标签:splay strong block width obj display border pytho tom
1.1写入空文件
若将文本写入文件,在调用open()时候需要提供另外一个实参,告诉Python你要写入打开的文件
file_path = ‘txt\MyFavoriteFruit.txt‘ with open(file_path,‘w‘) as file_object: file_object.write(‘I like appple.‘)
在这个实例中,调用open()提供了两个实参,第一个实参是要打开文件的路径与名称,第二个实参(‘w‘)告诉Python,我们将要以写的方式打开这个文件
r 读取模式
w 写模式
a 附加模式
r+ 可读可写
Python在不指定打开模式时,默认为读模式
若文件已经存在,那么Python在返回文件对象前会清空文件
注意:Python只能将字符串写入文件,如果要存储数据到文本文件,需要使用str()将其转化为字符串格式
1.2写入多行
file_path = ‘txt\MyFavoriteFruit.txt‘ with open(file_path,‘w‘) as file_object: file_object.write(‘I like appple.‘) file_object.write(‘I like pear.‘) file_object.write(‘I like orange.‘)
使用上边的代码写入多行文本,打开文件后可以看到
文本内容都写到一行上了,在文本中这样写,显得乱七八糟的,那么我们想把文件分成多行怎么办呢?
使用换行符即可
file_path = ‘txt\MyFavoriteFruit.txt‘ with open(file_path,‘w‘) as file_object: file_object.write(‘I like appple.\n‘) file_object.write(‘I like pear.\n‘) file_object.write(‘I like orange.\n‘)
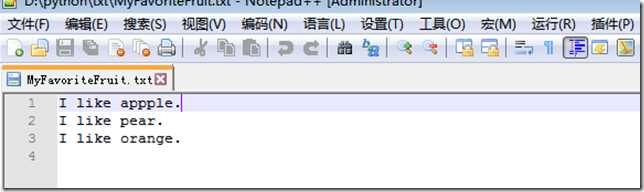
1.3附加到文件
上边我们已经在文件中写入了3行数据,那么我们想附加一个结束语end,又如何操作呢?
file_path = ‘txt\MyFavoriteFruit.txt‘ with open(file_path,‘a‘) as file_object: file_object.write(‘end‘)
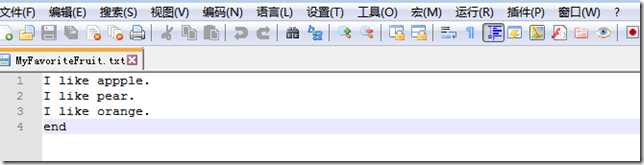
end轻松添加到了文件的末尾
标签:splay strong block width obj display border pytho tom
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/OliverQin/p/7899016.html