Spring框架的四大原则:
1)使用POJO进行轻量级和最小侵入式的开发。
2)通过依赖注入和基于接口编程实现松耦合。
3)通过AOP和默认习惯进行声明式编程。
4)使用AOP和模板(template)减少模式化代码。
1.1依赖注入:
控制反转(Inversion of Control - IOC)与依赖注入(dependency injection - DI)在Spring环境下是同等的概念。
控制反转是通过依赖注入实现的。所谓的控制反转指的是:容器负责创建对象和维护对象间的依赖关系。
依赖注入的主要目的是实现解耦,添加一个功能一般有两种方式:继承父类、组合另一个具有该功能的类。
组合相对于继承父类来说,其耦合度是较低的。
SpringIoC容器(ApplicationContext)负责创建Bean,并通过容器将功能类Bean注入到需要的Bean中去。Spring通过XML、注解、java配置实现IoC(DI)。
XML、注解、java配置都是配置元数据。
元数据:用来描述数据的数据。
元数据不具备任何可执行能力,只能通过外界代码来对元数据进行解析然后赋予特定的功能。Spring容器解析这些配置元数据后进行Bean的初始化、配置和管理依赖。
声明Bean的注解:
@Component:没有明确的角色
@Service: 在业务逻辑层使用
@Repository:在数据访问层(dao)使用
@Controller:在MVC层使用
注:上面四个注解功能是一样的,不过为了业务区分采用了不同的表现。
注入Bean的注解:
@Autowired :Spring提供的注解
@Inject :JSR-330提供的注解
@Resource :JSR-330提供的注解
上面三个注解一般可用于set方法或者属性上,但是一般习惯写法是用在属性上。
基于注解的Bean的初始化与依赖注入,Spring容器选用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext。
功能类Bean:
@Service
public class FunService {
public String sayHello(String word) {
return "Hello " + word + " !";
}
}
注:@Service声明当前FunService类是一个Spring管理的Bean,其中使用@Component、@Service、@Repository、@Controller是等效的。
使用功能类的Bean:
@Service
public class UseFunService {
@Autowired
private FunService FunService;
public String sayHello(String word) {
return FunService.sayHello(word);
}
}
注:@Service声明当前类是Spring管理的Bean
@Autowired将FunService的实体注入到UseFunService中,使其能够使用其中的方法。
配置类:
@ComponentScan("learn.learn.spring.ioc")
@Configuration
public class Diconfig {
}
注:@ComponentScan,自动扫描指定包下的所有使用@Component、@Controller、@Service、@Repository的类,并注册为Bean。
运行:
public class App
{
public static void main( String[] args ) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Diconfig.class);//1
UseFunService UseFunService =
context.getBean(UseFunService.class);//2
System.out.println(UseFunService.sayHello("di"));
context.close();
}
}
注:1)使用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext作为Spring的容器,接受一个配置类作为参数。
2)获取声明配置的UseFunService的Bean。
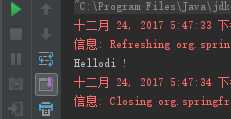
结果:
1.2java配置:
Java配置是Spring4.x推荐使用的配置方式,可以完全取代XML配置;java配置也是springboot中推荐使用的配置方式。
java配置是通过@Configuration和@Bean实现的。
@configuration声明当前类是一个配置类,相当于Spring配置的XML文件。
@Bean注解在方法上,声明当前方法返回值为一个Bean。
注:实际工作中java配置的方式往往与XML实现的方式一样,主要是用于数据库的配置等一些常用的数据配置,当然你也可以根据业务需要来做自己需要的配置方式。
一般配置原则:全局配置使用java配置(如数据库,MVC等配置);业务Bean使用注解配置(@Component、@Controller、@Service、@Repository)。
示例:
功能类的Bean:
public class FunctionService {
public String say(String word) {
return "Hello" + word + " !";
}
}
注:此处没有使用@Service声明Bean
使用功能类Bean:
//1
public class UseFunctionService {
//2
FunService FunService;
public void set(FunService FunService) {
this.FunService = FunService;
}
public String say(String word) {
return FunService.sayHello(word);
}
}
注:1:此处没有使用@Service声明Bean
2:此处没有使用@Autowired注解注入Bean
配置类:
@Configuration//1
public class DiConfig {
@Bean
public FunctionService functionService() {
return new FunctionService();
}
@Bean
public UseFunctionService useFunctionService() {
return new UseFunctionService();
}
}
注:1:@Configuration表明此类是一个Spring配置类,类似于XML文件。
运行:
public class App {
public static void main( String[] args ) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(DiConfig.class);//1
UseFunctionService useFunctionService =
context.getBean(UseFunctionService.class);
System.out.println(useFunctionService.say("di"));
context.close();
}
}
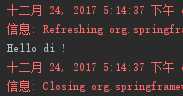
结果: