目录讲解:
一、服务提供者与服务消费者的概念
二、编写一个服务提供者的测试类(code)
1.1、 使用微服务构建的是分布式系统,微服务之间通过网络进行通信。我们使用微服务提供者与服务消费者来描述微服务之间的调用关系。
如下:

在生活中就有这样的例子,在我们看电影的时候,用户发起一个购票的请求。在进行购票的业务操作前,电影微服务需要调用用户微服务的接口,
查询当前用户的余额是多少,是不是符合购票标准等等。在这种场景下,用户微服务就是一个服务提供者,电影微服务则是一个服务消费者。

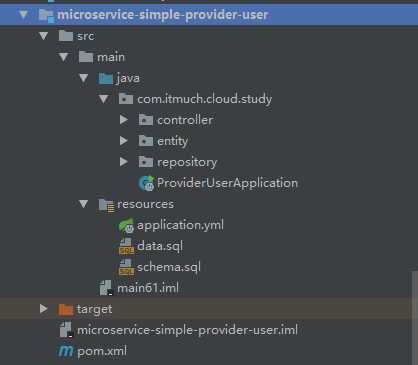
2.2 编写一个服务提供者
框架结构如下:
步骤:
2.1 创建一个maven项目,架构如上,pom.xml的内容如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.itmuch.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>microservice-simple-provider-user</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>jar</packaging> <!-- 引入spring boot的依赖 --> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>1.4.3.RELEASE</version> </parent> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <java.version>1.8</java.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.h2database</groupId> <artifactId>h2</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies> <!-- 引入spring cloud的依赖 --> <dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId> <version>Camden.SR4</version> <type>pom</type> <scope>import</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> </dependencyManagement> <!-- 添加spring-boot的maven插件 --> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
2.2 准备好建表语句
drop table user if exists; create table user (id bigint generated by default as identity, username varchar(40), name varchar(20), age int(3), balance decimal(10,2), primary key (id));
2.2 准备好几条语句
insert into user (id, username, name, age, balance) values (1, ‘account1‘, ‘张三‘, 20, 100.00); insert into user (id, username, name, age, balance) values (2, ‘account2‘, ‘李四‘, 28, 180.00); insert into user (id, username, name, age, balance) values (3, ‘account3‘, ‘王五‘, 32, 280.00);
2.3 准备实体类
package com.itmuch.cloud.study.entity;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
@Entity
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private Long id;
@Column
private String username;
@Column
private String name;
@Column
private Integer age;
@Column
private BigDecimal balance;
public Long getId() {
return this.id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return this.username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return this.age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public BigDecimal getBalance() {
return this.balance;
}
public void setBalance(BigDecimal balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
}
2.3 编写Dao类
2.3 编写controller类
package com.itmuch.cloud.study.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.itmuch.cloud.study.entity.User;
import com.itmuch.cloud.study.repository.UserRepository;
@RestController
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public User findById(@PathVariable Long id) {
User findOne = this.userRepository.findOne(id);
return findOne;
}
}
2.4 编写启动类
package com.itmuch.cloud.study;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class ProviderUserApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ProviderUserApplication.class, args);
}
}
2.5 编写配置文件
server:
port: 8000
spring:
jpa:
generate-ddl: false
show-sql: true
hibernate:
ddl-auto: none
datasource: # 指定数据源
platform: h2 # 指定数据源类型
schema: classpath:schema.sql # 指定h2数据库的建表脚本
data: classpath:data.sql # 指定h2数据库的数据脚本
logging: # 配置日志级别,让hibernate打印出执行的SQL
level:
root: INFO
org.hibernate: INFO
org.hibernate.type.descriptor.sql.BasicBinder: TRACE
org.hibernate.type.descriptor.sql.BasicExtractor: TRACE
## INFO
info:
app:
name: @project.artifactId@
encoding: @project.build.sourceEncoding@
java:
source: @java.version@
target: @java.version@
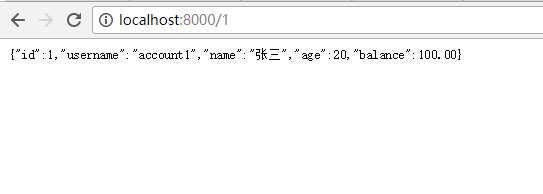
最后在浏览器里面输入:localhost:8000/1 看见了用户信息,则成功了
后续再为大家总结,有写的不周到的地方,欢迎大家提出来
