JDBC数据库连接
1.Jdbc是什么?
我们之前提到了数据库,如何使用java代码来操作数据库呢,程序要通过sql语句来操作数据库库,而必须拥有一个类库,类库提供sql语句的执行方法 jdbc就是因此而产生的,jdbc是java中提供的一个接口 允许程序员通过这个接口来操作数据库。
2.如何使用jdbc来完成数据的增删该查
Jdbc拥有自己的驱动使用前需要加载
- Jdbc加载驱动获得连接
- Jdbc执行sql语句
- Jdbc关闭连接
从连接数据库到操作数据库的详细步骤如下
首先加载驱动程序 class.forname(“com.mysql.jdbc.driver”)加载mysql数据库驱动 需要导入相应的jar包
mysql-connector-java-5.1.7-bin.jar
这里可能会抛出一个异常 就是classnotfoundexception 找不到这个类,我们可以打印出错误信息堆栈。
加载好驱动程序后,就是获得与数据库的连接
Connection conn=null; conn=DriverManager.getConnection(“jdbc:mysql://localhost/javaweb1?seUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8”,”root”,”root”);//填入你的数据库的信息,后两个参数为账号和密码
通过PrepareStatement Statement这两个类执行sql语句
PrepareStatement stat=null; stat=conn.preparestatment(“sql语句”);
ResultSet这个类来获取sql语句执行后的结果
ResultSet rs= stat.executequery(“”);//执行
如果是更新语句 update等
则务必使用
stat.executeUpdate();
来进行结果的提交 否则无效
最后 在使用完jdbc后 一定要关闭资源!!! 否则数据库的连接过多造成数据库的崩溃
stat.close(); conn.close();
相关的代码
获取study1中所有信息 人的姓名 年龄 性别等信息。

1 package abc; 2 import java.sql.Connection; 3 import java.sql.DriverManager; 4 import java.sql.PreparedStatement; 5 import java.sql.ResultSet; 6 import java.sql.SQLException; 7 8 public class main 9 { 10 11 public static void main(String[] args) 12 { 13 try 14 { 15 16 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); 17 } 18 catch (ClassNotFoundException e) 19 { 20 System.out.println("mysql jdbc错误"+e.getMessage()); 21 return ; 22 } 23 24 Connection conn= null; 25 PreparedStatement stmt =null; 26 ResultSet resultSet = null; 27 28 29 //DriverManager 30 try 31 { 32 conn=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost/study1?seUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8","root","root"); 33 System.out.println(conn.getClass()); 34 stmt = conn.prepareStatement("select * from t_person"); 35 resultSet = stmt.executeQuery(); 36 while(resultSet.next()) 37 { 38 String name = resultSet.getString("Name"); 39 int age=resultSet.getInt("Age"); 40 boolean gender = resultSet.getBoolean("Gender"); 41 System.out.println("名字:"+name+"年龄"+age+"性别"+(gender?"男":"女")); 42 } 43 int i=stmt.executeUpdate(); 44 45 46 } 47 catch (SQLException e) 48 { 49 System.out.println(""+e.getMessage()); 50 } 51 finally 52 { 53 54 JDBCGB.closeQuiety(conn); 55 JDBCGB.closeQuiety(stmt); 56 57 } 58 59 } 60 61 }
3.SQL注入漏洞防范
所谓SQL注入,它是利用现有应用程序,将(恶意的)SQL命令注入到后台数据库引擎执行的能力
首先来简单演示一下:假设我们通过scanner来模拟用户的登陆

1 package zr; 2 import java.sql.Connection; 3 import java.sql.DriverManager; 4 import java.sql.PreparedStatement; 5 import java.sql.ResultSet; 6 import java.sql.SQLException; 7 import java.util.Scanner; 8 9 public class main2 10 { 11 12 public static void main(String[] args) 13 { 14 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); 15 System.out.println("请输入用户名"); 16 String username = sc.nextLine(); 17 System.out.println("请输入密码"); 18 String password = sc.nextLine(); 19 try 20 { 21 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); 22 } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) 23 { 24 System.out.println("加载驱动失败"+e.getMessage()); 25 26 } 27 Connection conn = null; 28 PreparedStatement ps = null; 29 ResultSet rs = null; 30 try{ 31 conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost/study1?seUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF8", "root", "root"); 32 String sql = "select count(*) c from T_Users where UserName=‘"+username+"‘ and PassWord = ‘"+password+"‘"; 33 ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); 34 /* 35 * 存在注入漏洞 a‘ or ‘a‘=‘a 36 * 需要对其过滤 37 */ 38 /*String sql ="select count(*) c from T_Users where UserName=? and PassWord =?"; 39 40 ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); 41 ps.setString(1, username); 42 ps.setString(2, password);*/ 43 rs = ps.executeQuery(); 44 rs.next(); 45 int c = rs.getInt("c"); 46 System.out.println(c); 47 if(c<=0){ 48 System.out.println("登录失败"); 49 50 } 51 else{ 52 System.out.println("登陆成功"); 53 } 54 }catch(SQLException ex){ 55 System.out.println("执行数据库出错"+ ex); 56 } 57 finally{ 58 JDBCGB.closeQuiety(ps); 59 JDBCGB.closeQuiety(conn); 60 JDBCGB.closeQuiety(rs); 61 } 62 } 63 }
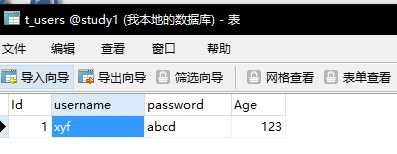
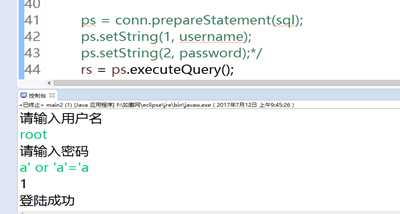
账号随意输入
密码为
a’ or ‘a’ =’a
都可以登陆成功
其原因是
password的结果永远为true 整个sql语句 也会为true
这样就成功的执行到了sql语句
3.1如何防范
上面代码中其实已经注释标记出来了
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); ps.setString(1, username); ps.setString(2, password);
我们需要对sql语句进行简单的过滤操作
采用 setstring来进行预编译处理
最终实现了系统的安全性
4. JDBC如何取出数据库中的null
5. Integer iAge = (Integer)rs.getObject("Age");
6. if(objI==null)
7. {
8. System.out.println("布吉岛呀");
9. }
10. else
11. {
12. int age = iAge;
将查询结果包装为一个integer的包装类型,这样integer可以为null
就可以通过程序来进行判断了
5.JDBCUtils工具类
5.1JDBCGB资源关闭
使用该类对资源进行统一的关闭回收。

1 package abc; 2 import java.sql.Connection; 3 import java.sql.PreparedStatement; 4 import java.sql.ResultSet; 5 import java.sql.SQLException; 6 7 //安静的关闭 8 public class JDBCGB 9 { 10 public static void closeQuiety(PreparedStatement stmt) 11 { 12 if(stmt!=null) 13 { 14 try 15 { 16 stmt.close(); 17 } 18 19 catch (SQLException e) 20 { 21 //System.out.println("无法关闭数据流"); 22 } 23 } 24 25 } 26 public static void closeQuiety(Connection conn) 27 { 28 if(conn!=null) 29 { 30 try 31 { 32 conn.close(); 33 } 34 catch (SQLException e) 35 { 36 // TODO 自动生成的 catch 块 37 // e.printStackTrace(); 38 } 39 } 40 } 41 public static void closeQuiety(ResultSet rs) 42 { 43 44 { 45 if(rs!=null) 46 { 47 try 48 { 49 rs.close(); 50 } 51 52 catch (SQLException e) 53 { 54 //System.out.println("无法关闭数据流"); 55 } 56 57 } 58 } 59 } 60 61 }
5.2JDBCUtils可变长参数的运用
为什么要使用可变长参数?
如果在数据库的操作中
String sql = "select * from admin where username= "+name;
直接使用sql语句来拼接的话
在数据库中会查询出这样一个结果
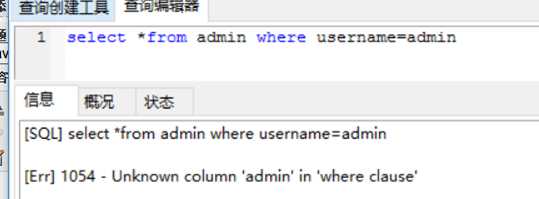
由于我们需要将admin加上单引号而 字符串的拼接过程中没有加上单引号造成查询结果出错
抛出sql异常
解决方法有
String sql="select * from admin where username =‘"+name+"‘";
这样来实现数据库的拼接,但是如果每次都这样拼接是不是特别麻烦
所以才需要使用一个参数 为可变长参数,可变长参数可以优化查询使查询传递的参数更多。

1 public static ResultSet executeQuery(Connection conn, String sql, 2 Object... parameters) throws SQLException 3 { 4 PreparedStatement ps = null; 5 try 6 { 7 ResultSet rs = null; 8 ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); 9 for (int i = 0; i < parameters.length; i++) 10 { 11 ps.setObject(i + 1, parameters[i]); 12 } 13 rs = ps.executeQuery(); 14 return rs; 15 } catch (SQLException ex) 16 { 17 close(ps); 18 throw ex; 19 } 20 }
5.3JDBCUtils 通过读取配置文件来获得连接
首先还是定义一个配置文件,名称为config.pro
放在src目录下面
配置文件中定义数据库的详细信息
- drivername=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
- dburl=jdbc:mysql://localhost/study1?seUnicode=true&&characterEcoding=UTF8
- dbusername=root
- dbpassword=root
JDBC完整代码,在程序中通过class.forname 来加载到数据库的配置信息

1 package com.scetc; 2 import java.io.IOException; 3 import java.io.InputStream; 4 import java.sql.Connection; 5 import java.sql.DriverManager; 6 import java.sql.PreparedStatement; 7 import java.sql.ResultSet; 8 import java.sql.SQLException; 9 import java.sql.Statement; 10 import java.util.Properties; 11 12 public class JDBCGB 13 { 14 private static final String drivername; 15 private static final String dburl; 16 private static final String dbusername; 17 private static final String dbpassword; 18 static 19 { 20 InputStream instream=null; 21 22 try{ 23 instream = JDBCGB.class.getResourceAsStream("config.pro"); 24 Properties prop = new Properties(); 25 //加载配置文件 26 prop.load(instream); 27 drivername=prop.getProperty("drivername"); 28 dburl=prop.getProperty("dburl"); 29 dbusername=prop.getProperty("dbusername"); 30 dbpassword = prop.getProperty("dbpassword"); 31 } 32 33 catch(IOException ex) 34 { 35 throw new RuntimeException("config",ex); 36 37 } 38 finally 39 { 40 if(instream!=null) 41 { 42 try 43 { 44 instream.close(); 45 46 }catch(IOException e) 47 { 48 // 49 50 } 51 52 } 53 54 55 56 } 57 try 58 { 59 Class.forName(drivername); 60 } 61 catch (ClassNotFoundException e) 62 { 63 throw new RuntimeException("mysql jdbc",e); 64 } 65 66 } 67 /** 68 * 创建数据库的连接 69 * @return 70 * @throws SQLException 71 */ 72 public static Connection createConnection() throws SQLException 73 { 74 return DriverManager.getConnection(dburl,dbusername,dbpassword); 75 76 } 77 public static int executeUpdate(Connection conn,String sql,Object ...parameters)throws SQLException 78 { 79 PreparedStatement ps=null; 80 try 81 { 82 ps=conn.prepareStatement(sql); 83 for(int i=0;i<parameters.length;i++) 84 { 85 ps.setObject(i+1, parameters[i]); 86 87 } 88 return ps.executeUpdate(); 89 } 90 finally 91 { 92 closeQuiety(ps); 93 } 94 } 95 /**执行sql语句并且 96 * 获得数据库的返回值 97 * @param conn 98 * @param sql 99 * @param parameters 100 * @return 101 * @throws SQLException 102 */ 103 public static ResultSet executeQuery(Connection conn,String sql,Object...parameters)throws SQLException 104 { 105 PreparedStatement ps=conn.prepareStatement(sql); 106 for(int i=0;i<parameters.length;i++) 107 { 108 ps.setObject(i+1, parameters[i]); 109 110 } 111 112 113 return ps.executeQuery(); 114 115 116 } 117 /** 118 * 执行sql语句更新操作 119 * @param sql 120 * @param parameters 121 * @return 122 * @throws SQLException 123 */ 124 public static int executeUpdate(String sql,Object...parameters)throws SQLException 125 { 126 Connection conn=null; 127 try 128 { 129 conn = createConnection(); 130 return executeUpdate(conn,sql,parameters); 131 } 132 finally 133 { 134 closeQuiety(conn); 135 } 136 137 } 138 public static ResultSet executeQuery(String sql,Object...parameters)throws SQLException 139 { 140 Connection conn =createConnection(); 141 142 return executeQuery(sql, parameters); 143 144 145 146 } 147 /** 148 * 关闭操作 149 * @param rs 150 */ 151 public static void closeAll(ResultSet rs) 152 { 153 Statement stmt =null; 154 Connection conn =null; 155 try 156 { 157 stmt=rs.getStatement(); 158 conn=stmt.getConnection(); 159 } 160 catch (SQLException e) 161 { 162 } 163 finally 164 { 165 JDBCGB.closeQuiety(rs); 166 JDBCGB.closeQuiety(stmt); 167 JDBCGB.closeQuiety(conn); 168 169 } 170 171 } 172 public static void closeQuiety(Statement stmt) 173 { 174 if(stmt!=null) 175 { 176 try 177 { 178 stmt.close(); 179 } 180 181 catch (SQLException e) 182 { 183 } 184 } 185 186 } 187 public static void closeQuiety(Connection conn) 188 { 189 if(conn!=null) 190 { 191 try 192 { 193 conn.close(); 194 } 195 catch (SQLException e) 196 { 197 } 198 } 199 } 200 201 public static void closeQuiety(ResultSet rs) 202 { 203 204 { 205 if(rs!=null) 206 { 207 try 208 { 209 rs.close(); 210 } 211 212 catch (SQLException e) 213 { 214 } 215 216 } 217 } 218 } 219 220 }
5.4JDBCUtils事务
事务有四大特性:原子性,隔离性,一致性,持久性
在这里只说到事务的原子性
原子性:要么全部提交成功 , 要么全部失败
Jdbc中需要用到的就是事务的原子性commit 和 rollback
提交和回滚操作
事务相关测试代码

1 public static void main(String [] args) 2 { 3 Connection conn = null; 4 ResultSet rs=null; 5 try 6 { 7 conn=JDBCGB.createConnection(); 8 conn.setAutoCommit(false); 9 JDBCGB.executeUpdate(conn, "Update t_abc set Amout=Amount-1000, where Number=‘0001"); 10 /* String s=null; 11 System.out.println(s.length());*/ 12 //如果在这里报错 则不会执行下一段代码 13 //这样整个就会出错 14 /* 15 * 原子性,一致性,隔离性,持久性 16 */ 17 JDBCGB.executeUpdate(conn, "Update t_abc set Amout=Amount+1000, where Number=‘0002"); 18 conn.commit(); 19 } 20 catch(SQLException e) 21 { 22 e.printStackTrace(); 23 conn.rollback(); 24 } 25 26 finally 27 { 28 JDBCGB.closeQuiety(conn); 29 30 31 } 32 }
如果抛出异常,一些常见的错误,则提交失败 事务回滚 。更新的数据也会从其中消失。常用于数据敏感的地方,比如银行系统等交易地方。
5.4addBatch批量提交
如果在事务中,想要一次性提交多组数据,则可以使用addBatch批量提交,它配合于事务的基本条件,一旦其中一步出现异常则数据全部回滚,不会修改数据库。
一次性向数据库提交多组数据 通常都是上千条数据一起插入

1 package com.scetc; 2 3 import java.sql.Connection; 4 import java.sql.PreparedStatement; 5 import java.sql.ResultSet; 6 import java.sql.SQLException; 7 import java.sql.Statement; 8 9 import javax.naming.spi.DirStateFactory.Result; 10 11 public class TEST5 12 { 13 public static void main(String [] args) 14 { 15 Connection conn = null; 16 ResultSet rs=null; 17 PreparedStatement ps=null; 18 try 19 { 20 ps = conn.prepareStatement("Insert into T _Persons(Name,Age,Gender) values(?,?,?)"); 21 long startMS = System.currentTimeMillis(); 22 for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) 23 { 24 ps.clearParameters(); 25 ps.setString(1, "xyf" + i); 26 ps.setInt(2, i); 27 ps.setBoolean(3, true); 28 ps.executeUpdate(); 29 } 30 long endMS = System.currentTimeMillis(); 31 System.out.println("耗时:" + (endMS - startMS)); 32 33 34 conn.commit(); 35 } 36 catch(SQLException e) 37 { 38 e.printStackTrace(); 39 40 } 41 42 finally 43 { 44 JDBCGB.closeQuiety(conn); 45 46 47 } 48 49 50 51 } 52 }
5.5last_insert获取刚插入的自增字段

1 Connection conn = null; 2 ResultSet rs = null; 3 try 4 { 5 conn = JdbcUtils.createConnection(); 6 JdbcUtils.executeUpdate(conn, "insert into t_users(UserName,Password) values(‘1‘,‘1‘)"); 7 rs = JdbcUtils.executeQuery(conn, "select last_insert_id() id"); 8 rs.next(); 9 long id = rs.getLong("id"); 10 System.out.println(id); 11 } 12 catch(SQLException ex) 13 { 14 15 } 16 finally 17 { 18 JdbcUtils.closeAll(rs); 19 }
2018-01-06 11:30:02

