本次实现数据的CRUD功能,数据依然以VO类形式进行数据接收。
一,建立Message.java类操作,负责数据的接收操作。
package com.SpringMVC.vo; public class Type { private String title; public String getTitle() { return title; } public void setTitle(String title) { this.title = title; } @Override public String toString() { return "Type [title=" + title + "]"; } }
和
package com.SpringMVC.vo; import java.io.Serializable; import java.util.Date; @SuppressWarnings("serial") public class Message implements Serializable{ private Integer mid; private String title; private Double price; private Date pubdate; private Type type; public Integer getMid() { return mid; } public void setMid(Integer mid) { this.mid = mid; } public String getTitle() { return title; } public void setTitle(String title) { this.title = title; } public Double getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(Double price) { this.price = price; } public Date getPubdate() { return pubdate; } public void setPubdate(Date pubdate) { this.pubdate = pubdate; } public Type getType() { return type; } public void setType(Type type) { this.type = type; } @Override public String toString() { return "Message [mid=" + mid + ", title=" + title + ", price=" + price + ", pubdate=" + pubdate + ", type=" + type + "]"; } }
2,定义Action。
范例:定义MessageAction
package com.SpringMVC.action; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import com.SpringMVC.vo.Message; @Controller //定义控制器 @RequestMapping("/pages/back/message/*") //整体访问路径 public class MessageAction { @RequestMapping("hello_demo") //为demo方法定义映射子路径 public void demo(Message msg) { System.out.println(msg); } }
下面由于第一次执行,可以直接利用地址重写方式传递所需要数据。
http://localhost:8080/SpringMVC/pages/back/message/hello_demo.action?mid=12&title=今日头条&price=8&type.title=天天新闻
后台服务器结果:
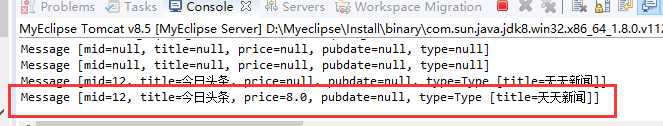
以上地址组成结构如下:
1,action的父路径:http://localhost:8080/SpringMVC/pages/back/message/
2,配置的方法路径:/hello_demo.action。
3,表示Message对象的组成:?mid=12&title=今日头条&price=8&type.title=天天新闻。
此时的代码最大特点是,控制器不需要编写类属性接收参数,所有的接收参数放到了处理的业务方法上。
同时避免了的实例化对象问题。
而整个操作过程中最为关键的问题是:传递的参数只需要传递属性名称即可。如果是引用的关系,则只需要按照“.”排列即可(如上面的type.title)。
在springMVC中还可以设置某一个业务方法的请求类型。如对之前的action进行修改:
package com.SpringMVC.action; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod; import com.SpringMVC.vo.Message; @Controller //定义控制器 @RequestMapping("/pages/back/message/*") //整体访问路径 public class MessageAction { @RequestMapping(value="hello_demo",method=RequestMethod.GET) //为demo方法定义映射子路径 public void demo(Message msg) { System.out.println(msg); } }
如果使用这种语法表示配置的方法只能使用get请求模式进行触发。也可以修改为post请求。
@Controller //定义控制器 @RequestMapping("/pages/back/message/*") //整体访问路径 public class MessageAction { @RequestMapping(value="hello_demo",method=RequestMethod.POST) //为demo方法定义映射子路径 public void demo(Message msg) { System.out.println(msg); } }
如果业务处理方法设置为POST请求,那么就表示只能怪由表单提交到此方法上。
如果某个业务操作方法,即支持POST,也可以支持GET,那么不要写RequestMethod。
对于返回值的处理,Spring MVC有一些要求,在正常开发中,往往会提供一共forword.jsp页面。这个页面的功能是进行操作功能完成后的信息提示。
范例:定义forword.jsp页面:
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%> <% String path = request.getContextPath(); String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/"; %> <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"> <html> <head> <base href="<%=basePath%>"> <title>My JSP ‘forword.jsp‘ starting page</title> <meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache"> <meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache"> <meta http-equiv="expires" content="0"> <meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3"> <meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page"> <!-- <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css"> --> </head> <body> <script type="text/javascript"> window.alert("${msg}"); window.location="<%=basePath%>${url}"; </script> </body> </html>

如果由一共控制器,跳转到forword.jsp页面,至少需要以下内容:
1,控制器需要知道forword.jsp页面的路径。
2,控制器需要传递若干个request属性(如上面的$(msg)和$(url))。
正因为如此,在springMVC中专门设计了一个类:ModelAndView,而这个类里面定义了如下操作方法:
1,构造方法:public ModelAndView()。
2,构造方法:public ModelAndView(String viewName),viewName,跳转的路径地址;
3,保存属性:public ModelAndView addObject(String attrivbuteName,Object attrivateValue) ;
范例:更好的处理跳转:
package com.SpringMVC.action; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod; import org.springframework.web.portlet.ModelAndView; import com.SpringMVC.vo.Message; @Controller //定义控制器 @RequestMapping("/pages/back/message/*") //整体访问路径 public class MessageAction { @RequestMapping(value="hello_demo") //为demo方法定义映射子路径 public ModelAndView demo(Message msg) { ModelAndView md=new ModelAndView("/Pages/forword.jsp"); md.addObject("msg","消息信息添加成功"); md.addObject("url","/index.jsp"); System.out.println(msg); return md; } }
这里通过ModelAndView ,跳转到forword.jsp页面,同时,给这个页面传递两个属性值,msg和url。
效果:
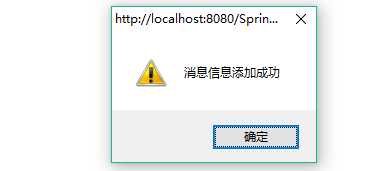
然后跳到了下一页

通过以上程序分析就可以总结出MVC设计的优势
1,避免了复杂的路径跳转的配置操作。
2,避免了项目中出现过多的“.”作为参数的情况。
