class AbstractCollection<E> implements Collection<E> { 4 5 protected AbstractCollection() { 6 } 7 8 public abstract Iterator<E> iterator(); 9 10 public abstract int size(); 11 12 //判断集合中是否有数据 13 public boolean isEmpty() { 14 return size() == 0; 15 } 16 17 /** 18 * 判断是否包含指定的元素 19 * (1)如果参数为null,查找值为null的元素,如果存在,返回true,否则返回false。 20 * (2)如果参数不为null,则根据equals方法查找与参数相等的元素,如果存在,则返回true,否则返回false。 21 * 注意:这里必须对null单独处理,否则null.equals会报空指针异常 22 */ 23 public boolean contains(Object o) { 24 Iterator<E> it = iterator(); 25 if (o==null) { 26 while (it.hasNext()) 27 if (it.next()==null) 28 return true; 29 } else { 30 while (it.hasNext()) 31 if (o.equals(it.next())) 32 return true; 33 } 34 return false; 35 } 36 37 /** 38 * 功能:将集合元素转换为数组 39 * 实现: 40 * (1)创建一个数组,大小为集合中元素的数量 41 * (2)通过迭代器遍历集合,将当前集合中的元素复制到数组中(复制引用) 42 * (3)如果集合中元素比预期的少,则调用Arrays.copyOf()方法将数组的元素复制到新数组中,并返回新数组,Arrays.copyOf的源码在后续文章中会分析. 43 * (4)如果集合中元素比预期的多,则调用finishToArray方法生成新数组,并返回新数组,否则返回(1)中创建的数组 44 */ 45 public Object[] toArray() { 46 Object[] r = new Object[size()]; 47 Iterator<E> it = iterator(); 48 for (int i = 0; i < r.length; i++) { 49 if (! it.hasNext()) // fewer elements than expected 50 return Arrays.copyOf(r, i); 51 r[i] = it.next(); 52 } 53 return it.hasNext() ? finishToArray(r, it) : r; 54 } 55 56 /** 57 * 功能:通过泛型约束返回指定类型的数组 58 * 实现: 59 * (1)如果传入数组的长度的长度大于等于集合的长度,则将当前集合的元素复制到传入的数组中 60 * (2)如果传入数组的长度小于集合的大小,则将创建一个新的数组来进行集合元素的存储 61 */ 62 public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) { 63 // Estimate size of array; be prepared to see more or fewer elements 64 int size = size(); 65 T[] r = a.length >= size ? a : 66 (T[])java.lang.reflect.Array 67 .newInstance(a.getClass().getComponentType(), size); 68 Iterator<E> it = iterator(); 69 70 for (int i = 0; i < r.length; i++) { 71 //集合元素大小小于数组的长度 72 if (! it.hasNext()) { // fewer elements than expected 73 if (a == r) {//如果数组是参数中的数组,则将剩余部分的值都设置为null 74 r[i] = null; // null-terminate 75 } else if (a.length < i) {//如果传入的数组长度小于集合长度,则通过Arrays.copyOf将之前数组中的元素复制到新数组中 76 return Arrays.copyOf(r, i); 77 } else {//如果传入数组的长度比集合大,则将多的元素设置为空 78 System.arraycopy(r, 0, a, 0, i); 79 if (a.length > i) { 80 a[i] = null; 81 } 82 } 83 return a; 84 } 85 r[i] = (T)it.next(); 86 } 87 // more elements than expected 88 //集合元素大小大于数组的长度 89 return it.hasNext() ? finishToArray(r, it) : r; 90 } 91 92 private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8; 93 94 /** 95 * 功能:数组扩容 96 * (1)当数组索引指向最后一个元素+1时,对数组进行扩容:即创建一个更长的数组,然后将原数组的内容复制到新数组中 97 * (2)扩容大小:cap + cap/2 +1 98 * (3)扩容前需要先判断是否数组长度是否溢出 99 * 注意:这里的迭代器是从上层的方法(toArray)传过来的,并且这个迭代器已执行了一部分,而不是从头开始迭代的 100 */ 101 private static <T> T[] finishToArray(T[] r, Iterator<?> it) { 102 int i = r.length; 103 while (it.hasNext()) { 104 int cap = r.length; 105 if (i == cap) { 106 int newCap = cap + (cap >> 1) + 1; 107 // overflow-conscious code 108 if (newCap - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) 109 newCap = hugeCapacity(cap + 1); 110 r = Arrays.copyOf(r, newCap); 111 } 112 r[i++] = (T)it.next(); 113 } 114 // trim if overallocated 115 return (i == r.length) ? r : Arrays.copyOf(r, i); 116 } 117 118 /** 119 * 判断数组容量是否溢出,最大为整型数据的最大值 120 */ 121 private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) { 122 if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow 123 throw new OutOfMemoryError 124 ("Required array size too large"); 125 return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? 126 Integer.MAX_VALUE : 127 MAX_ARRAY_SIZE; 128 } 129 130 /** 131 * 未实现 132 */ 133 public boolean add(E e) { 134 throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); 135 } 136 137 /** 138 * 功能:移除指定元素 139 * (1)如果参数为null,则找到第一个值为null的元素,并将其删除,返回true,如果不存在null的元素,返回false。 140 * (2)如果参数不为null,则根据equals方法找到第一个与参数相等的元素,并将其删除,返回true,如果找不到,返回false。 141 */ 142 public boolean remove(Object o) { 143 Iterator<E> it = iterator(); 144 if (o==null) { 145 while (it.hasNext()) { 146 if (it.next()==null) { 147 it.remove(); 148 return true; 149 } 150 } 151 } else { 152 while (it.hasNext()) { 153 if (o.equals(it.next())) { 154 it.remove(); 155 return true; 156 } 157 } 158 } 159 return false; 160 } 161 162 /** 163 * 遍历参数集合,依次判断参数集合中的元素是否在当前集合中, 164 * 只要有一个不存在,则返回false 165 * 如果参数集合中所有的元素都在当前集合中,则返回true 166 */ 167 public boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c) { 168 for (Object e : c) 169 if (!contains(e)) 170 return false; 171 return true; 172 } 173 174 /** 175 * 遍历参数集合,依次将参数集合中的元素添加当前集合中 176 */ 177 public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) { 178 boolean modified = false; 179 for (E e : c) 180 if (add(e)) 181 modified = true; 182 return modified; 183 } 184 185 /** 186 * 功能:移除参数集合的元素 187 * (1)获取当前集合的迭代器进行遍历 188 * (2)如果当前集合中的元素包含在参数集合中,则删除当前集合中的元素 189 * 注:只要参数集合中有任何一个元素在当前元素中,则返回true,表示当前集合有发送变化,否则返回false。 190 */ 191 public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) { 192 boolean modified = false; 193 Iterator<?> it = iterator(); 194 while (it.hasNext()) { 195 if (c.contains(it.next())) { 196 it.remove(); 197 modified = true; 198 } 199 } 200 return modified; 201 } 202 203 /*** 204 * 功能:求参数集合与当前集合的交集 205 * (1)获取当前集合的迭代器进行遍历 206 * (2)如果当前集合中的元素不在参数集合中,则将其移除。 207 * 注意:如果当前集合是参数集合中的子集,则返回false,表示当前集合未发送变化,否则返回true。 208 */ 209 public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) { 210 boolean modified = false; 211 Iterator<E> it = iterator(); 212 while (it.hasNext()) { 213 if (!c.contains(it.next())) { 214 it.remove(); 215 modified = true; 216 } 217 } 218 return modified; 219 } 220 221 //删除所有元素 222 public void clear() { 223 Iterator<E> it = iterator(); 224 while (it.hasNext()) { 225 it.next(); 226 it.remove(); 227 } 228 } 229 230 231 public String toString() { 232 Iterator<E> it = iterator(); 233 if (! it.hasNext()) 234 return "[]"; 235 236 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); 237 sb.append(‘[‘); 238 for (;;) { 239 E e = it.next(); 240 sb.append(e == this ? "(this Collection)" : e); 241 if (! it.hasNext()) 242 return sb.append(‘]‘).toString(); 243 sb.append(‘,‘).append(‘ ‘); 244 } 245 } 246 247 }
整体上来说,AbstractCollection的源码还是比较容易理解,尤其是集合增、删、查等操作都非常简单。比较复杂的是关于集合转数组的操作,有几个点不是特别好理解,这里解释一下:
(1)MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8,为什么最大长度要减8,根据官方的解释:
/**
* The maximum size of array to allocate.
* Some VMs reserve some header words in an array.
* Attempts to allocate larger arrays may result in
* OutOfMemoryError: Requested array size exceeds VM limit
*/
这段话的意思就是有的虚拟机实现,数组对象的头部会占用这8个字节。
(2)转换为数组的操作时,为什么长度会比size()长或者短?这个的原因还是考虑到并发情况下,当然,在并发环境上面的机制不一定可行,如在ArrayList中就重写了该方法,遇到size()与hasNext不一致的情况会直接报错。不过有些场景下可以通过这种方式保持弱一致性,具体后续遇到这种情况的时候再具体说明。
(3)这里面执行数组拷贝时,用到两个方法,一个是Arrays.copyOf,另一个是System.arraycopy(r, 0, a, 0, i)方法,这两个方法的区别也会在后续文章中讨论,这里暂不细说。
三、总结
本文主要分析了AbstractCollection类的源码,很多实现类会重写AbstractCollection中已实现的方法。但是弄明白AbstractCollection源码之后,再看其子类的实现,会更容易理解其源码实现背后的设计原因,其实,很多源码本身不难理解,难理解的地方在于其背后的设计思想和原因,这也是我们去看源码和真正要学习的东西。
标签:value strong rac his header for may 间接 设计
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/xiaozuoliunian/p/7794217.html