模拟退火算法的物理背景:
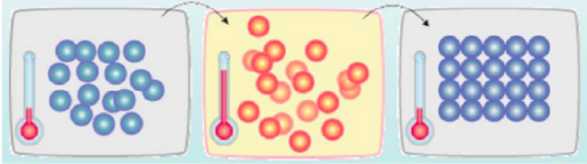
模拟退火算法的核心思想与热力学的原理极为相似,在高温下,液体的大量分子彼此之间进行相对移动,如果液体慢慢冷却,原子的可动性就会消失,原子自行排列成行,形成一个纯净的晶体. 如果温度冷却迅速,那它不一定能达到这个状态,这一个过程的本质在于,慢慢冷却,使原子在丧失可动性之前重新排列,达到低能状态的必要条件.
模拟退火算法的描述:
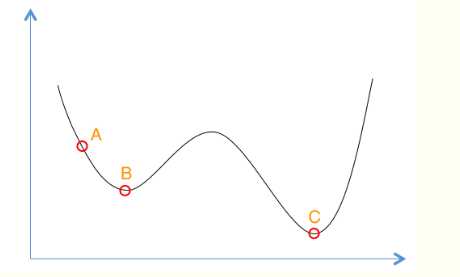
模拟退火算法实质是一种贪心算法,但和贪心算法不同的是,模拟退火算法在搜索过程中加入了随机的因素,它在搜索的过程中,会以一定的概率来接受比当前解要更差的解,因此有可能会跳出这个局部最优解,找到全局的最优值.
如图,假设从A点出发,搜索过程中找到了局部最优解B,模拟退火算法会以一定的概率接受比B更差的解,从而找到全局最优解C
模拟退火算法流程图
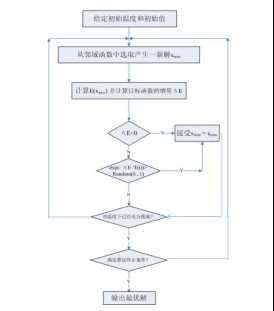
模拟退火算法主要分三个步骤:
1.在当前解的基础上产生一个新 解
2.利用Metropolis准则(即以e(- ?E/T)的概率接受最优解),判 断新解是否被接受.
3.当新解确定被接受时,用新解 代替当前解,在此基础上进行 下一轮实验,当新解被判定舍 弃时,在原解的基础上进行下 一轮实验
模拟退火算法伪代码:

模拟退火算法解决实际问题:
1.TSP问题:
旅行商问题(Traveling Salesman Problem,TSP),是数学领域一个著名问题之一,假设有一个旅行商人要拜访n个城市,他必须选择所要走的路径,路径的限制是每个城市只能拜访一次,而且最后要回到原来出发的城市,路径的选择目标是要求的路径的路程为所有路径中的最小值 .
执行代码
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <math.h> 4 #include <time.h> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 #include <iostream> 7 using namespace std; 8 9 int N; //城市的数量 10 const double T=3000; //初始温度 11 const double k=0.98; //温度下降比例 12 const double mint=1e-8; //温度的极值 13 14 const int Oloop=1000; //温度控制的最小值为t*0.98^20 15 const int Iloop=15000; //寻找一定温度下的最大值 16 const int lim=10000; //概率选择次数的最大值 17 18 double dist[100][100]; //任意两座城市之间的距离 19 20 struct Path 21 { 22 int city[100]; 23 double len; //路径的总长度 24 }; 25 26 27 struct Point //城市点的坐标 28 { 29 double x; 30 double y; 31 }; 32 33 Path bestpath; //记录最优路径 34 Path currpath; //记录当前的路径 35 Point p[100]; //各点的坐标 36 37 void input() 38 { 39 scanf("%d",&N); 40 for(int i=0;i<N;i++) 41 { 42 scanf("%lf%lf",&p[i].x,&p[i].y); 43 } 44 } 45 46 //计算任意两点之间的距离 47 void compu() 48 { 49 for(int i=0;i<N;i++) 50 { 51 for(int j=i+1;j<N;j++) 52 { 53 dist[i][j]=dist[j][i]=sqrt((p[i].x-p[j].x)*(p[i].x-p[j].x)+(p[i].y-p[j].y)*(p[i].y-p[j].y)); 54 } 55 } 56 } 57 58 //初始化最优路径 59 void init() 60 { 61 bestpath.len=0; 62 bestpath.city[0]=0; 63 for(int i=1;i<N;i++) 64 { 65 bestpath.city[i]=i; 66 bestpath.len=bestpath.len+dist[i-1][i]; 67 } 68 bestpath.len=bestpath.len+dist[0][N-1]; 69 } 70 71 //随机选择目的优化路径,此处有两种方式,一是随机选取两个节点交换,二是随机排列 72 Path choose(Path newpath) 73 { 74 int city1,city2; 75 city1=(int)rand()%N; 76 city2=(int)rand()%N; 77 while(city1==city2) 78 { 79 city1=(int)rand()%N; 80 city2=(int)rand()%N; 81 } 82 swap(newpath.city[city1],newpath.city[city2]); 83 newpath.len=0; 84 for(int i=1;i<N;i++) 85 { 86 newpath.len=newpath.len+dist[newpath.city[i-1]][newpath.city[i]]; 87 } 88 newpath.len=newpath.len+dist[newpath.city[0]][newpath.city[N-1]]; 89 return newpath; 90 } 91 92 //模拟退火算法核心代码 93 Path sa() 94 { 95 srand((unsigned)(time(NULL)));//时刻更新随机模板 96 Path newpath=bestpath; 97 Path currpath=bestpath; 98 int pl=0; //以一定概率接受此路径的次数 99 int pf=0; 100 double t2=T; 101 double t; 102 while(true){ 103 for(int i=0;i<Iloop;i++) 104 { 105 newpath=choose(currpath); 106 t=newpath.len-currpath.len; 107 if(t<0) 108 { 109 currpath=newpath; 110 pl=0; 111 pf=0; 112 113 } 114 else 115 { 116 double ran=rand()/(RAND_MAX+1.0); 117 double exx=-t*1.0/t2*1.0; 118 double ex=exp(exx); 119 if(ran<ex) 120 { 121 currpath=newpath; 122 } 123 pl++; 124 } 125 if(pl>lim){ 126 pf++; 127 break; 128 } 129 } 130 if(currpath.len<bestpath.len) 131 { 132 bestpath=currpath; 133 } 134 if(pf>Oloop||t2<mint) 135 { 136 break; 137 } 138 t2=t2*k; 139 } 140 } 141 142 void Print() 143 { 144 for(int i=0;i<N;i++) 145 { 146 printf("%d ",bestpath.city[i]); 147 } 148 printf("length:%lf\n",bestpath.len); 149 } 150 151 int main() 152 { 153 for(int i=0;i<50;i++){ 154 freopen("in.txt","r",stdin); 155 input(); 156 compu(); 157 init(); 158 sa(); 159 Print(); 160 } 161 return 0; 162 }
验证数据:
1 27 2 41 94 3 37 84 4 53 67 5 25 62 6 7 64 7 2 99 8 68 58 9 71 44 10 54 62 11 83 69 12 64 60 13 18 54 14 22 60 15 83 46 16 91 38 17 25 38 18 24 42 19 58 69 20 71 71 21 74 78 22 87 76 23 18 40 24 13 40 25 82 7 26 62 32 27 58 35 28 45 21
执行过程
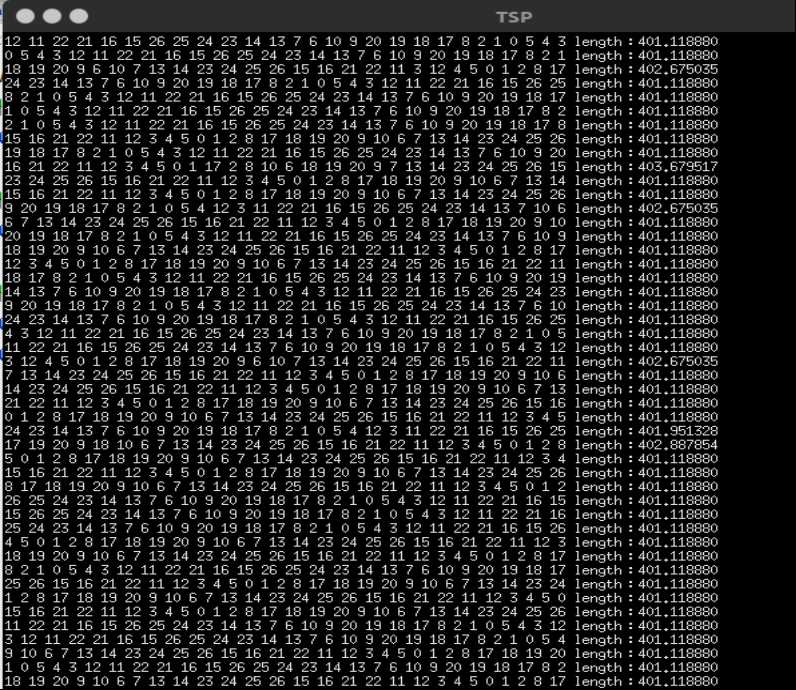
答案大概在401左右
2.求函数f(x,y)=5cos(xy)+xy+y^3的最小值,其中x的取值范围是(-5,5),y的取值范围是(-5,5)
执行代码:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <math.h> 3 #include <time.h> 4 #include <stdlib.h> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 #include <iostream> 7 8 using namespace std; 9 10 const double MAXx=5.0; //x的最大值 11 const double MINx=-5.0; //x的最小值 12 const double MAXy=5.0; //y的最大值 13 const double MINy=-5.0; //y的最小值 14 const double T=100; //初始温度 15 const double S=0.5; //每次的变化量 16 const double K=0.99; //温度递减率 17 const double ex=1e-9; 18 double Bestx; 19 double Besty; 20 21 double functionf(double x1,double y1) //所要求解的函数 22 { 23 return 5*cos(x1*y1)+x1*y1+y1*y1*y1; 24 } 25 26 void sa() 27 { 28 srand((unsigned)(time(NULL))); 29 double currx,curry; 30 double newx,newy; 31 double Bestfun,currfun,newfun; 32 double t=T; 33 double de; 34 Bestx=MINx+(MAXx-MINx)*rand()/RAND_MAX; 35 Besty=MINy+(MAXx-MINy)*rand()/RAND_MAX; 36 Bestfun=functionf(Bestx,Besty); 37 currx=Bestx; 38 curry=Besty; 39 while(t>0.00001) 40 { int P=0; 41 for(int i=0;i<10;i++) 42 { 43 int p=0; 44 while(p==0) 45 { 46 newx=currx+S*(MINx+(MAXx-MINx)*rand()/RAND_MAX); 47 if(newx>=MINx&&newx<=MAXx) 48 { 49 p=1; 50 } 51 } 52 de=functionf(currx,curry)-functionf(newx,newy); 53 double dexp=exp(de/t); 54 if(de>0) 55 { 56 currx=newx; 57 //P++; 58 } 59 else 60 { 61 if(dexp>(rand()/RAND_MAX+1)) 62 { 63 currx=newx; 64 //P++; 65 } 66 } 67 for(int j=0;j<10;j++) 68 { 69 p=0; 70 while(p==0){ 71 newy=curry+S*(MINy+(MAXy-MINy)*rand()/RAND_MAX); 72 if(newy>=MINy&&newy<=MAXy) 73 { 74 p=1; 75 } 76 } 77 de=functionf(currx,curry)-functionf(newx,newy); 78 double dexp=exp(de/t); 79 if(de>0) 80 { 81 curry=newy; 82 } 83 else 84 { 85 if(dexp>rand()/RAND_MAX+1) 86 { 87 curry=newy; 88 } 89 } 90 } 91 92 93 94 // double y2=curry; 95 // for(int j=0;j<10;j++) 96 // { 97 // p=0; 98 // while(p==0){ 99 // newy=y2+S*(MINy+(MAXy-MINy)*rand()/RAND_MAX); 100 // if(newy>=MINy&&newy<=MAXy) 101 // { 102 // p=1; 103 // } 104 // } 105 // de=functionf(currx,y2)-functionf(newx,newy); 106 // double dexp=exp(de/t); 107 // if(de>0) 108 // { 109 // y2=newy; 110 // } 111 // else 112 // { 113 // if(dexp>rand()/RAND_MAX+1) 114 // { 115 // y2=newy; 116 // } 117 // } 118 // } 119 // 120 // if(functionf(currx,y2)<functionf(currx,curry)) 121 // { 122 // curry=y2; 123 // } 124 // if(P>300){ 125 // P=0; 126 // break; 127 // } 128 129 130 } 131 if(functionf(currx,curry)<functionf(Bestx,Besty)) 132 { 133 Bestx=currx; 134 Besty=curry; 135 } 136 t=t*K; 137 } 138 } 139 140 int main() 141 { 142 for(int i=1;i<205;i++) 143 { 144 sa(); 145 printf("%f ",functionf(Bestx,Besty)); 146 if(i%6==0) 147 printf("\n"); 148 } 149 printf("\n"); 150 }
执行过程
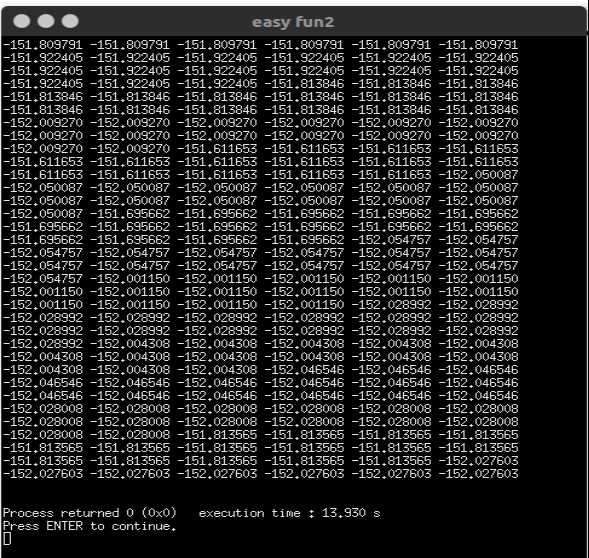
答案在-151.1左右
总结:
模拟退火算法计算过程简单,引入概率跳出局部最优解,全局性较强. 但在执行过程中,算法的执行时间较长,相关参数的变化对算法性能影响大,例如,如果在某一温度下充分搜索,很容易陷入到局部最优解中,并且收敛速度慢,但如果不充分搜索,那么很难的到全局最优解. 所以,约束条件的选择,参数控制都非常关键,有待进一步研究.
