转:http://blog.csdn.net/spy19881201/article/details/5867721
https://www.cnblogs.com/hexiaochun/archive/2012/09/03/2668324.html
一、冒泡排序
- package sort.bubble;
- import java.util.Random;
- /**
- * 依次比较相邻的两个数,将小数放在前面,大数放在后面
- * 冒泡排序,具有稳定性
- * 时间复杂度为O(n^2)
- * 不及堆排序,快速排序O(nlogn,底数为2)
- * @author liangge
- *
- */
- public class Main {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Random ran = new Random();
- int[] sort = new int[10];
- for(int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++){
- sort[i] = ran.nextInt(50);
- }
- System.out.print("排序前的数组为");
- for(int i : sort){
- System.out.print(i+" ");
- }
- buddleSort(sort);
- System.out.println();
- System.out.print("排序后的数组为");
- for(int i : sort){
- System.out.print(i+" ");
- }
- }
- /**
- * 冒泡排序
- * @param sort
- */
- private static void buddleSort(int[] sort){
- for(int i=1;i<sort.length;i++){
- for(int j=0;j<sort.length-i;j++){
- if(sort[j]>sort[j+1]){
- int temp = sort[j+1];
- sort[j+1] = sort[j];
- sort[j] = temp;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
二、选择排序
- package sort.select;
- import java.util.Random;
- /**
- * 选择排序
- * 每一趟从待排序的数据元素中选出最小(或最大)的一个元素,
- * 顺序放在已排好序的数列的最后,直到全部待排序的数据元素排完。
- * 选择排序是不稳定的排序方法。
- * @author liangge
- *
- */
- public class Main {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Random ran = new Random();
- int[] sort = new int[10];
- for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
- sort[i] = ran.nextInt(50);
- }
- System.out.print("排序前的数组为");
- for (int i : sort) {
- System.out.print(i + " ");
- }
- selectSort(sort);
- System.out.println();
- System.out.print("排序后的数组为");
- for (int i : sort) {
- System.out.print(i + " ");
- }
- }
- /**
- * 选择排序
- * @param sort
- */
- private static void selectSort(int[] sort){
- for(int i =0;i<sort.length-1;i++){
- for(int j = i+1;j<sort.length;j++){
- if(sort[j]<sort[i]){
- int temp = sort[j];
- sort[j] = sort[i];
- sort[i] = temp;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
三、快速排序
1 package com.quick;
2
3 public class quick {
4 public void quick_sort(int[] arrays, int lenght) {
5 if (null == arrays || lenght < 1) {
6 System.out.println("input error!");
7 return;
8 }
9 _quick_sort(arrays, 0, lenght - 1);
10 }
11
12 public void _quick_sort(int[] arrays, int start, int end) {
13 if(start>=end){
14 return;
15 }
16
17 int i = start;
18 int j = end;
19 int value = arrays[i];
20 boolean flag = true;
21 while (i != j) {
22 if (flag) {
23 if (value > arrays[j]) {
24 swap(arrays, i, j);
25 flag=false;
26
27 } else {
28 j--;
29 }
30 }else{
31 if(value<arrays[i]){
32 swap(arrays, i, j);
33 flag=true;
34 }else{
35 i++;
36 }
37 }
38 }
39 snp(arrays);
40 _quick_sort(arrays, start, j-1);
41 _quick_sort(arrays, i+1, end);
42
43 }
44
45 public void snp(int[] arrays) {
46 for (int i = 0; i < arrays.length; i++) {
47 System.out.print(arrays[i] + " ");
48 }
49 System.out.println();
50 }
51
52 private void swap(int[] arrays, int i, int j) {
53 int temp;
54 temp = arrays[i];
55 arrays[i] = arrays[j];
56 arrays[j] = temp;
57 }
58
59 public static void main(String args[]) {
60 quick q = new quick();
61 int[] a = { 49, 38, 65,12,45,5 };
62 q.quick_sort(a,6);
63 }
64
65 }
快速排序讲解
所谓的快速排序的思想就是,首先把数组的第一个数拿出来做为一个key,在前后分别设置一个i,j做为标识,然后拿这个key对这个数组从后面往前遍历,及j--,直到找到第一个小于这个key的那个数,然后交换这两个值,交换完成后,我们拿着这个key要从i往后遍历了,及i++;一直循环到i=j结束,当这里结束后,我们会发现大于这个key的值都会跑到这个key的后面,不是的话就可能你写错了,小于这个key的就会跑到这个值的前面;然后我们对这个分段的数组再时行递归调用就可以完成整个数组的排序。
用图形法表示由下:
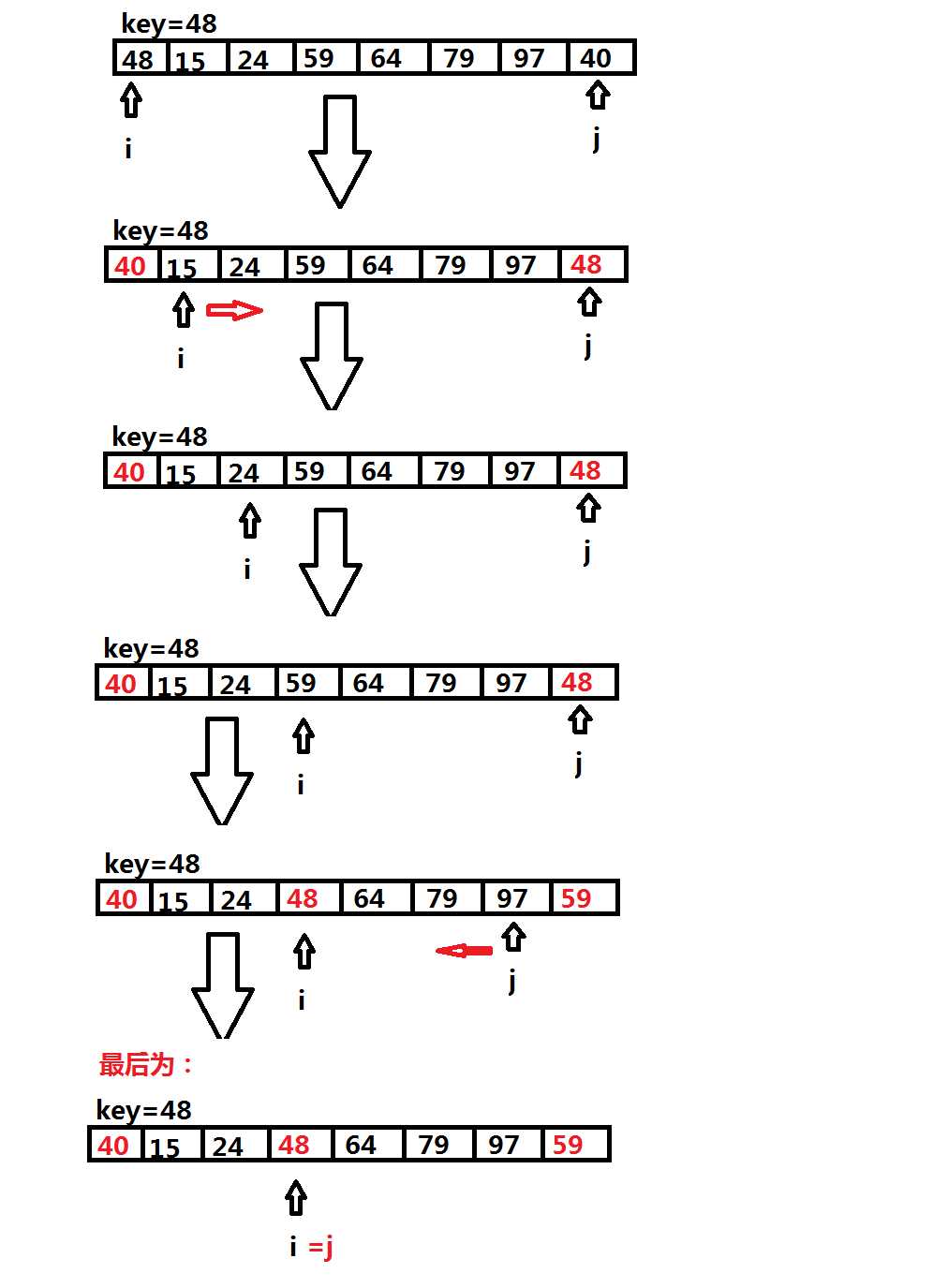
这样就以key分为了两个段,我们把这两个段再递进去就可以解决问题了
