从学习java开始就知道,hashCode()方法是object类本身就有的方法,所有的类都继承了object,也就了hashCode()这个方法。
在学java的时候,就被告知在重写equals方法时,也要重写hashCode方法。当时没细想,以为这个是语法规定。
后来了解到,这个确实java规定:
hashcode相等的两个对象内容不一定相等。
对象内容相等的两个对象hashcode一定相等!
如果比较两个对象是否相等。比较两个对象的内容涉及的东西比较多,但是hashcode只是一个int数字,要比较还是不简单!性能上比equals快多了。在set,map等集合类中,代码中都是先利用hashcode判断key是否存在和重复。这也就是如果自定义类作为key时,要求要重写hashCode方法。
默认的hashcode的值是对象在内存中的地址。
随便提一下,String也是重写了hashCode方法的。
String类关键代码如下:

/**
* Returns a hash code for this string. The hash code for a
* {@code String} object is computed as
* <blockquote><pre>
* s[0]*31^(n-1) + s[1]*31^(n-2) + ... + s[n-1]
* </pre></blockquote>
* using {@code int} arithmetic, where {@code s[i]} is the
* <i>i</i>th character of the string, {@code n} is the length of
* the string, and {@code ^} indicates exponentiation.
* (The hash value of the empty string is zero.)
*
* @return a hash code value for this object.
*/
public int hashCode() {
int h = hash;
if (h == 0 && value.length > 0) {
char val[] = value;
for (int i = 0; i < value.length; i++) {
h = 31 * h + val[i];
}
hash = h;
}
return h;
}
就是它了,根据内容来决定hashcode的值的。
测试代码如下:
public class Dog {
private int age;
private String name;
public Dog(String name,int age){
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
public class Hash {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String a="abc";
String b=new String("abc");
String c=new String("abc");
String d="abc";
System.out.println(" a hashcode:"+a.hashCode()+"--"+(a==d));
System.out.println(" b hashcode:"+b.hashCode()+"--"+(b==c));
System.out.println("c hashcode:"+c.hashCode());
System.out.println("d hashcode:" +d.hashCode());
Dog dog1=new Dog("aa", 1);
Dog dog2=new Dog("aa", 1);
System.out.println(dog1.hashCode());
System.out.println(dog2.hashCode());
}
}
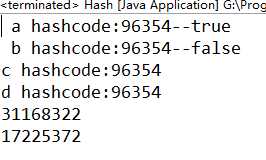
运行结果(每次运行dog的hashcode的结果不一样。下图仅仅是参考):