标签:数据 index strong pre code 实现 pos reading city
I/O指的是计算机与外部世界,或者程序与计算机其他部分的接口,即输入/输出。
在JAVA中,通常都以流的方式完成I/O,通过一个Stream对象操作。这种操作方法是堵塞的,无法移动读取位置的(只能一直往下读,不能后退),并且效率较低。JAVA为了提高I/O效率,在1.4之后,推出了NIO。
| I/O | NIO |
| 面向流,一次读取一个或多个字节,在流中无法前后移动 | 面向缓存,读取的数据先统一放在缓存中,在缓存中能前后移动 |
| 堵塞,从流读取数据时,线程无法做其他事情 | 非堵塞,数据还未完整读取到缓存中时,线程可以先做其他事 |
| 一对一:一条线程负责一个数据操作任务 | 一对多,一条线程负责多个数据操作任务 |
NIO要实现面向缓存的非堵塞数据读取,依赖"Channel(通道)"和"Buffer(缓冲区)";
NIO要实现一条线程管理多个数据操作,依赖"Selector(选择器)"。
A channel represents an open connection to an entity such as a hardware device, a file, a network socket, or a program component that is capable of performing one or more distinct I/O operations, for example reading or writing.
即通过Channel,你可以和外部进行数据的读写。
虽然NIO的Channel和I/O的stream很像,不过还是有区别的:
根据Channel数据来源不同,Channel有不同的实现:
I/O 和 NIO 数据操作对比
// I/O流操作 FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("io.txt"); byte[] data = new byte[1024]; while(inputStream.read(data) != -1){ // 从流中读取多个字节,进行操作 }
// NIO channel操作 // 从文件流中获取channel FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("nio.txt"); FileChannel fileChannel = inputStream.getChannel(); // 新建缓存,用于存放Channel读取的数据 ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); // 通过Channel读取数据到缓存中 fileChannel.read(buffer);
对于FileChannel之间,利用transferFrom和transferTo可以直接进行数据传输,提高性能。
将fromChannel中数据传输到toChannel 中,position指toChannel中开始的位置,count指接收的数据:
toChannel.transferFrom(fromChannel, position, count) 或
fromChannel.transferTo(position, count, toChannel)
A container for data of a specific primitive type.
A buffer is a linear, finite sequence of elements of a specific primitive type. Aside from its content, the essential properties of a buffer are its capacity, limit, and position.
buffer缓冲区是一块内存,用于存放原始类型数据。它的特点是:线性,有限,有序,只能存一种原始类型数据。
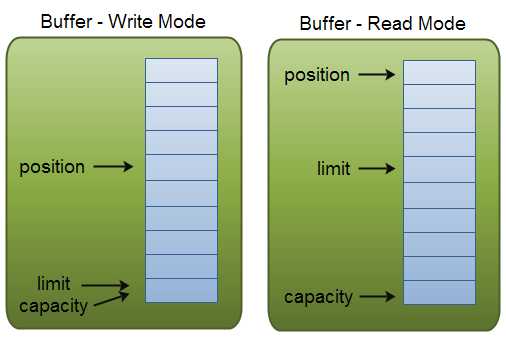
根据buffer中存放的原始类型不同,有以下几种Buffer实现
标签:数据 index strong pre code 实现 pos reading city
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/kejicjk/p/7820019.html