标签:alt var 注意 函数 star 调用 addition 第一个 运用
1、some
如果数组中至少有一个元素满足测试函数,则返回 true,否则返回 false。
function isBigEnough(element, index, array) { return (element >= 10); } var passed = [2, 5, 8, 1, 4].some(isBigEnough); // passed is false passed = [12, 5, 8, 1, 4].some(isBigEnough); // passed is true
2、filter
将所有在过滤函数中返回 true 的数组元素放进一个新数组中并返回。
const isBigEnough = value => value >= 10; let [...spraed]= [12, 5, 8, 130, 44]; let filtered = spraed.filter(isBigEnough);
3、find
找到第一个满足测试函数的元素并返回那个元素的值,如果找不到,则返回 undefined。
var inventory = [ {name: ‘apples‘, quantity: 2}, {name: ‘bananas‘, quantity: 0}, {name: ‘cherries‘, quantity: 5} ]; function findCherries(fruit) { return fruit.name === ‘cherries‘; } console.log(inventory.find(findCherries)); // { name: ‘cherries‘, quantity: 5 }
// 运用find寻找质数 function isPrime(element, index, array) { var start = 2; while (start <= Math.sqrt(element)) { if (element % start++ < 1) { return false; } } return element > 1; } console.log([4, 5, 8, 12].find(isPrime)); // undefined, not found
4、reduce
从左到右为每个数组元素执行一次回调函数,并把上次回调函数的返回值放在一个暂存器中传给下次回调函数,并返回最后一次回调函数的返回值。
// 计算数组中每个元素出现的次数 var names = [‘Alice‘, ‘Bob‘, ‘Tiff‘, ‘Bruce‘, ‘Alice‘]; var countedNamesTmp = names.reduce((allNames,name)=>{ if (name in allNames) { allNames[name]++; } else { allNames[name] = 1; } return allNames; },{}) console.log(countedNamesTmp);
// 使用扩展运算符和initialValue绑定包含在对象数组中的数组 var friends = [{ name: ‘Anna‘, books: [‘Bible‘, ‘Harry Potter‘], age: 21 }, { name: ‘Bob‘, books: [‘War and peace‘, ‘Romeo and Juliet‘], age: 26 }, { name: ‘Alice‘, books: [‘The Lord of the Rings‘, ‘The Shining‘], age: 18 }]; // allbooks - list which will contain all friends‘ books + // additional list contained in initialValue var allbooks = friends.reduce(function(prev, curr) { return [...prev, ...curr.books]; }, [‘Alphabet‘]); console.log(allbooks)
ES6提供了三个新方法:entries()、keys()和values(),用来遍历数组。它们都返回一个遍历器对象,可以用for...of循环进行遍历,唯一的区别是keys()是对数组的键名的遍历、values()是对数组键值的遍历,entries()方法是对数值的键值对的遍历。
for (let index of [‘a‘, ‘b‘].keys()) {
console.log(index);
}
// 0
// 1
for (let elem of [‘a‘, ‘b‘].values()) {
console.log(elem);
}
// ‘a‘
// ‘b‘
for (let [index, elem] of [‘a‘, ‘b‘].entries()) {
console.log(index, elem);
}
// 0 "a"
// 1 "b"
entries若使用for...of循环
let letter = [‘a‘, ‘b‘, ‘c‘];
let entries = letter.entries();
for (let e of entries) {
console.log(e);
}
运行结果:
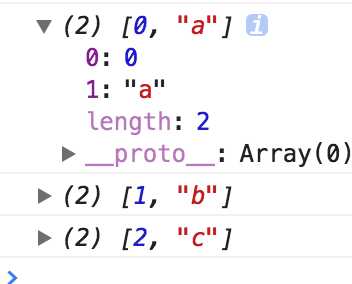
如果不使用for...of循环,可以手动调用遍历器对象的next方法,进行遍历
let letter = [‘a‘, ‘b‘, ‘c‘];
let entries = letter.entries();
console.log(entries.next().value); // [0, ‘a‘]
console.log(entries.next().value); // [1, ‘b‘]
console.log(entries.next().value); // [2, ‘c‘]
注意:for in遍历的是数组的索引(即键名),而for of遍历的是数组元素值;for of遍历的只是数组内的元素,而不包括数组的原型属性。
标签:alt var 注意 函数 star 调用 addition 第一个 运用
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/xiaoli52qd/p/7954616.html