标签:证明 -- oid code 否则 system 选择排序 test png
其实冒泡排序应该用例子证明,设数组长度为N。
1.比较相邻的前后二个数据,如果前面数据大于后面的数据,就将二个数据交换。
2.这样对数组的第0个数据到N-1个数据进行一次遍历后,最大的一个数据就“沉”到数组第N-1个位置。
3.N=N-1,如果N不为0就重复前面二步,否则排序完成。
看了基本的方法,就写个代码验证下
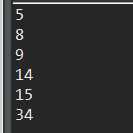
1 // 2.冒泡排序 2 @Test 3 public void test2() { 4 int[] arr={14,9,8,15,34,5}; 5 int temp=0; 6 for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){ 7 for(int j=0;j<arr.length-1;j++){ 8 if(arr[j]>arr[j+1]){ 9 temp=arr[j]; 10 arr[j]=arr[j+1]; 11 arr[j+1]=temp; 12 } 13 } 14 } 15 16 //遍历输出有三种输出方式,可以参考我博客的3中遍历输出的方式 17 for(int a:arr){ 18 System.out.println(a); 19 } 20 }
思想:先在所有序列中先找到最小的,然后放到第一个位置。之后再看剩余元素中最小的,放到第二个位置……以此类推,就可以完成整个的排序工作了。
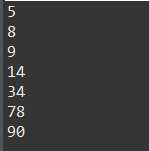
1 @Test 2 public void test4() { 3 int[] arr = { 14, 9, 8, 90, 34, 5,78 }; 4 int minIndex; 5 int temp; 6 for (int i = 0; i < arr.length-1; i++) { 7 minIndex=i; 8 for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) { 9 if (arr[j] < arr[minIndex]) { 10 minIndex =j; 11 } 12 } 13 if(minIndex!=i){ 14 temp=arr[i]; 15 arr[i]=arr[minIndex]; 16 arr[minIndex]=temp; 17 } 18 } 19 for (int i : arr) { 20 System.out.println(i); 21 } 22 23 }
标签:证明 -- oid code 否则 system 选择排序 test png
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/chenyanlong/p/7818964.html