标签:lag been nat when 存在 make efi array 处理
4.52以后的题目中的代码大多是书上的,如需使用请联系 randy.bryant@cs.cmu.edu
流水线部分只写了偶数题号的,这几天太浮躁,落下了好多课。。。
4.45
A. 不正确,当REG为%rsp时,这样会压入%rsp - 8而非%rsp
B. 对于 pushq REG:
movq REG, -8(%rsp)
subq $8, %rsp4.46
A. 不正确,当REG为%rsp是,这样会使得%rsp的值为(%rsp) + 8 而非(%rsp)
B. 对于popq REG:
addq $8, %rsp
movq 8(%rsp), REG4.47
A. (不知道这题有什么意义。。。)
/* Bubble sort: Array version */
void bubble_p(long *data, long count)
{
long i, last;
for(last = count - 1; last > 0; last--)
{
for(i = 0; i < last; i++)
{
if(*(data+i+1) < *(data+i))
{
long t = *(data+i+1);
*(data+i+1) = *(data+i);
*(data+i) = t;
}
}
}
}B. bubblesort.ys:
# Execution begins at address 0
.pos 0
irmovq stack, %rsp # Set up stack pointer
call main # Execute main program
halt # Terminate program
# Array of 8 elements
.align 8
data:
.quad 0xa000a000a000
.quad 0x0b000b000b00
.quad 0x00c000c000c0
.quad 0x000d000d000d
main: irmovq data,%rdi
irmovq $4,%rsi
call bubble_p # bubble_p(data, 8)
ret
# void bubble_p(long *data, long count)
# data in %rdi, count in %rsi
bubble_p:
rrmovq %rsi, %r9
irmovq $1, %r11
subq %r11, %r9
jmp L2
L4:
rrmovq %rdi, %rdx
rrmovq %rax, %rcx
irmovq $8, %r10
loop:
subq %r11, %rcx
jl end_loop
addq %r10, %rdx
jmp loop
end_loop:
mrmovq (%rdx), %r8
rrmovq %rdx, %rsi
addq %r10, %rsi
mrmovq (%rsi), %rcx
rrmovq %rcx, %r10
subq %r8, %r10
jge L3
rmmovq %r8, (%rsi)
rmmovq %rcx, (%rdx)
L3:
addq %r11, %rax
jmp L5
L6:
xorq %rax, %rax
L5:
rrmovq %rax, %r10
subq %r9, %r10
jl L4
subq %r11, %r9
L2:
jg L6
ret
# Stack starts here and grows to lower addresses
.pos 0x200
stack:运行结果如下:
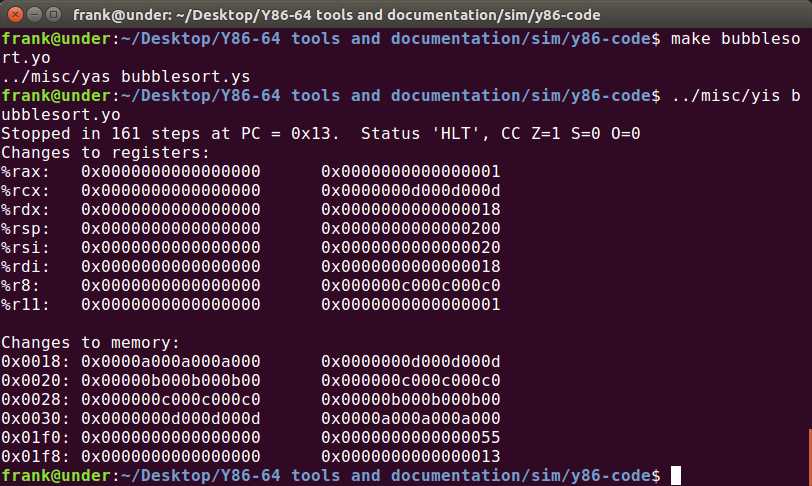
可以看到,之前由大到小的数组被排列成了由小到大的顺序。另外,0x01f0和0x01f8处是压入的两个返回地址,不是数组边界溢出。
4.48
书上6-11行为:
if(*(data+i+1) < *(data+i))
{
long t = *(data+i+1);
*(data+i+1) = *(data+i);
*(data+i) = t;
}其对应4.47里面的:
mrmovq (%rdx), %r8
rrmovq %rdx, %rsi
addq %r10, %rsi
mrmovq (%rsi), %rcx
rrmovq %rcx, %r10
subq %r8, %r10
jge L3
rmmovq %r8, (%rsi)
rmmovq %rcx, (%rdx)将其改为条件转移,使用了两个cmovl:
mrmovq (%rdx), %r8
rrmovq %rdx, %rsi
addq %r10, %rsi
mrmovq (%rsi), %rcx
rrmovq %rcx, %r10
subq %r8, %r10
rrmovq %rcx, %r10
cmovl %r8, %r10
rmmovq %r10, (%rsi)
rrmovq %r8, %r10
cmovl %rcx, %r10
rmmovq %r10, (%rdx)运行结果如下:
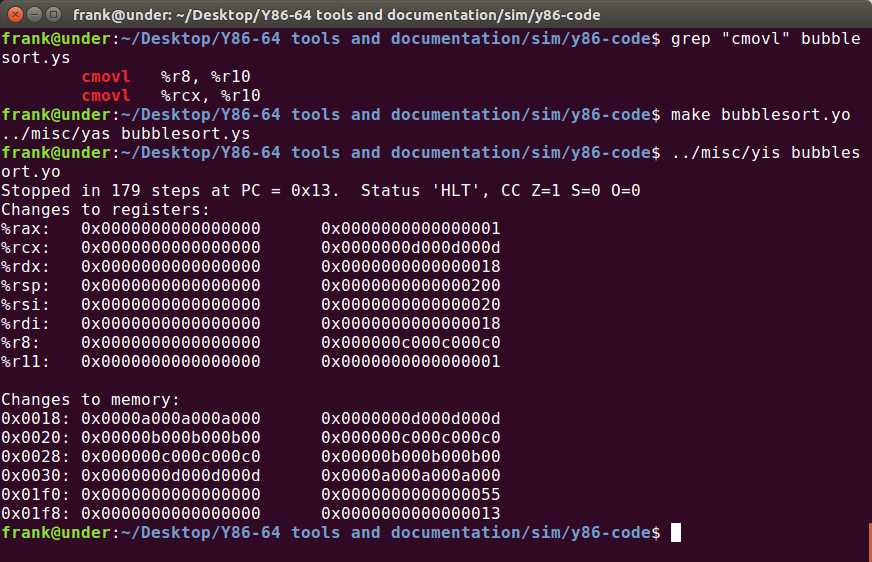
4.49
这一题要求只能使用一个cmov指令实现书上的6-11行。我们首先分析一下4.48里面两条cmov冗余的地方:我们使用了两个cmovl ,其实这两个的条件码是一样的。于是我们可以使用一个cmovl 到一个寄存器A,然后在另一个寄存器B用算术运算将其线性关联起来(例如减法)。例如,如果我们要交换[A],[B],我们先将[A]存在%r1, -[A]存在%r2,cmovl [B], %r1,addq %r1, %r2,这时如果[A]大于[B],%r1中为[B],%r2中为[B]-[A],否则%r1中为[A],%r2中为0。随后,我们将%r1赋值给A,[B]-%r2赋值给B即可。
代码如下:
mrmovq (%rdx), %r8
rrmovq %rdx, %rsi
addq %r10, %rsi
mrmovq (%rsi), %rcx
rrmovq %rcx, %r10
subq %r8, %r10
cmovl %rcx, %r8
xorq %r12, %r12
mrmovq (%rdx), %r10
subq %r10, %r12
addq %r8, %r12
rmmovq %r8, (%rdx)
subq %r12, %rcx
rmmovq %rcx, (%rsi)这里要注意一下,我这里为了方便使用了%r12寄存器,但是它是一个Callee saved的,所以我们要在bubblesort首尾分别加上pushq %r12和popq %r12 .
运行结果如下:
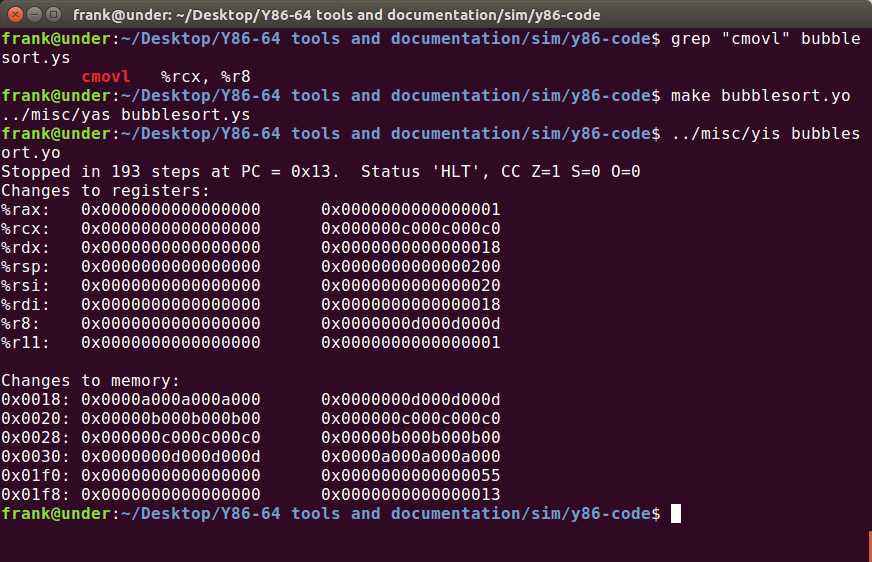
4.50
代码如下:
# Execution begins at address 0
.pos 0
irmovq stack, %rsp # Set up stack pointer
call main # Execute main program
halt # Terminate program
# Array of 8 elements
.align 8
vals:
.quad 0x000000000000
.quad 0x000000000000
.quad 0x000000000000
.quad 0x000000000000
.quad 0x000000000000
.quad 0x000000000000
.quad 0x000000000000
.quad 0x000000000000
jump_table:
.quad L1
.quad L4
.quad L2
.quad L3
.quad L4
.quad L2
main:
irmovq vals, %r12
irmovq $-1,%rdi
call switchv # switchv(-1)
rmmovq %rax, (%r12)
irmovq $0,%rdi
call switchv # switchv(0)
rmmovq %rax, 0x8(%r12)
irmovq $1,%rdi
call switchv # switchv(1)
rmmovq %rax, 0x10(%r12)
irmovq $2,%rdi
call switchv # switchv(2)
rmmovq %rax, 0x18(%r12)
irmovq $3,%rdi
call switchv # switchv(3)
rmmovq %rax, 0x20(%r12)
irmovq $4,%rdi
call switchv # switchv(4)
rmmovq %rax, 0x28(%r12)
irmovq $5,%rdi
call switchv # switchv(5)
rmmovq %rax, 0x30(%r12)
irmovq $6,%rdi
call switchv # switchv(6)
rmmovq %rax, 0x38(%r12)
ret
# long switchv(long idx)
# idx in %rdi
switchv:
rrmovq %rdi, %r8
irmovq $5, %r9
subq %r9, %r8
jg L4
andq %rdi, %rdi
jl L4
irmovq jump_table, %r8
irmovq $8, %r9
irmovq $1, %r10
loop:
subq %r10, %rdi
jl endloop
addq %r9, %r8
jmp loop
endloop:
mrmovq (%r8), %r8
pushq %r8
ret
L1: # case 0
irmovq 0xaaa, %rax
ret
L2: #case 2 or case 5
irmovq 0xbbb, %rax
ret
L3:
irmovq 0xccc, %rax #case 3
ret
L4:
irmovq 0xddd, %rax #default
ret
# Stack starts here and grows to lower addresses
.pos 0x400
stack:这里要特别注意到原来的stack为0x200,这个时候的代码量会导致代码区段淹没到栈的部分,所以要将stack的位置增高一些。
运行结果如下:
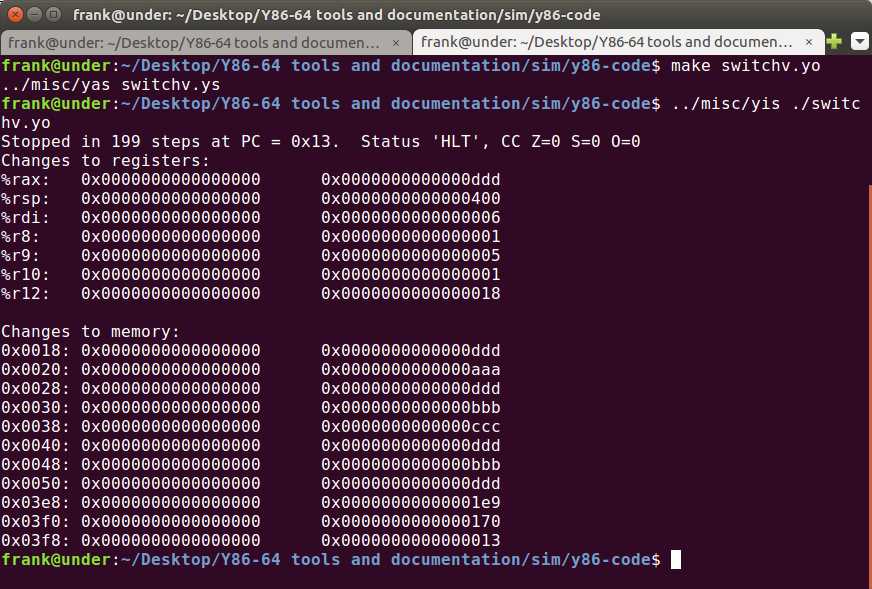
4.51
iaddq V, rB
Fetch:
? icode:ifun <-- M1[PC]
? rA:rB <-- M1[PC+1]
? valC <-- M8[PC+2]
? valP <-- PC+10
Decode:
? valB <-- R[rB]
Execute:
? ValE <-- valB + valC
Memory:
Write back:
? R[rB] <-- valE
PC update:
? PC <-- valP
4.52
由4.51 ,在seq-full.hcl中添加IIADDQ,得到如下代码:
#/* $begin seq-all-hcl */
####################################################################
# HCL Description of Control for Single Cycle Y86-64 Processor SEQ #
# Copyright (C) Randal E. Bryant, David R. O‘Hallaron, 2010 #
####################################################################
## Your task is to implement the iaddq instruction
## The file contains a declaration of the icodes
## for iaddq (IIADDQ)
## Your job is to add the rest of the logic to make it work
####################################################################
# C Include‘s. Don‘t alter these #
####################################################################
quote ‘#include <stdio.h>‘
quote ‘#include "isa.h"‘
quote ‘#include "sim.h"‘
quote ‘int sim_main(int argc, char *argv[]);‘
quote ‘word_t gen_pc(){return 0;}‘
quote ‘int main(int argc, char *argv[])‘
quote ‘ {plusmode=0;return sim_main(argc,argv);}‘
####################################################################
# Declarations. Do not change/remove/delete any of these #
####################################################################
##### Symbolic representation of Y86-64 Instruction Codes #############
wordsig INOP ‘I_NOP‘
wordsig IHALT ‘I_HALT‘
wordsig IRRMOVQ ‘I_RRMOVQ‘
wordsig IIRMOVQ ‘I_IRMOVQ‘
wordsig IRMMOVQ ‘I_RMMOVQ‘
wordsig IMRMOVQ ‘I_MRMOVQ‘
wordsig IOPQ ‘I_ALU‘
wordsig IJXX ‘I_JMP‘
wordsig ICALL ‘I_CALL‘
wordsig IRET ‘I_RET‘
wordsig IPUSHQ ‘I_PUSHQ‘
wordsig IPOPQ ‘I_POPQ‘
# Instruction code for iaddq instruction
wordsig IIADDQ ‘I_IADDQ‘
##### Symbolic represenations of Y86-64 function codes #####
wordsig FNONE ‘F_NONE‘ # Default function code
##### Symbolic representation of Y86-64 Registers referenced explicitly #####
wordsig RRSP ‘REG_RSP‘ # Stack Pointer
wordsig RNONE ‘REG_NONE‘ # Special value indicating "no register"
##### ALU Functions referenced explicitly #####
wordsig ALUADD ‘A_ADD‘ # ALU should add its arguments
##### Possible instruction status values #####
wordsig SAOK ‘STAT_AOK‘ # Normal execution
wordsig SADR ‘STAT_ADR‘ # Invalid memory address
wordsig SINS ‘STAT_INS‘ # Invalid instruction
wordsig SHLT ‘STAT_HLT‘ # Halt instruction encountered
##### Signals that can be referenced by control logic ####################
##### Fetch stage inputs #####
wordsig pc ‘pc‘ # Program counter
##### Fetch stage computations #####
wordsig imem_icode ‘imem_icode‘ # icode field from instruction memory
wordsig imem_ifun ‘imem_ifun‘ # ifun field from instruction memory
wordsig icode ‘icode‘ # Instruction control code
wordsig ifun ‘ifun‘ # Instruction function
wordsig rA ‘ra‘ # rA field from instruction
wordsig rB ‘rb‘ # rB field from instruction
wordsig valC ‘valc‘ # Constant from instruction
wordsig valP ‘valp‘ # Address of following instruction
boolsig imem_error ‘imem_error‘ # Error signal from instruction memory
boolsig instr_valid ‘instr_valid‘ # Is fetched instruction valid?
##### Decode stage computations #####
wordsig valA ‘vala‘ # Value from register A port
wordsig valB ‘valb‘ # Value from register B port
##### Execute stage computations #####
wordsig valE ‘vale‘ # Value computed by ALU
boolsig Cnd ‘cond‘ # Branch test
##### Memory stage computations #####
wordsig valM ‘valm‘ # Value read from memory
boolsig dmem_error ‘dmem_error‘ # Error signal from data memory
####################################################################
# Control Signal Definitions. #
####################################################################
################ Fetch Stage ###################################
# Determine instruction code
word icode = [
imem_error: INOP;
1: imem_icode; # Default: get from instruction memory
];
# Determine instruction function
word ifun = [
imem_error: FNONE;
1: imem_ifun; # Default: get from instruction memory
];
bool instr_valid = icode in
{ INOP, IHALT, IRRMOVQ, IIRMOVQ, IIADDQ, IRMMOVQ, IMRMOVQ,
IOPQ, IJXX, ICALL, IRET, IPUSHQ, IPOPQ };
# Does fetched instruction require a regid byte?
bool need_regids =
icode in { IRRMOVQ, IOPQ, IPUSHQ, IPOPQ,
IIRMOVQ, IIADDQ, IRMMOVQ, IMRMOVQ };
# Does fetched instruction require a constant word?
bool need_valC =
icode in { IIRMOVQ, IIADDQ, IRMMOVQ, IMRMOVQ, IJXX, ICALL };
################ Decode Stage ###################################
## What register should be used as the A source?
word srcA = [
icode in { IRRMOVQ, IRMMOVQ, IOPQ, IPUSHQ } : rA;
icode in { IPOPQ, IRET } : RRSP;
1 : RNONE; # Don‘t need register
];
## What register should be used as the B source?
word srcB = [
icode in { IOPQ, IRMMOVQ, IMRMOVQ, IIADDQ } : rB;
icode in { IPUSHQ, IPOPQ, ICALL, IRET } : RRSP;
1 : RNONE; # Don‘t need register
];
## What register should be used as the E destination?
word dstE = [
icode in { IRRMOVQ } && Cnd : rB;
icode in { IIRMOVQ, IOPQ, IIADDQ} : rB;
icode in { IPUSHQ, IPOPQ, ICALL, IRET } : RRSP;
1 : RNONE; # Don‘t write any register
];
## What register should be used as the M destination?
word dstM = [
icode in { IMRMOVQ, IPOPQ } : rA;
1 : RNONE; # Don‘t write any register
];
################ Execute Stage ###################################
## Select input A to ALU
word aluA = [
icode in { IRRMOVQ, IOPQ } : valA;
icode in { IIRMOVQ, IRMMOVQ, IMRMOVQ, IIADDQ } : valC;
icode in { ICALL, IPUSHQ } : -8;
icode in { IRET, IPOPQ } : 8;
# Other instructions don‘t need ALU
];
## Select input B to ALU
word aluB = [
icode in { IRMMOVQ, IMRMOVQ, IOPQ, ICALL,
IPUSHQ, IRET, IPOPQ, IIADDQ } : valB;
icode in { IRRMOVQ, IIRMOVQ } : 0;
# Other instructions don‘t need ALU
];
## Set the ALU function
word alufun = [
icode == IOPQ : ifun;
1 : ALUADD;
];
## Should the condition codes be updated?
bool set_cc = icode in { IOPQ, IIADDQ };
################ Memory Stage ###################################
## Set read control signal
bool mem_read = icode in { IMRMOVQ, IPOPQ, IRET };
## Set write control signal
bool mem_write = icode in { IRMMOVQ, IPUSHQ, ICALL };
## Select memory address
word mem_addr = [
icode in { IRMMOVQ, IPUSHQ, ICALL, IMRMOVQ } : valE;
icode in { IPOPQ, IRET } : valA;
# Other instructions don‘t need address
];
## Select memory input data
word mem_data = [
# Value from register
icode in { IRMMOVQ, IPUSHQ } : valA;
# Return PC
icode == ICALL : valP;
# Default: Don‘t write anything
];
## Determine instruction status
word Stat = [
imem_error || dmem_error : SADR;
!instr_valid: SINS;
icode == IHALT : SHLT;
1 : SAOK;
];
################ Program Counter Update ############################
## What address should instruction be fetched at
word new_pc = [
# Call. Use instruction constant
icode == ICALL : valC;
# Taken branch. Use instruction constant
icode == IJXX && Cnd : valC;
# Completion of RET instruction. Use value from stack
icode == IRET : valM;
# Default: Use incremented PC
1 : valP;
];
#/* $end seq-all-hcl */运行结果如下:
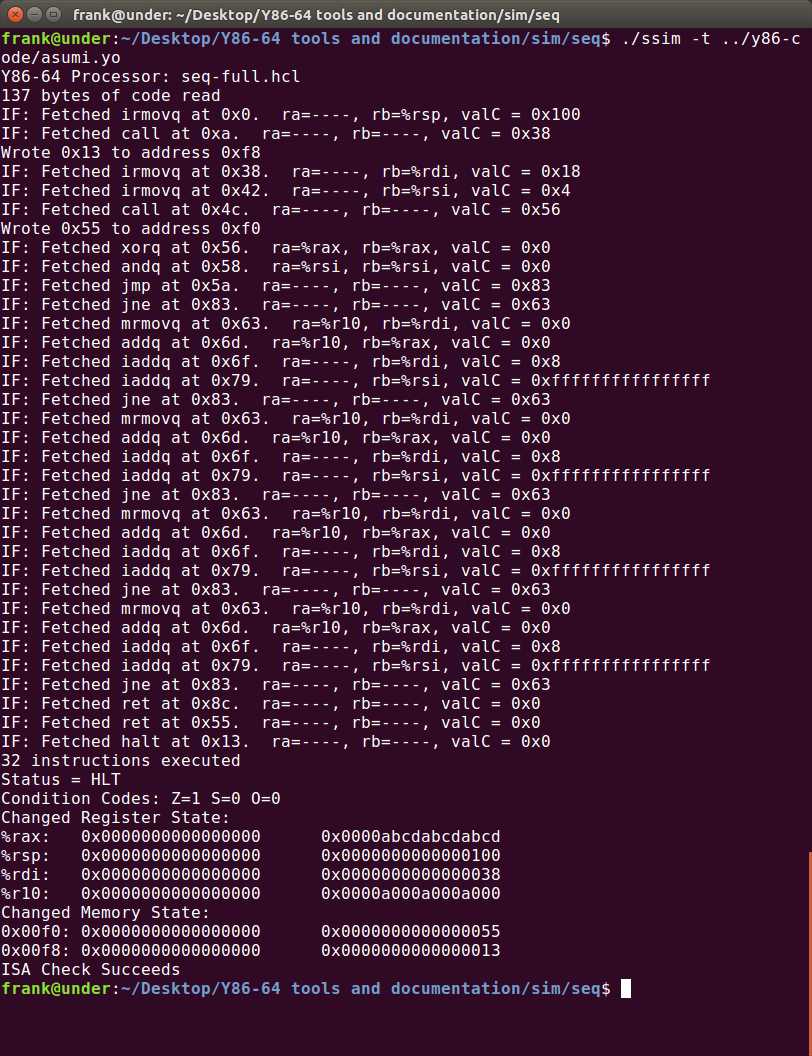
4.54
pipe-full.hcl:
#/* $begin pipe-all-hcl */
####################################################################
# HCL Description of Control for Pipelined Y86-64 Processor #
# Copyright (C) Randal E. Bryant, David R. O‘Hallaron, 2014 #
####################################################################
## Your task is to implement the iaddq instruction
## The file contains a declaration of the icodes
## for iaddq (IIADDQ)
## Your job is to add the rest of the logic to make it work
####################################################################
# C Include‘s. Don‘t alter these #
####################################################################
quote ‘#include <stdio.h>‘
quote ‘#include "isa.h"‘
quote ‘#include "pipeline.h"‘
quote ‘#include "stages.h"‘
quote ‘#include "sim.h"‘
quote ‘int sim_main(int argc, char *argv[]);‘
quote ‘int main(int argc, char *argv[]){return sim_main(argc,argv);}‘
####################################################################
# Declarations. Do not change/remove/delete any of these #
####################################################################
##### Symbolic representation of Y86-64 Instruction Codes #############
wordsig INOP ‘I_NOP‘
wordsig IHALT ‘I_HALT‘
wordsig IRRMOVQ ‘I_RRMOVQ‘
wordsig IIRMOVQ ‘I_IRMOVQ‘
wordsig IRMMOVQ ‘I_RMMOVQ‘
wordsig IMRMOVQ ‘I_MRMOVQ‘
wordsig IOPQ ‘I_ALU‘
wordsig IJXX ‘I_JMP‘
wordsig ICALL ‘I_CALL‘
wordsig IRET ‘I_RET‘
wordsig IPUSHQ ‘I_PUSHQ‘
wordsig IPOPQ ‘I_POPQ‘
# Instruction code for iaddq instruction
wordsig IIADDQ ‘I_IADDQ‘
##### Symbolic represenations of Y86-64 function codes #####
wordsig FNONE ‘F_NONE‘ # Default function code
##### Symbolic representation of Y86-64 Registers referenced #####
wordsig RRSP ‘REG_RSP‘ # Stack Pointer
wordsig RNONE ‘REG_NONE‘ # Special value indicating "no register"
##### ALU Functions referenced explicitly ##########################
wordsig ALUADD ‘A_ADD‘ # ALU should add its arguments
##### Possible instruction status values #####
wordsig SBUB ‘STAT_BUB‘ # Bubble in stage
wordsig SAOK ‘STAT_AOK‘ # Normal execution
wordsig SADR ‘STAT_ADR‘ # Invalid memory address
wordsig SINS ‘STAT_INS‘ # Invalid instruction
wordsig SHLT ‘STAT_HLT‘ # Halt instruction encountered
##### Signals that can be referenced by control logic ##############
##### Pipeline Register F ##########################################
wordsig F_predPC ‘pc_curr->pc‘ # Predicted value of PC
##### Intermediate Values in Fetch Stage ###########################
wordsig imem_icode ‘imem_icode‘ # icode field from instruction memory
wordsig imem_ifun ‘imem_ifun‘ # ifun field from instruction memory
wordsig f_icode ‘if_id_next->icode‘ # (Possibly modified) instruction code
wordsig f_ifun ‘if_id_next->ifun‘ # Fetched instruction function
wordsig f_valC ‘if_id_next->valc‘ # Constant data of fetched instruction
wordsig f_valP ‘if_id_next->valp‘ # Address of following instruction
boolsig imem_error ‘imem_error‘ # Error signal from instruction memory
boolsig instr_valid ‘instr_valid‘ # Is fetched instruction valid?
##### Pipeline Register D ##########################################
wordsig D_icode ‘if_id_curr->icode‘ # Instruction code
wordsig D_rA ‘if_id_curr->ra‘ # rA field from instruction
wordsig D_rB ‘if_id_curr->rb‘ # rB field from instruction
wordsig D_valP ‘if_id_curr->valp‘ # Incremented PC
##### Intermediate Values in Decode Stage #########################
wordsig d_srcA ‘id_ex_next->srca‘ # srcA from decoded instruction
wordsig d_srcB ‘id_ex_next->srcb‘ # srcB from decoded instruction
wordsig d_rvalA ‘d_regvala‘ # valA read from register file
wordsig d_rvalB ‘d_regvalb‘ # valB read from register file
##### Pipeline Register E ##########################################
wordsig E_icode ‘id_ex_curr->icode‘ # Instruction code
wordsig E_ifun ‘id_ex_curr->ifun‘ # Instruction function
wordsig E_valC ‘id_ex_curr->valc‘ # Constant data
wordsig E_srcA ‘id_ex_curr->srca‘ # Source A register ID
wordsig E_valA ‘id_ex_curr->vala‘ # Source A value
wordsig E_srcB ‘id_ex_curr->srcb‘ # Source B register ID
wordsig E_valB ‘id_ex_curr->valb‘ # Source B value
wordsig E_dstE ‘id_ex_curr->deste‘ # Destination E register ID
wordsig E_dstM ‘id_ex_curr->destm‘ # Destination M register ID
##### Intermediate Values in Execute Stage #########################
wordsig e_valE ‘ex_mem_next->vale‘ # valE generated by ALU
boolsig e_Cnd ‘ex_mem_next->takebranch‘ # Does condition hold?
wordsig e_dstE ‘ex_mem_next->deste‘ # dstE (possibly modified to be RNONE)
##### Pipeline Register M #########################
wordsig M_stat ‘ex_mem_curr->status‘ # Instruction status
wordsig M_icode ‘ex_mem_curr->icode‘ # Instruction code
wordsig M_ifun ‘ex_mem_curr->ifun‘ # Instruction function
wordsig M_valA ‘ex_mem_curr->vala‘ # Source A value
wordsig M_dstE ‘ex_mem_curr->deste‘ # Destination E register ID
wordsig M_valE ‘ex_mem_curr->vale‘ # ALU E value
wordsig M_dstM ‘ex_mem_curr->destm‘ # Destination M register ID
boolsig M_Cnd ‘ex_mem_curr->takebranch‘ # Condition flag
boolsig dmem_error ‘dmem_error‘ # Error signal from instruction memory
##### Intermediate Values in Memory Stage ##########################
wordsig m_valM ‘mem_wb_next->valm‘ # valM generated by memory
wordsig m_stat ‘mem_wb_next->status‘ # stat (possibly modified to be SADR)
##### Pipeline Register W ##########################################
wordsig W_stat ‘mem_wb_curr->status‘ # Instruction status
wordsig W_icode ‘mem_wb_curr->icode‘ # Instruction code
wordsig W_dstE ‘mem_wb_curr->deste‘ # Destination E register ID
wordsig W_valE ‘mem_wb_curr->vale‘ # ALU E value
wordsig W_dstM ‘mem_wb_curr->destm‘ # Destination M register ID
wordsig W_valM ‘mem_wb_curr->valm‘ # Memory M value
####################################################################
# Control Signal Definitions. #
####################################################################
################ Fetch Stage ###################################
## What address should instruction be fetched at
word f_pc = [
# Mispredicted branch. Fetch at incremented PC
M_icode == IJXX && !M_Cnd : M_valA;
# Completion of RET instruction
W_icode == IRET : W_valM;
# Default: Use predicted value of PC
1 : F_predPC;
];
## Determine icode of fetched instruction
word f_icode = [
imem_error : INOP;
1: imem_icode;
];
# Determine ifun
word f_ifun = [
imem_error : FNONE;
1: imem_ifun;
];
# Is instruction valid?
bool instr_valid = f_icode in
{ INOP, IHALT, IRRMOVQ, IIRMOVQ, IRMMOVQ, IMRMOVQ,
IOPQ, IJXX, ICALL, IRET, IPUSHQ, IPOPQ, IIADDQ };
# Determine status code for fetched instruction
word f_stat = [
imem_error: SADR;
!instr_valid : SINS;
f_icode == IHALT : SHLT;
1 : SAOK;
];
# Does fetched instruction require a regid byte?
bool need_regids =
f_icode in { IRRMOVQ, IOPQ, IPUSHQ, IPOPQ,
IIRMOVQ, IRMMOVQ, IMRMOVQ, IIADDQ };
# Does fetched instruction require a constant word?
bool need_valC =
f_icode in { IIRMOVQ, IRMMOVQ, IMRMOVQ, IJXX, ICALL, IIADDQ };
# Predict next value of PC
word f_predPC = [
f_icode in { IJXX, ICALL } : f_valC;
1 : f_valP;
];
################ Decode Stage ######################################
## What register should be used as the A source?
word d_srcA = [
D_icode in { IRRMOVQ, IRMMOVQ, IOPQ, IPUSHQ } : D_rA;
D_icode in { IPOPQ, IRET } : RRSP;
1 : RNONE; # Don‘t need register
];
## What register should be used as the B source?
word d_srcB = [
D_icode in { IOPQ, IRMMOVQ, IMRMOVQ, IIADDQ } : D_rB;
D_icode in { IPUSHQ, IPOPQ, ICALL, IRET } : RRSP;
1 : RNONE; # Don‘t need register
];
## What register should be used as the E destination?
word d_dstE = [
D_icode in { IRRMOVQ, IIRMOVQ, IOPQ, IIADDQ} : D_rB;
D_icode in { IPUSHQ, IPOPQ, ICALL, IRET } : RRSP;
1 : RNONE; # Don‘t write any register
];
## What register should be used as the M destination?
word d_dstM = [
D_icode in { IMRMOVQ, IPOPQ } : D_rA;
1 : RNONE; # Don‘t write any register
];
## What should be the A value?
## Forward into decode stage for valA
word d_valA = [
D_icode in { ICALL, IJXX } : D_valP; # Use incremented PC
d_srcA == e_dstE : e_valE; # Forward valE from execute
d_srcA == M_dstM : m_valM; # Forward valM from memory
d_srcA == M_dstE : M_valE; # Forward valE from memory
d_srcA == W_dstM : W_valM; # Forward valM from write back
d_srcA == W_dstE : W_valE; # Forward valE from write back
1 : d_rvalA; # Use value read from register file
];
word d_valB = [
d_srcB == e_dstE : e_valE; # Forward valE from execute
d_srcB == M_dstM : m_valM; # Forward valM from memory
d_srcB == M_dstE : M_valE; # Forward valE from memory
d_srcB == W_dstM : W_valM; # Forward valM from write back
d_srcB == W_dstE : W_valE; # Forward valE from write back
1 : d_rvalB; # Use value read from register file
];
################ Execute Stage #####################################
## Select input A to ALU
word aluA = [
E_icode in { IRRMOVQ, IOPQ } : E_valA;
E_icode in { IIRMOVQ, IRMMOVQ, IMRMOVQ, IIADDQ } : E_valC;
E_icode in { ICALL, IPUSHQ } : -8;
E_icode in { IRET, IPOPQ } : 8;
# Other instructions don‘t need ALU
];
## Select input B to ALU
word aluB = [
E_icode in { IRMMOVQ, IMRMOVQ, IOPQ, ICALL,
IPUSHQ, IRET, IPOPQ, IIADDQ } : E_valB;
E_icode in { IRRMOVQ, IIRMOVQ } : 0;
# Other instructions don‘t need ALU
];
## Set the ALU function
word alufun = [
E_icode == IOPQ : E_ifun;
1 : ALUADD;
];
## Should the condition codes be updated?
bool set_cc = (E_icode == IOPQ || E_icode == IIADDQ) &&
# State changes only during normal operation
!m_stat in { SADR, SINS, SHLT } && !W_stat in { SADR, SINS, SHLT };
## Generate valA in execute stage
word e_valA = E_valA; # Pass valA through stage
## Set dstE to RNONE in event of not-taken conditional move
word e_dstE = [
E_icode == IRRMOVQ && !e_Cnd : RNONE;
1 : E_dstE;
];
################ Memory Stage ######################################
## Select memory address
word mem_addr = [
M_icode in { IRMMOVQ, IPUSHQ, ICALL, IMRMOVQ } : M_valE;
M_icode in { IPOPQ, IRET } : M_valA;
# Other instructions don‘t need address
];
## Set read control signal
bool mem_read = M_icode in { IMRMOVQ, IPOPQ, IRET };
## Set write control signal
bool mem_write = M_icode in { IRMMOVQ, IPUSHQ, ICALL };
#/* $begin pipe-m_stat-hcl */
## Update the status
word m_stat = [
dmem_error : SADR;
1 : M_stat;
];
#/* $end pipe-m_stat-hcl */
## Set E port register ID
word w_dstE = W_dstE;
## Set E port value
word w_valE = W_valE;
## Set M port register ID
word w_dstM = W_dstM;
## Set M port value
word w_valM = W_valM;
## Update processor status
word Stat = [
W_stat == SBUB : SAOK;
1 : W_stat;
];
################ Pipeline Register Control #########################
# Should I stall or inject a bubble into Pipeline Register F?
# At most one of these can be true.
bool F_bubble = 0;
bool F_stall =
# Conditions for a load/use hazard
E_icode in { IMRMOVQ, IPOPQ } &&
E_dstM in { d_srcA, d_srcB } ||
# Stalling at fetch while ret passes through pipeline
IRET in { D_icode, E_icode, M_icode };
# Should I stall or inject a bubble into Pipeline Register D?
# At most one of these can be true.
bool D_stall =
# Conditions for a load/use hazard
E_icode in { IMRMOVQ, IPOPQ } &&
E_dstM in { d_srcA, d_srcB };
bool D_bubble =
# Mispredicted branch
(E_icode == IJXX && !e_Cnd) ||
# Stalling at fetch while ret passes through pipeline
# but not condition for a load/use hazard
!(E_icode in { IMRMOVQ, IPOPQ } && E_dstM in { d_srcA, d_srcB }) &&
IRET in { D_icode, E_icode, M_icode };
# Should I stall or inject a bubble into Pipeline Register E?
# At most one of these can be true.
bool E_stall = 0;
bool E_bubble =
# Mispredicted branch
(E_icode == IJXX && !e_Cnd) ||
# Conditions for a load/use hazard
E_icode in { IMRMOVQ, IPOPQ } &&
E_dstM in { d_srcA, d_srcB};
# Should I stall or inject a bubble into Pipeline Register M?
# At most one of these can be true.
bool M_stall = 0;
# Start injecting bubbles as soon as exception passes through memory stage
bool M_bubble = m_stat in { SADR, SINS, SHLT } || W_stat in { SADR, SINS, SHLT };
# Should I stall or inject a bubble into Pipeline Register W?
bool W_stall = W_stat in { SADR, SINS, SHLT };
bool W_bubble = 0;
#/* $end pipe-all-hcl */
运行结果如下:
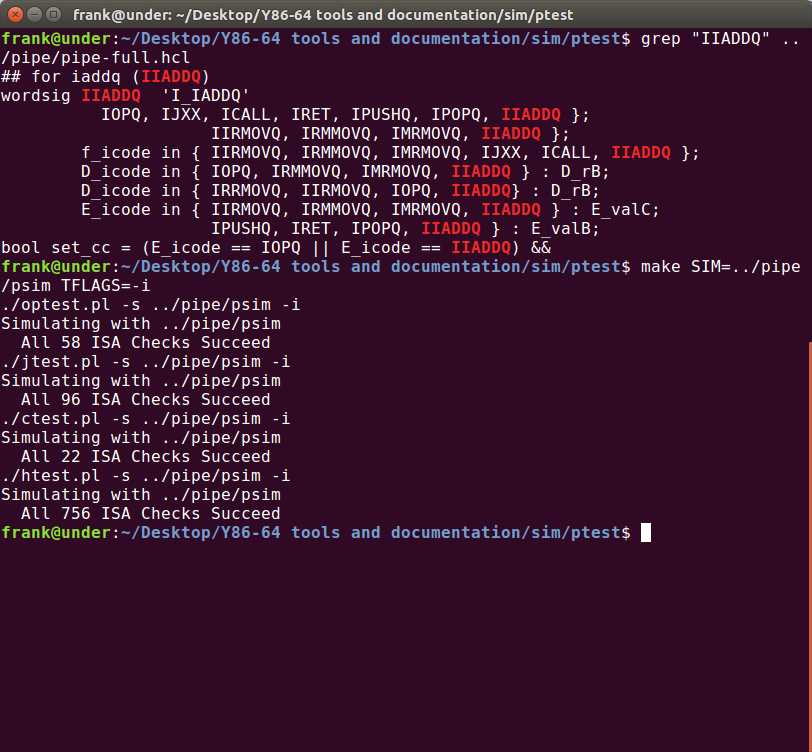
4.56
pipe-btfnt.hcl:
#/* $begin pipe-all-hcl */
####################################################################
# HCL Description of Control for Pipelined Y86-64 Processor #
# Copyright (C) Randal E. Bryant, David R. O‘Hallaron, 2014 #
####################################################################
## Your task is to modify the design so that conditional branches are
## predicted as being taken when backward and not-taken when forward
## The code here is nearly identical to that for the normal pipeline.
## Comments starting with keyword "BBTFNT" have been added at places
## relevant to the exercise.
####################################################################
# C Include‘s. Don‘t alter these #
####################################################################
quote ‘#include <stdio.h>‘
quote ‘#include "isa.h"‘
quote ‘#include "pipeline.h"‘
quote ‘#include "stages.h"‘
quote ‘#include "sim.h"‘
quote ‘int sim_main(int argc, char *argv[]);‘
quote ‘int main(int argc, char *argv[]){return sim_main(argc,argv);}‘
####################################################################
# Declarations. Do not change/remove/delete any of these #
####################################################################
##### Symbolic representation of Y86-64 Instruction Codes #############
wordsig INOP ‘I_NOP‘
wordsig IHALT ‘I_HALT‘
wordsig IRRMOVQ ‘I_RRMOVQ‘
wordsig IIRMOVQ ‘I_IRMOVQ‘
wordsig IRMMOVQ ‘I_RMMOVQ‘
wordsig IMRMOVQ ‘I_MRMOVQ‘
wordsig IOPQ ‘I_ALU‘
wordsig IJXX ‘I_JMP‘
wordsig ICALL ‘I_CALL‘
wordsig IRET ‘I_RET‘
wordsig IPUSHQ ‘I_PUSHQ‘
wordsig IPOPQ ‘I_POPQ‘
##### Symbolic represenations of Y86-64 function codes #####
wordsig FNONE ‘F_NONE‘ # Default function code
##### Symbolic representation of Y86-64 Registers referenced #####
wordsig RRSP ‘REG_RSP‘ # Stack Pointer
wordsig RNONE ‘REG_NONE‘ # Special value indicating "no register"
##### ALU Functions referenced explicitly ##########################
wordsig ALUADD ‘A_ADD‘ # ALU should add its arguments
## BBTFNT: For modified branch prediction, need to distinguish
## conditional vs. unconditional branches
##### Jump conditions referenced explicitly
wordsig UNCOND ‘C_YES‘ # Unconditional transfer
##### Possible instruction status values #####
wordsig SBUB ‘STAT_BUB‘ # Bubble in stage
wordsig SAOK ‘STAT_AOK‘ # Normal execution
wordsig SADR ‘STAT_ADR‘ # Invalid memory address
wordsig SINS ‘STAT_INS‘ # Invalid instruction
wordsig SHLT ‘STAT_HLT‘ # Halt instruction encountered
##### Signals that can be referenced by control logic ##############
##### Pipeline Register F ##########################################
wordsig F_predPC ‘pc_curr->pc‘ # Predicted value of PC
##### Intermediate Values in Fetch Stage ###########################
wordsig imem_icode ‘imem_icode‘ # icode field from instruction memory
wordsig imem_ifun ‘imem_ifun‘ # ifun field from instruction memory
wordsig f_icode ‘if_id_next->icode‘ # (Possibly modified) instruction code
wordsig f_ifun ‘if_id_next->ifun‘ # Fetched instruction function
wordsig f_valC ‘if_id_next->valc‘ # Constant data of fetched instruction
wordsig f_valP ‘if_id_next->valp‘ # Address of following instruction
boolsig imem_error ‘imem_error‘ # Error signal from instruction memory
boolsig instr_valid ‘instr_valid‘ # Is fetched instruction valid?
##### Pipeline Register D ##########################################
wordsig D_icode ‘if_id_curr->icode‘ # Instruction code
wordsig D_rA ‘if_id_curr->ra‘ # rA field from instruction
wordsig D_rB ‘if_id_curr->rb‘ # rB field from instruction
wordsig D_valP ‘if_id_curr->valp‘ # Incremented PC
##### Intermediate Values in Decode Stage #########################
wordsig d_srcA ‘id_ex_next->srca‘ # srcA from decoded instruction
wordsig d_srcB ‘id_ex_next->srcb‘ # srcB from decoded instruction
wordsig d_rvalA ‘d_regvala‘ # valA read from register file
wordsig d_rvalB ‘d_regvalb‘ # valB read from register file
##### Pipeline Register E ##########################################
wordsig E_icode ‘id_ex_curr->icode‘ # Instruction code
wordsig E_ifun ‘id_ex_curr->ifun‘ # Instruction function
wordsig E_valC ‘id_ex_curr->valc‘ # Constant data
wordsig E_srcA ‘id_ex_curr->srca‘ # Source A register ID
wordsig E_valA ‘id_ex_curr->vala‘ # Source A value
wordsig E_srcB ‘id_ex_curr->srcb‘ # Source B register ID
wordsig E_valB ‘id_ex_curr->valb‘ # Source B value
wordsig E_dstE ‘id_ex_curr->deste‘ # Destination E register ID
wordsig E_dstM ‘id_ex_curr->destm‘ # Destination M register ID
##### Intermediate Values in Execute Stage #########################
wordsig e_valE ‘ex_mem_next->vale‘ # valE generated by ALU
boolsig e_Cnd ‘ex_mem_next->takebranch‘ # Does condition hold?
wordsig e_dstE ‘ex_mem_next->deste‘ # dstE (possibly modified to be RNONE)
##### Pipeline Register M #########################
wordsig M_stat ‘ex_mem_curr->status‘ # Instruction status
wordsig M_icode ‘ex_mem_curr->icode‘ # Instruction code
wordsig M_ifun ‘ex_mem_curr->ifun‘ # Instruction function
wordsig M_valA ‘ex_mem_curr->vala‘ # Source A value
wordsig M_dstE ‘ex_mem_curr->deste‘ # Destination E register ID
wordsig M_valE ‘ex_mem_curr->vale‘ # ALU E value
wordsig M_dstM ‘ex_mem_curr->destm‘ # Destination M register ID
boolsig M_Cnd ‘ex_mem_curr->takebranch‘ # Condition flag
boolsig dmem_error ‘dmem_error‘ # Error signal from instruction memory
##### Intermediate Values in Memory Stage ##########################
wordsig m_valM ‘mem_wb_next->valm‘ # valM generated by memory
wordsig m_stat ‘mem_wb_next->status‘ # stat (possibly modified to be SADR)
##### Pipeline Register W ##########################################
wordsig W_stat ‘mem_wb_curr->status‘ # Instruction status
wordsig W_icode ‘mem_wb_curr->icode‘ # Instruction code
wordsig W_dstE ‘mem_wb_curr->deste‘ # Destination E register ID
wordsig W_valE ‘mem_wb_curr->vale‘ # ALU E value
wordsig W_dstM ‘mem_wb_curr->destm‘ # Destination M register ID
wordsig W_valM ‘mem_wb_curr->valm‘ # Memory M value
####################################################################
# Control Signal Definitions. #
####################################################################
################ Fetch Stage ###################################
## What address should instruction be fetched at
word f_pc = [
# Mispredicted branch. Fetch at incremented PC
# backward
M_icode == IJXX && M_ifun != UNCOND && M_valE < M_valA && !M_Cnd : M_valA;
# forward
M_icode == IJXX && M_ifun != UNCOND && M_valE >= M_valA && M_Cnd : M_valE;
# Completion of RET instruction
W_icode == IRET : W_valM;
# Default: Use predicted value of PC
1 : F_predPC;
];
## Determine icode of fetched instruction
word f_icode = [
imem_error : INOP;
1: imem_icode;
];
# Determine ifun
word f_ifun = [
imem_error : FNONE;
1: imem_ifun;
];
# Is instruction valid?
bool instr_valid = f_icode in
{ INOP, IHALT, IRRMOVQ, IIRMOVQ, IRMMOVQ, IMRMOVQ,
IOPQ, IJXX, ICALL, IRET, IPUSHQ, IPOPQ };
# Determine status code for fetched instruction
word f_stat = [
imem_error: SADR;
!instr_valid : SINS;
f_icode == IHALT : SHLT;
1 : SAOK;
];
# Does fetched instruction require a regid byte?
bool need_regids =
f_icode in { IRRMOVQ, IOPQ, IPUSHQ, IPOPQ,
IIRMOVQ, IRMMOVQ, IMRMOVQ };
# Does fetched instruction require a constant word?
bool need_valC =
f_icode in { IIRMOVQ, IRMMOVQ, IMRMOVQ, IJXX, ICALL };
# Predict next value of PC
word f_predPC = [
# BBTFNT: This is where you‘ll change the branch prediction rule
f_icode == IJXX && f_ifun != UNCOND && f_valC < f_valP : f_valC;
f_icode == IJXX && f_ifun != UNCOND && f_valC >= f_valP : f_valP;
f_icode in { IJXX, ICALL } : f_valC;
1 : f_valP;
];
################ Decode Stage ######################################
## What register should be used as the A source?
word d_srcA = [
D_icode in { IRRMOVQ, IRMMOVQ, IOPQ, IPUSHQ } : D_rA;
D_icode in { IPOPQ, IRET } : RRSP;
1 : RNONE; # Don‘t need register
];
## What register should be used as the B source?
word d_srcB = [
D_icode in { IOPQ, IRMMOVQ, IMRMOVQ } : D_rB;
D_icode in { IPUSHQ, IPOPQ, ICALL, IRET } : RRSP;
1 : RNONE; # Don‘t need register
];
## What register should be used as the E destination?
word d_dstE = [
D_icode in { IRRMOVQ, IIRMOVQ, IOPQ} : D_rB;
D_icode in { IPUSHQ, IPOPQ, ICALL, IRET } : RRSP;
1 : RNONE; # Don‘t write any register
];
## What register should be used as the M destination?
word d_dstM = [
D_icode in { IMRMOVQ, IPOPQ } : D_rA;
1 : RNONE; # Don‘t write any register
];
## What should be the A value?
## Forward into decode stage for valA
word d_valA = [
D_icode in { ICALL, IJXX } : D_valP; # Use incremented PC
d_srcA == e_dstE : e_valE; # Forward valE from execute
d_srcA == M_dstM : m_valM; # Forward valM from memory
d_srcA == M_dstE : M_valE; # Forward valE from memory
d_srcA == W_dstM : W_valM; # Forward valM from write back
d_srcA == W_dstE : W_valE; # Forward valE from write back
1 : d_rvalA; # Use value read from register file
];
word d_valB = [
d_srcB == e_dstE : e_valE; # Forward valE from execute
d_srcB == M_dstM : m_valM; # Forward valM from memory
d_srcB == M_dstE : M_valE; # Forward valE from memory
d_srcB == W_dstM : W_valM; # Forward valM from write back
d_srcB == W_dstE : W_valE; # Forward valE from write back
1 : d_rvalB; # Use value read from register file
];
################ Execute Stage #####################################
# BBTFNT: When some branches are predicted as not-taken, you need some
# way to get valC into pipeline register M, so that
# you can correct for a mispredicted branch.
## Select input A to ALU
word aluA = [
E_icode in { IRRMOVQ, IOPQ } : E_valA;
E_icode in { IIRMOVQ, IRMMOVQ, IMRMOVQ, IJXX } : E_valC;
E_icode in { ICALL, IPUSHQ } : -8;
E_icode in { IRET, IPOPQ } : 8;
# Other instructions don‘t need ALU
];
## Select input B to ALU
word aluB = [
E_icode in { IRMMOVQ, IMRMOVQ, IOPQ, ICALL,
IPUSHQ, IRET, IPOPQ } : E_valB;
E_icode in { IRRMOVQ, IIRMOVQ, IJXX } : 0;
# Other instructions don‘t need ALU
];
## Set the ALU function
word alufun = [
E_icode == IOPQ : E_ifun;
1 : ALUADD;
];
## Should the condition codes be updated?
bool set_cc = E_icode == IOPQ &&
# State changes only during normal operation
!m_stat in { SADR, SINS, SHLT } && !W_stat in { SADR, SINS, SHLT };
## Generate valA in execute stage
word e_valA = E_valA; # Pass valA through stage
## Set dstE to RNONE in event of not-taken conditional move
word e_dstE = [
E_icode == IRRMOVQ && !e_Cnd : RNONE;
1 : E_dstE;
];
################ Memory Stage ######################################
## Select memory address
word mem_addr = [
M_icode in { IRMMOVQ, IPUSHQ, ICALL, IMRMOVQ } : M_valE;
M_icode in { IPOPQ, IRET } : M_valA;
# Other instructions don‘t need address
];
## Set read control signal
bool mem_read = M_icode in { IMRMOVQ, IPOPQ, IRET };
## Set write control signal
bool mem_write = M_icode in { IRMMOVQ, IPUSHQ, ICALL };
#/* $begin pipe-m_stat-hcl */
## Update the status
word m_stat = [
dmem_error : SADR;
1 : M_stat;
];
#/* $end pipe-m_stat-hcl */
## Set E port register ID
word w_dstE = W_dstE;
## Set E port value
word w_valE = W_valE;
## Set M port register ID
word w_dstM = W_dstM;
## Set M port value
word w_valM = W_valM;
## Update processor status
word Stat = [
W_stat == SBUB : SAOK;
1 : W_stat;
];
################ Pipeline Register Control #########################
# Should I stall or inject a bubble into Pipeline Register F?
# At most one of these can be true.
bool F_bubble = 0;
bool F_stall =
# Conditions for a load/use hazard
E_icode in { IMRMOVQ, IPOPQ } &&
E_dstM in { d_srcA, d_srcB } ||
# Stalling at fetch while ret passes through pipeline
IRET in { D_icode, E_icode, M_icode };
# Should I stall or inject a bubble into Pipeline Register D?
# At most one of these can be true.
bool D_stall =
# Conditions for a load/use hazard
E_icode in { IMRMOVQ, IPOPQ } &&
E_dstM in { d_srcA, d_srcB };
bool D_bubble =
# Mispredicted branch: backward taken error or forward not-taken error
(
(E_icode == IJXX && E_ifun != UNCOND && E_valC < E_valA && !e_Cnd) ||
(E_icode == IJXX && E_ifun != UNCOND && E_valC >= E_valA && e_Cnd)
) ||
# BBTFNT: This condition will change
# Stalling at fetch while ret passes through pipeline
# but not condition for a load/use hazard
!(E_icode in { IMRMOVQ, IPOPQ } && E_dstM in { d_srcA, d_srcB }) &&
IRET in { D_icode, E_icode, M_icode };
# Should I stall or inject a bubble into Pipeline Register E?
# At most one of these can be true.
bool E_stall = 0;
bool E_bubble =
# Mispredicted branch: backward taken error or forward not-taken error
(
(E_icode == IJXX && E_ifun != UNCOND && E_valC < E_valA && !e_Cnd) ||
(E_icode == IJXX && E_ifun != UNCOND && E_valC >= E_valA && e_Cnd)
) ||
# BBTFNT: This condition will change
# Conditions for a load/use hazard
E_icode in { IMRMOVQ, IPOPQ } &&
E_dstM in { d_srcA, d_srcB};
# Should I stall or inject a bubble into Pipeline Register M?
# At most one of these can be true.
bool M_stall = 0;
# Start injecting bubbles as soon as exception passes through memory stage
bool M_bubble = m_stat in { SADR, SINS, SHLT } || W_stat in { SADR, SINS, SHLT };
# Should I stall or inject a bubble into Pipeline Register W?
bool W_stall = W_stat in { SADR, SINS, SHLT };
bool W_bubble = 0;
#/* $end pipe-all-hcl */
运行结果如下:
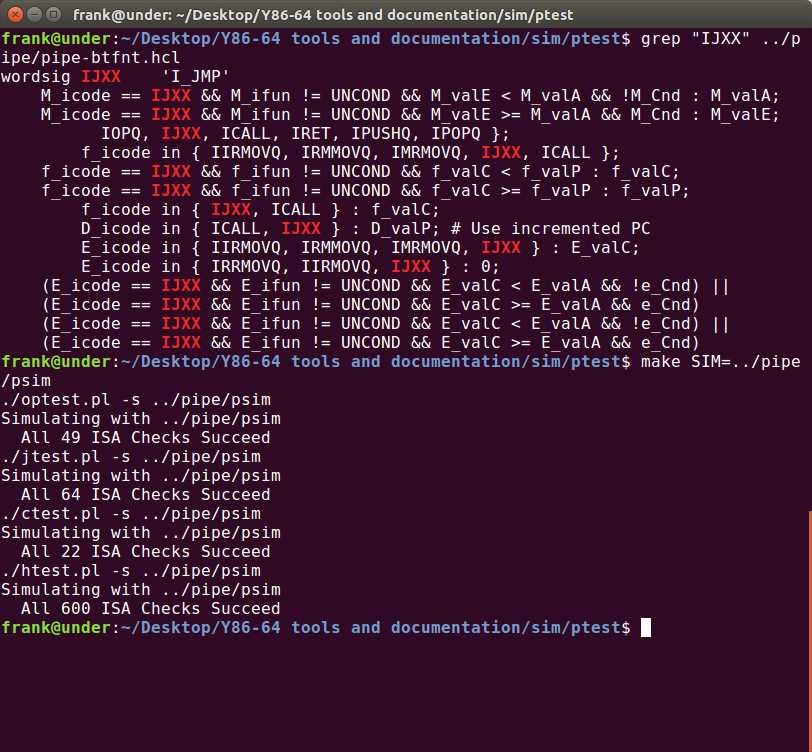
4.58
这个题巴拉巴拉说了一大堆就是要处理popq的情况。其中有一个方法就是使用4.46里面的替换策略,将popq动态替换为(这里我们先实现为iaddq ):
iaddq $8, %rsp
mrmovq 8(%rsp), REG处理iaddq后,在第二次fetch的时候PC不变,但是icode变为一个特殊的编码(书上说的是IPOP2),以此来识别进行mrmovq 8(%rsp), REG的操作。书上把要改变的地方用“1W”标出来了。
pipi-1w.hcl:
#/* $begin pipe-all-hcl */
####################################################################
# HCL Description of Control for Pipelined Y86-64 Processor #
# Copyright (C) Randal E. Bryant, David R. O‘Hallaron, 2014 #
####################################################################
## Your task is to modify the design so that on any cycle, only
## one of the two possible (valE and valM) register writes will occur.
## This requires special handling of the popq instruction.
## Overall strategy: IPOPQ passes through pipe,
## treated as stack pointer increment, but not incrementing the PC
## On refetch, modify fetched icode to indicate an instruction "IPOP2",
## which reads from memory.
## This requires modifying the definition of f_icode
## and lots of other changes. Relevant positions to change
## are indicated by comments starting with keyword "1W".
####################################################################
# C Include‘s. Don‘t alter these #
####################################################################
quote ‘#include <stdio.h>‘
quote ‘#include "isa.h"‘
quote ‘#include "pipeline.h"‘
quote ‘#include "stages.h"‘
quote ‘#include "sim.h"‘
quote ‘int sim_main(int argc, char *argv[]);‘
quote ‘int main(int argc, char *argv[]){return sim_main(argc,argv);}‘
####################################################################
# Declarations. Do not change/remove/delete any of these #
####################################################################
##### Symbolic representation of Y86-64 Instruction Codes #############
wordsig INOP ‘I_NOP‘
wordsig IHALT ‘I_HALT‘
wordsig IRRMOVQ ‘I_RRMOVQ‘
wordsig IIRMOVQ ‘I_IRMOVQ‘
wordsig IRMMOVQ ‘I_RMMOVQ‘
wordsig IMRMOVQ ‘I_MRMOVQ‘
wordsig IOPQ ‘I_ALU‘
wordsig IJXX ‘I_JMP‘
wordsig ICALL ‘I_CALL‘
wordsig IRET ‘I_RET‘
wordsig IPUSHQ ‘I_PUSHQ‘
wordsig IPOPQ ‘I_POPQ‘
# 1W: Special instruction code for second try of popq
wordsig IPOP2 ‘I_POP2‘
##### Symbolic represenations of Y86-64 function codes #####
wordsig FNONE ‘F_NONE‘ # Default function code
##### Symbolic representation of Y86-64 Registers referenced #####
wordsig RRSP ‘REG_RSP‘ # Stack Pointer
wordsig RNONE ‘REG_NONE‘ # Special value indicating "no register"
##### ALU Functions referenced explicitly ##########################
wordsig ALUADD ‘A_ADD‘ # ALU should add its arguments
##### Possible instruction status values #####
wordsig SBUB ‘STAT_BUB‘ # Bubble in stage
wordsig SAOK ‘STAT_AOK‘ # Normal execution
wordsig SADR ‘STAT_ADR‘ # Invalid memory address
wordsig SINS ‘STAT_INS‘ # Invalid instruction
wordsig SHLT ‘STAT_HLT‘ # Halt instruction encountered
##### Signals that can be referenced by control logic ##############
##### Pipeline Register F ##########################################
wordsig F_predPC ‘pc_curr->pc‘ # Predicted value of PC
##### Intermediate Values in Fetch Stage ###########################
wordsig imem_icode ‘imem_icode‘ # icode field from instruction memory
wordsig imem_ifun ‘imem_ifun‘ # ifun field from instruction memory
wordsig f_icode ‘if_id_next->icode‘ # (Possibly modified) instruction code
wordsig f_ifun ‘if_id_next->ifun‘ # Fetched instruction function
wordsig f_valC ‘if_id_next->valc‘ # Constant data of fetched instruction
wordsig f_valP ‘if_id_next->valp‘ # Address of following instruction
## 1W: Provide access to the PC value for the current instruction
wordsig f_pc ‘f_pc‘ # Address of fetched instruction
boolsig imem_error ‘imem_error‘ # Error signal from instruction memory
boolsig instr_valid ‘instr_valid‘ # Is fetched instruction valid?
##### Pipeline Register D ##########################################
wordsig D_icode ‘if_id_curr->icode‘ # Instruction code
wordsig D_rA ‘if_id_curr->ra‘ # rA field from instruction
wordsig D_rB ‘if_id_curr->rb‘ # rB field from instruction
wordsig D_valP ‘if_id_curr->valp‘ # Incremented PC
##### Intermediate Values in Decode Stage #########################
wordsig d_srcA ‘id_ex_next->srca‘ # srcA from decoded instruction
wordsig d_srcB ‘id_ex_next->srcb‘ # srcB from decoded instruction
wordsig d_rvalA ‘d_regvala‘ # valA read from register file
wordsig d_rvalB ‘d_regvalb‘ # valB read from register file
##### Pipeline Register E ##########################################
wordsig E_icode ‘id_ex_curr->icode‘ # Instruction code
wordsig E_ifun ‘id_ex_curr->ifun‘ # Instruction function
wordsig E_valC ‘id_ex_curr->valc‘ # Constant data
wordsig E_srcA ‘id_ex_curr->srca‘ # Source A register ID
wordsig E_valA ‘id_ex_curr->vala‘ # Source A value
wordsig E_srcB ‘id_ex_curr->srcb‘ # Source B register ID
wordsig E_valB ‘id_ex_curr->valb‘ # Source B value
wordsig E_dstE ‘id_ex_curr->deste‘ # Destination E register ID
wordsig E_dstM ‘id_ex_curr->destm‘ # Destination M register ID
##### Intermediate Values in Execute Stage #########################
wordsig e_valE ‘ex_mem_next->vale‘ # valE generated by ALU
boolsig e_Cnd ‘ex_mem_next->takebranch‘ # Does condition hold?
wordsig e_dstE ‘ex_mem_next->deste‘ # dstE (possibly modified to be RNONE)
##### Pipeline Register M #########################
wordsig M_stat ‘ex_mem_curr->status‘ # Instruction status
wordsig M_icode ‘ex_mem_curr->icode‘ # Instruction code
wordsig M_ifun ‘ex_mem_curr->ifun‘ # Instruction function
wordsig M_valA ‘ex_mem_curr->vala‘ # Source A value
wordsig M_dstE ‘ex_mem_curr->deste‘ # Destination E register ID
wordsig M_valE ‘ex_mem_curr->vale‘ # ALU E value
wordsig M_dstM ‘ex_mem_curr->destm‘ # Destination M register ID
boolsig M_Cnd ‘ex_mem_curr->takebranch‘ # Condition flag
boolsig dmem_error ‘dmem_error‘ # Error signal from instruction memory
##### Intermediate Values in Memory Stage ##########################
wordsig m_valM ‘mem_wb_next->valm‘ # valM generated by memory
wordsig m_stat ‘mem_wb_next->status‘ # stat (possibly modified to be SADR)
##### Pipeline Register W ##########################################
wordsig W_stat ‘mem_wb_curr->status‘ # Instruction status
wordsig W_icode ‘mem_wb_curr->icode‘ # Instruction code
wordsig W_dstE ‘mem_wb_curr->deste‘ # Destination E register ID
wordsig W_valE ‘mem_wb_curr->vale‘ # ALU E value
wordsig W_dstM ‘mem_wb_curr->destm‘ # Destination M register ID
wordsig W_valM ‘mem_wb_curr->valm‘ # Memory M value
####################################################################
# Control Signal Definitions. #
####################################################################
################ Fetch Stage ###################################
## What address should instruction be fetched at
word f_pc = [
# Mispredicted branch. Fetch at incremented PC
M_icode == IJXX && !M_Cnd : M_valA;
# Completion of RET instruction
W_icode == IRET : W_valM;
# Default: Use predicted value of PC
1 : F_predPC;
];
## Determine icode of fetched instruction
## 1W: To split ipopq into two cycles, need to be able to
## modify value of icode,
## so that it will be IPOP2 when fetched for second time.
word f_icode = [
imem_error : INOP;
D_icode == IPOPQ : IPOP2;
1: imem_icode;
];
# Determine ifun
word f_ifun = [
imem_error : FNONE;
1: imem_ifun;
];
# Is instruction valid?
bool instr_valid = f_icode in
{ INOP, IHALT, IRRMOVQ, IIRMOVQ, IRMMOVQ, IMRMOVQ,
IOPQ, IJXX, ICALL, IRET, IPUSHQ, IPOPQ, IPOP2 };
# Determine status code for fetched instruction
word f_stat = [
imem_error: SADR;
!instr_valid : SINS;
f_icode == IHALT : SHLT;
1 : SAOK;
];
# Does fetched instruction require a regid byte?
bool need_regids =
f_icode in { IRRMOVQ, IOPQ, IPUSHQ, IPOPQ,
IIRMOVQ, IRMMOVQ, IMRMOVQ, IPOP2 };
# Does fetched instruction require a constant word?
bool need_valC =
f_icode in { IIRMOVQ, IRMMOVQ, IMRMOVQ, IJXX, ICALL };
# Predict next value of PC
word f_predPC = [
f_icode in { IJXX, ICALL } : f_valC;
## 1W: Want to refetch popq one time
f_icode == IPOPQ : f_pc;
1 : f_valP;
];
################ Decode Stage ######################################
## W1: Strategy. Decoding of popq rA should be treated the same
## as would iaddq $8, %rsp
## Decoding of pop2 rA treated same as mrmovq -8(%rsp), rA
## What register should be used as the A source?
word d_srcA = [
D_icode in { IRRMOVQ, IRMMOVQ, IOPQ, IPUSHQ } : D_rA;
D_icode in { IRET } : RRSP;
1 : RNONE; # Don‘t need register
];
## What register should be used as the B source?
word d_srcB = [
D_icode in { IOPQ, IRMMOVQ, IMRMOVQ } : D_rB;
D_icode in { IPUSHQ, IPOPQ, ICALL, IRET, IPOP2 } : RRSP;
1 : RNONE; # Don‘t need register
];
## What register should be used as the E destination?
word d_dstE = [
D_icode in { IRRMOVQ, IIRMOVQ, IOPQ} : D_rB;
D_icode in { IPUSHQ, IPOPQ, ICALL, IRET } : RRSP;
1 : RNONE; # Don‘t write any register
];
## What register should be used as the M destination?
word d_dstM = [
D_icode in { IMRMOVQ, IPOP2 } : D_rA;
1 : RNONE; # Don‘t write any register
];
## What should be the A value?
## Forward into decode stage for valA
word d_valA = [
D_icode in { ICALL, IJXX } : D_valP; # Use incremented PC
d_srcA == e_dstE : e_valE; # Forward valE from execute
d_srcA == M_dstM : m_valM; # Forward valM from memory
d_srcA == M_dstE : M_valE; # Forward valE from memory
d_srcA == W_dstM : W_valM; # Forward valM from write back
d_srcA == W_dstE : W_valE; # Forward valE from write back
1 : d_rvalA; # Use value read from register file
];
word d_valB = [
d_srcB == e_dstE : e_valE; # Forward valE from execute
d_srcB == M_dstM : m_valM; # Forward valM from memory
d_srcB == M_dstE : M_valE; # Forward valE from memory
d_srcB == W_dstM : W_valM; # Forward valM from write back
d_srcB == W_dstE : W_valE; # Forward valE from write back
1 : d_rvalB; # Use value read from register file
];
################ Execute Stage #####################################
## Select input A to ALU
word aluA = [
E_icode in { IRRMOVQ, IOPQ } : E_valA;
E_icode in { IIRMOVQ, IRMMOVQ, IMRMOVQ } : E_valC;
E_icode in { ICALL, IPUSHQ, IPOP2 } : -8;
E_icode in { IRET, IPOPQ } : 8;
# Other instructions don‘t need ALU
];
## Select input B to ALU
word aluB = [
E_icode in { IRMMOVQ, IMRMOVQ, IOPQ, ICALL,
IPUSHQ, IRET, IPOPQ, IPOP2 } : E_valB;
E_icode in { IRRMOVQ, IIRMOVQ } : 0;
# Other instructions don‘t need ALU
];
## Set the ALU function
word alufun = [
E_icode == IOPQ : E_ifun;
1 : ALUADD;
];
## Should the condition codes be updated?
bool set_cc = E_icode == IOPQ &&
# State changes only during normal operation
!m_stat in { SADR, SINS, SHLT } && !W_stat in { SADR, SINS, SHLT };
## Generate valA in execute stage
word e_valA = E_valA; # Pass valA through stage
## Set dstE to RNONE in event of not-taken conditional move
word e_dstE = [
E_icode == IRRMOVQ && !e_Cnd : RNONE;
1 : E_dstE;
];
################ Memory Stage ######################################
## Select memory address
word mem_addr = [
M_icode in { IRMMOVQ, IPUSHQ, ICALL, IMRMOVQ, IPOP2 } : M_valE;
M_icode in { IRET } : M_valA;
# Other instructions don‘t need address
];
## Set read control signal
bool mem_read = M_icode in { IMRMOVQ, IPOP2, IRET };
## Set write control signal
bool mem_write = M_icode in { IRMMOVQ, IPUSHQ, ICALL };
#/* $begin pipe-m_stat-hcl */
## Update the status
word m_stat = [
dmem_error : SADR;
1 : M_stat;
];
#/* $end pipe-m_stat-hcl */
################ Write back stage ##################################
## 1W: For this problem, we introduce a multiplexor that merges
## valE and valM into a single value for writing to register port E.
## DO NOT CHANGE THIS LOGIC
## Merge both write back sources onto register port E
## Set E port register ID
word w_dstE = [
## writing from valM
W_dstM != RNONE : W_dstM;
1: W_dstE;
];
## Set E port value
word w_valE = [
W_dstM != RNONE : W_valM;
1: W_valE;
];
## Disable register port M
## Set M port register ID
word w_dstM = RNONE;
## Set M port value
word w_valM = 0;
## Update processor status
word Stat = [
W_stat == SBUB : SAOK;
1 : W_stat;
];
################ Pipeline Register Control #########################
# Should I stall or inject a bubble into Pipeline Register F?
# At most one of these can be true.
bool F_bubble = 0;
bool F_stall =
# Conditions for a load/use hazard
E_icode in { IMRMOVQ, IPOP2 } &&
E_dstM in { d_srcA, d_srcB } ||
# Stalling at fetch while ret passes through pipeline
IRET in { D_icode, E_icode, M_icode };
# Should I stall or inject a bubble into Pipeline Register D?
# At most one of these can be true.
bool D_stall =
# Conditions for a load/use hazard
E_icode in { IMRMOVQ, IPOP2 } &&
E_dstM in { d_srcA, d_srcB };
bool D_bubble =
# Mispredicted branch
(E_icode == IJXX && !e_Cnd) ||
# Stalling at fetch while ret passes through pipeline
# but not condition for a load/use hazard
!(E_icode in { IMRMOVQ, IPOP2 } && E_dstM in { d_srcA, d_srcB }) &&
# 1W: This condition will change
IRET in { D_icode, E_icode, M_icode };
# Should I stall or inject a bubble into Pipeline Register E?
# At most one of these can be true.
bool E_stall = 0;
bool E_bubble =
# Mispredicted branch
(E_icode == IJXX && !e_Cnd) ||
# Conditions for a load/use hazard
E_icode in { IMRMOVQ, IPOP2 } &&
E_dstM in { d_srcA, d_srcB};
# Should I stall or inject a bubble into Pipeline Register M?
# At most one of these can be true.
bool M_stall = 0;
# Start injecting bubbles as soon as exception passes through memory stage
bool M_bubble = m_stat in { SADR, SINS, SHLT } || W_stat in { SADR, SINS, SHLT };
# Should I stall or inject a bubble into Pipeline Register W?
bool W_stall = W_stat in { SADR, SINS, SHLT };
bool W_bubble = 0;
#/* $end pipe-all-hcl */
运行结果如下:
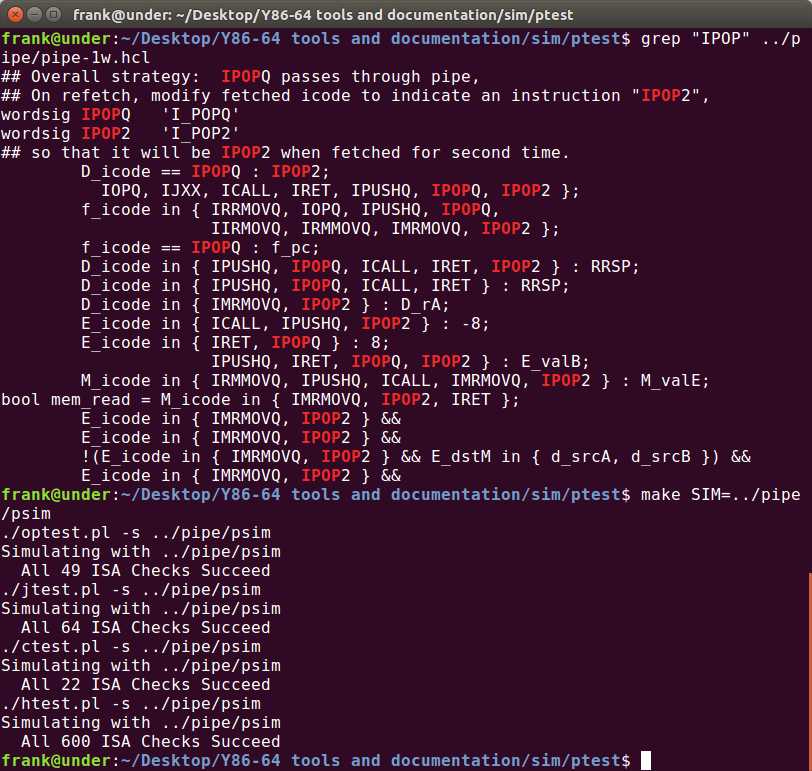
深入理解计算机系统_3e 第四章家庭作业(部分) CS:APP3e chapter 4 homework
标签:lag been nat when 存在 make efi array 处理
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/liqiuhao/p/7955711.html