- 最近一直在忙着做项目 本来想养成一个经常跟新博客的习惯 , 但是实在是太难了 , 每天加班到10点多 。8点能下班都是最好的了 , 小公司真不好待呀
- 分享一下最近半年的vue心得吧
- 我的项目是在他的基础上改的
PanJiaChen/vueAdmin-template
vuex 咋web上我觉得是鸡肋 , 用户刷新页面直接就没了。。。。。。。。。。。
这是我的目录 , 现在我遇到一个瓶颈 , 就是如何优化 build 的速度问题 , 这个问题随着页面原来越多已经发展到越来越恐怖的地方了现在打包一个项目起码的20分钟 , 我项目总共有323个页面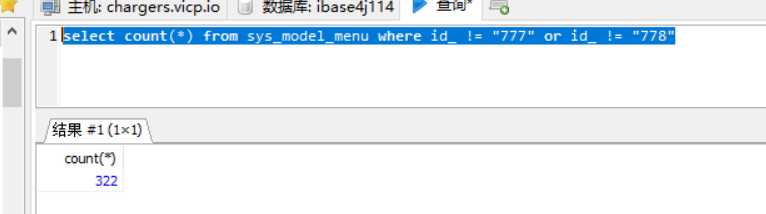

动态路由 322个页面 , 不算自己写的组件什么的
先说一下vue webpack 的配置的问题
"scripts": {
"dev": "node build/dev-server.js",
"build": "node build/build.js",
"lint": "eslint --ext .js,.vue src"
}
我们 npm run dev 便是运行的 第一条命令 , 类推
build/dev-server.js
require(‘./check-versions‘)() // 检查 Node 和 npm 版本 var config = require(‘../config‘) // 获取 config/index.js 的默认配置 /* ** 如果 Node 的环境无法判断当前是 dev / product 环境 ** 使用 config.dev.env.NODE_ENV 作为当前的环境 */ if (!process.env.NODE_ENV) process.env.NODE_ENV = JSON.parse(config.dev.env.NODE_ENV) var path = require(‘path‘) // 使用 NodeJS 自带的文件路径工具 var express = require(‘express‘) // 使用 express var webpack = require(‘webpack‘) // 使用 webpack var opn = require(‘opn‘) // 一个可以强制打开浏览器并跳转到指定 url 的插件 var proxyMiddleware = require(‘http-proxy-middleware‘) // 使用 proxyTable var webpackConfig = require(‘./webpack.dev.conf‘) // 使用 dev 环境的 webpack 配置 // default port where dev server listens for incoming traffic /* 如果没有指定运行端口,使用 config.dev.port 作为运行端口 */ var port = process.env.PORT || config.dev.port // Define HTTP proxies to your custom API backend // https://github.com/chimurai/http-proxy-middleware /* 使用 config.dev.proxyTable 的配置作为 proxyTable 的代理配置 */ var proxyTable = config.dev.proxyTable /* 使用 express 启动一个服务 */ var app = express() var compiler = webpack(webpackConfig) // 启动 webpack 进行编译 /* 启动 webpack-dev-middleware,将 编译后的文件暂存到内存中 */ var devMiddleware = require(‘webpack-dev-middleware‘)(compiler, { publicPath: webpackConfig.output.publicPath, stats: { colors: true, chunks: false } }) /* 启动 webpack-hot-middleware,也就是我们常说的 Hot-reload */ var hotMiddleware = require(‘webpack-hot-middleware‘)(compiler) // force page reload when html-webpack-plugin template changes compiler.plugin(‘compilation‘, function (compilation) { compilation.plugin(‘html-webpack-plugin-after-emit‘, function (data, cb) { hotMiddleware.publish({ action: ‘reload‘ }) cb() }) }) // proxy api requests // 将 proxyTable 中的请求配置挂在到启动的 express 服务上 Object.keys(proxyTable).forEach(function (context) { var options = proxyTable[context] if (typeof options === ‘string‘) { options = { target: options } } app.use(proxyMiddleware(context, options)) }) // handle fallback for HTML5 history API // 使用 connect-history-api-fallback 匹配资源,如果不匹配就可以重定向到指定地址 app.use(require(‘connect-history-api-fallback‘)()) // serve webpack bundle output // 将暂存到内存中的 webpack 编译后的文件挂在到 express 服务上 app.use(devMiddleware) // enable hot-reload and state-preserving // compilation error display // 将 Hot-reload 挂在到 express 服务上 app.use(hotMiddleware) // serve pure static assets // 拼接 static 文件夹的静态资源路径 var staticPath = path.posix.join(config.dev.assetsPublicPath, config.dev.assetsSubDirectory) // 为静态资源提供响应服务 app.use(staticPath, express.static(‘./static‘)) // 让我们这个 express 服务监听 port 的请求,并且将此服务作为 dev-server.js 的接口暴露 module.exports = app.listen(port, function (err) { if (err) { console.log(err) return } var uri = ‘http://localhost:‘ + port console.log(‘Listening at ‘ + uri + ‘\n‘) // when env is testing, don‘t need open it // 如果不是测试环境,自动打开浏览器并跳到我们的开发地址 if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== ‘testing‘) { opn(uri) } })
webpack.dev.conf.js
var config = require(‘../config‘) // 同样的使用了 config/index.js var webpack = require(‘webpack‘) // 使用 webpack var merge = require(‘webpack-merge‘) // 使用 webpack 配置合并插件 var utils = require(‘./utils‘) // 使用一些小工具 var baseWebpackConfig = require(‘./webpack.base.conf‘) // 加载 webpack.base.conf /* 使用 html-webpack-plugin 插件,这个插件可以帮我们自动生成 html 并且注入到 .html 文件中 */ var HtmlWebpackPlugin = require(‘html-webpack-plugin‘) // add hot-reload related code to entry chunks // 将 Hol-reload 相对路径添加到 webpack.base.conf 的 对应 entry 前 Object.keys(baseWebpackConfig.entry).forEach(function (name) { baseWebpackConfig.entry[name] = [‘./build/dev-client‘].concat(baseWebpackConfig.entry[name]) }) /* 将我们 webpack.dev.conf.js 的配置和 webpack.base.conf.js 的配置合并 */ module.exports = merge(baseWebpackConfig, { module: { // 使用 styleLoaders loaders: utils.styleLoaders({ sourceMap: config.dev.cssSourceMap }) }, // eval-source-map is faster for development // 使用 #eval-source-map 模式作为开发工具,此配置可参考 DDFE 往期文章详细了解 devtool: ‘#eval-source-map‘, plugins: [ /* definePlugin 接收字符串插入到代码当中, 所以你需要的话可以写上 JS 的字符串 */ new webpack.DefinePlugin({ ‘process.env‘: config.dev.env }), // https://github.com/glenjamin/webpack-hot-middleware#installation--usage new webpack.optimize.OccurenceOrderPlugin(), /* HotModule 插件在页面进行变更的时候只会重回对应的页面模块,不会重绘整个 html 文件 */ new webpack.HotModuleReplacementPlugin(), /* 使用了 NoErrorsPlugin 后页面中的报错不会阻塞,但是会在编译结束后报错 */ new webpack.NoErrorsPlugin(), // https://github.com/ampedandwired/html-webpack-plugin /* 将 index.html 作为入口,注入 html 代码后生成 index.html文件 */ new HtmlWebpackPlugin({ filename: ‘index.html‘, template: ‘index.html‘, inject: true }) ] })
webpack.base.conf.js
var path = require(‘path‘) // 使用 NodeJS 自带的文件路径插件 var config = require(‘../config‘) // 引入 config/index.js var utils = require(‘./utils‘) // 引入一些小工具 var projectRoot = path.resolve(__dirname, ‘../‘) // 拼接我们的工作区路径为一个绝对路径 /* 将 NodeJS 环境作为我们的编译环境 */ var env = process.env.NODE_ENV // check env & config/index.js to decide weither to enable CSS Sourcemaps for the // various preprocessor loaders added to vue-loader at the end of this file /* 是否在 dev 环境下开启 cssSourceMap ,在 config/index.js 中可配置 */ var cssSourceMapDev = (env === ‘development‘ && config.dev.cssSourceMap) /* 是否在 production 环境下开启 cssSourceMap ,在 config/index.js 中可配置 */ var cssSourceMapProd = (env === ‘production‘ && config.build.productionSourceMap) /* 最终是否使用 cssSourceMap */ var useCssSourceMap = cssSourceMapDev || cssSourceMapProd module.exports = { entry: { app: ‘./src/main.js‘ // 编译文件入口 }, output: { path: config.build.assetsRoot, // 编译输出的静态资源根路径 publicPath: process.env.NODE_ENV === ‘production‘ ? config.build.assetsPublicPath : config.dev.assetsPublicPath, // 正式发布环境下编译输出的上线路径的根路径 filename: ‘[name].js‘ // 编译输出的文件名 }, resolve: { // 自动补全的扩展名 extensions: [‘‘, ‘.js‘, ‘.vue‘], // 不进行自动补全或处理的文件或者文件夹 fallback: [path.join(__dirname, ‘../node_modules‘)], alias: { // 默认路径代理,例如 import Vue from ‘vue‘,会自动到 ‘vue/dist/vue.common.js‘中寻找 ‘vue$‘: ‘vue/dist/vue.common.js‘, ‘src‘: path.resolve(__dirname, ‘../src‘), ‘assets‘: path.resolve(__dirname, ‘../src/assets‘), ‘components‘: path.resolve(__dirname, ‘../src/components‘) } }, resolveLoader: { fallback: [path.join(__dirname, ‘../node_modules‘)] }, module: { preLoaders: [ // 预处理的文件及使用的 loader { test: /\.vue$/, loader: ‘eslint‘, include: projectRoot, exclude: /node_modules/ }, { test: /\.js$/, loader: ‘eslint‘, include: projectRoot, exclude: /node_modules/ } ], loaders: [ // 需要处理的文件及使用的 loader { test: /\.vue$/, loader: ‘vue‘ }, { test: /\.js$/, loader: ‘babel‘, include: projectRoot, exclude: /node_modules/ }, { test: /\.json$/, loader: ‘json‘ }, { test: /\.(png|jpe?g|gif|svg)(\?.*)?$/, loader: ‘url‘, query: { limit: 10000, name: utils.assetsPath(‘img/[name].[hash:7].[ext]‘) } }, { test: /\.(woff2?|eot|ttf|otf)(\?.*)?$/, loader: ‘url‘, query: { limit: 10000, name: utils.assetsPath(‘fonts/[name].[hash:7].[ext]‘) } } ] }, eslint: { // eslint 代码检查配置工具 formatter: require(‘eslint-friendly-formatter‘) }, vue: { // .vue 文件配置 loader 及工具 (autoprefixer) loaders: utils.cssLoaders({ sourceMap: useCssSourceMap }), postcss: [ require(‘autoprefixer‘)({ browsers: [‘last 2 versions‘] }) ] } }
config/index.js
var path = require(‘path‘) module.exports = { build: { // production 环境 env: require(‘./prod.env‘), // 使用 config/prod.env.js 中定义的编译环境 index: path.resolve(__dirname, ‘../dist/index.html‘), // 编译输入的 index.html 文件 assetsRoot: path.resolve(__dirname, ‘../dist‘), // 编译输出的静态资源路径 assetsSubDirectory: ‘static‘, // 编译输出的二级目录 assetsPublicPath: ‘/‘, // 编译发布的根目录,可配置为资源服务器域名或 CDN 域名 productionSourceMap: true, // 是否开启 cssSourceMap // Gzip off by default as many popular static hosts such as // Surge or Netlify already gzip all static assets for you. // Before setting to `true`, make sure to: // npm install --save-dev compression-webpack-plugin productionGzip: false, // 是否开启 gzip productionGzipExtensions: [‘js‘, ‘css‘] // 需要使用 gzip 压缩的文件扩展名 }, dev: { // dev 环境 env: require(‘./dev.env‘), // 使用 config/dev.env.js 中定义的编译环境 port: 8080, // 运行测试页面的端口 assetsSubDirectory: ‘static‘, // 编译输出的二级目录 assetsPublicPath: ‘/‘, // 编译发布的根目录,可配置为资源服务器域名或 CDN 域名 proxyTable: {}, // 需要 proxyTable 代理的接口(可跨域) // CSS Sourcemaps off by default because relative paths are "buggy" // with this option, according to the CSS-Loader README // (https://github.com/webpack/css-loader#sourcemaps) // In our experience, they generally work as expected, // just be aware of this issue when enabling this option. cssSourceMap: false // 是否开启 cssSourceMap } }
build.js
// https://github.com/shelljs/shelljs require(‘./check-versions‘)() // 检查 Node 和 npm 版本 require(‘shelljs/global‘) // 使用了 shelljs 插件,可以让我们在 node 环境的 js 中使用 shell env.NODE_ENV = ‘production‘ var path = require(‘path‘) // 不再赘述 var config = require(‘../config‘) // 加载 config.js var ora = require(‘ora‘) // 一个很好看的 loading 插件 var webpack = require(‘webpack‘) // 加载 webpack var webpackConfig = require(‘./webpack.prod.conf‘) // 加载 webpack.prod.conf console.log( // 输出提示信息 ~ 提示用户请在 http 服务下查看本页面,否则为空白页 ‘ Tip:\n‘ + ‘ Built files are meant to be served over an HTTP server.\n‘ + ‘ Opening index.html over file:// won\‘t work.\n‘ ) var spinner = ora(‘building for production...‘) // 使用 ora 打印出 loading + log spinner.start() // 开始 loading 动画 /* 拼接编译输出文件路径 */ var assetsPath = path.join(config.build.assetsRoot, config.build.assetsSubDirectory) /* 删除这个文件夹 (递归删除) */ rm(‘-rf‘, assetsPath) /* 创建此文件夹 */ mkdir(‘-p‘, assetsPath) /* 复制 static 文件夹到我们的编译输出目录 */ cp(‘-R‘, ‘static/*‘, assetsPath) // 开始 webpack 的编译 webpack(webpackConfig, function (err, stats) { // 编译成功的回调函数 spinner.stop() if (err) throw err process.stdout.write(stats.toString({ colors: true, modules: false, children: false, chunks: false, chunkModules: false }) + ‘\n‘) })
webpack.prod.conf.js
var path = require(‘path‘) // 不再赘述 var config = require(‘../config‘) // 加载 confi.index.js var utils = require(‘./utils‘) // 使用一些小工具 var webpack = require(‘webpack‘) // 加载 webpack var merge = require(‘webpack-merge‘) // 加载 webpack 配置合并工具 var baseWebpackConfig = require(‘./webpack.base.conf‘) // 加载 webpack.base.conf.js /* 一个 webpack 扩展,可以提取一些代码并且将它们和文件分离开 */ /* 如果我们想将 webpack 打包成一个文件 css js 分离开,那我们需要这个插件 */ var ExtractTextPlugin = require(‘extract-text-webpack-plugin‘) /* 一个可以插入 html 并且创建新的 .html 文件的插件 */ var HtmlWebpackPlugin = require(‘html-webpack-plugin‘) var env = config.build.env /* 合并 webpack.base.conf.js */ var webpackConfig = merge(baseWebpackConfig, { module: { /* 使用的 loader */ loaders: utils.styleLoaders({ sourceMap: config.build.productionSourceMap, extract: true }) }, /* 是否使用 #source-map 开发工具,更多信息可以查看 DDFE 往期文章 */ devtool: config.build.productionSourceMap ? ‘#source-map‘ : false, output: { /* 编译输出目录 */ path: config.build.assetsRoot, /* 编译输出文件名 */ filename: utils.assetsPath(‘js/[name].[chunkhash].js‘), // 我们可以在 hash 后加 :6 决定使用几位 hash 值 // 没有指定输出名的文件输出的文件名 chunkFilename: utils.assetsPath(‘js/[id].[chunkhash].js‘) }, vue: { /* 编译 .vue 文件时使用的 loader */ loaders: utils.cssLoaders({ sourceMap: config.build.productionSourceMap, extract: true }) }, plugins: [ /* 使用的插件 */ // http://vuejs.github.io/vue-loader/en/workflow/production.html /* definePlugin 接收字符串插入到代码当中, 所以你需要的话可以写上 JS 的字符串 */ new webpack.DefinePlugin({ ‘process.env‘: env }), /* 压缩 js (同样可以压缩 css) */ new webpack.optimize.UglifyJsPlugin({ compress: { warnings: false } }), new webpack.optimize.OccurrenceOrderPlugin(), // extract css into its own file /* 将 css 文件分离出来 */ new ExtractTextPlugin(utils.assetsPath(‘css/[name].[contenthash].css‘)), // generate dist index.html with correct asset hash for caching. // you can customize output by editing /index.html // see https://github.com/ampedandwired/html-webpack-plugin /* 输入输出的 .html 文件 */ new HtmlWebpackPlugin({ filename: config.build.index, template: ‘index.html‘, inject: true, // 是否注入 html minify: { // 压缩的方式 removeComments: true, collapseWhitespace: true, removeAttributeQuotes: true // more options: // https://github.com/kangax/html-minifier#options-quick-reference }, // necessary to consistently work with multiple chunks via CommonsChunkPlugin chunksSortMode: ‘dependency‘ }), // split vendor js into its own file /* 没有指定输出文件名的文件输出的静态文件名 */ new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({ name: ‘vendor‘, minChunks: function (module, count) { // any required modules inside node_modules are extracted to vendor return ( module.resource && /\.js$/.test(module.resource) && module.resource.indexOf( path.join(__dirname, ‘../node_modules‘) ) === 0 ) } }), // extract webpack runtime and module manifest to its own file in order to // prevent vendor hash from being updated whenever app bundle is updated /* 没有指定输出文件名的文件输出的静态文件名 */ new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({ name: ‘manifest‘, chunks: [‘vendor‘] }) ] }) /* 开启 gzip 的情况下使用下方的配置 */ if (config.build.productionGzip) { /* 加载 compression-webpack-plugin 插件 */ var CompressionWebpackPlugin = require(‘compression-webpack-plugin‘) /* 向webpackconfig.plugins中加入下方的插件 */ webpackConfig.plugins.push( /* 使用 compression-webpack-plugin 插件进行压缩 */ new CompressionWebpackPlugin({ asset: ‘[path].gz[query]‘, algorithm: ‘gzip‘, test: new RegExp( ‘\\.(‘ + config.build.productionGzipExtensions.join(‘|‘) + ‘)$‘ ), threshold: 10240, minRatio: 0.8 }) ) } module.exports = webpackConfig
