概述:
java中的io流主划分输入流和输出流;其中又各自分有字节流和字符流;两者的差别主要是在于读入/写出的单位大小不同;由于java采用的是GBK编码格式,因而一个字符占用2个字节,即字符流是16位,字节流是8位。还有一种划分就是:节点流和处理流;节点流:直接与数据源连接进行传输数据处理流:就是非直接,而是对节点流进行封装等使用(是一种比较好的方法)!!!!
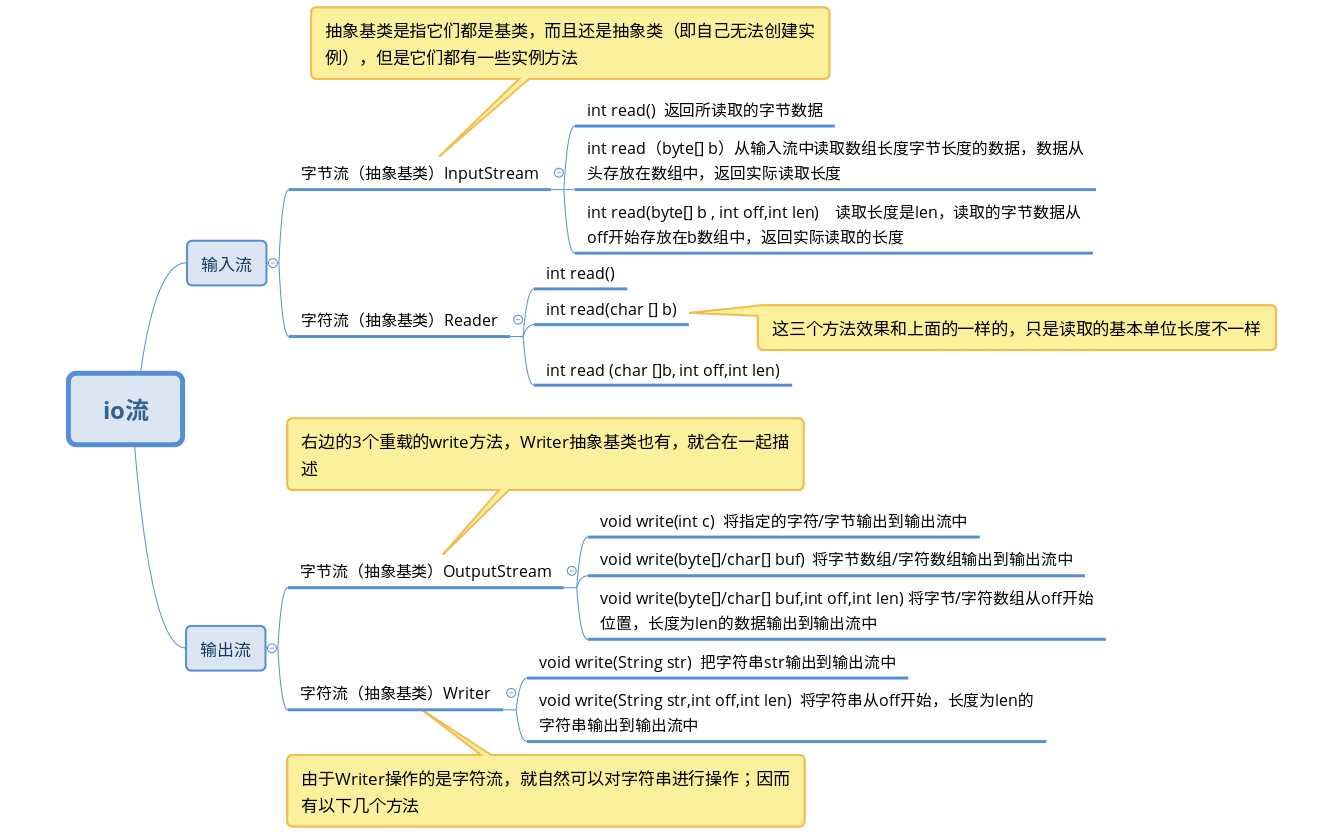
输入流有2个抽象基类:InputStream和Reader 输出流有2个抽象基类:OutputStream和Writer;其中,InputStream和OutputStream是属于字节流的8位Writer&Reader是属于字符流(2个字节 16位)
//检测InputStream流的read(byte[] b,int off,int len)方法
1 import java.io.*;
2
3 public class hellojava{
4 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
5 try{
6 FileInputStream fin1=new FileInputStream("/home/kylin/Desktop/操作PG数据库.txt");
7 byte []buf1=new byte[1024];
8 int HasRead1=0;
9 while((HasRead1=fin1.read(buf1,5,1019))>0){
10 System.out.println("HasRead1:"+HasRead1);
11 System.out.println(new String(buf1,5,HasRead1));
12 }
13 }
14 catch(IOException ex){
15 ex.printStackTrace();
16 }
17 }
18 }
//使用try catch会自动的调用 close(),而调用close()又会自动的调用flush();所以使用try catch方式可以自动的关闭IO流
// read(buf,off,len) 这里的len长度最大值一定是要小于 buf.length-off
//注意:由于java采取的是GBK编码,因而在读取的长度的设置(数组长度的设置上)要尽可能的大一些,不然可能会因为长度不够而乱码
//检测 Reader抽象基类中的read(char []b,int off,int len)方法;和上述方法的效果是差不多一致的
1 import java.io.*;
2
3 public class hellojava{
4 public static void main(String[] args)throws IOException {
5 try{
6 FileReader fin=new FileReader("/home/qilin/Desktop/操作PG数据库.txt");
7 int HasRead=0;
8 char []buf=new char[1024];
9 while((HasRead=fin.read(buf,5,100))>0){
10 System.out.println("HasRead:"+HasRead);
11 System.out.println(new String(buf, 5,HasRead));
12 }
13 }
14 catch(IOException ex){
15 ex.printStackTrace();
16 }
17 }
18 }
1 import java.io.*;
2
3 //尝试把文件A中的数据读取,然后写入到另外一个文件B中
4 public class hellojava{
5 public static void main(String[] args) {
6 try{
7 FileInputStream fin=new FileInputStream("/home/qilin/Desktop/操作PG数据库.txt");
8 FileOutputStream fout=new FileOutputStream("/home/qilin/Desktop/hello1.txt");
9 int hasRead=0;
10 byte []buf=new byte[1024];
11 //写入到buf数组中
12 while((hasRead=fin.read(buf))>0){
13 //从buf数组中输出到hello1.txt文件中
14 fout.write(buf, 0, hasRead);
15 }
16 }
17 catch(IOException ex){
18 ex.printStackTrace();
19 }
20
21 }
22 }
import java.io.*;
//当我没有清空缓冲区、和关闭流的时候,即使可以运行;但是并不会写到文件中!
//使用 try catch 也不会写入到文件中,只有当自己显式的清空缓冲区和关闭流才会成功写入;难道写的时候调用try catch不会关闭流??
//测试使用Writer的write,把字符串写入到文件中
public class hellojava{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileWriter fw=new FileWriter("/home/qilin/Desktop/hello3.txt");
fw.write("大家好\n");
// fw.write("新年快乐\n",0,6); 抛出异常,因为实际并没这么长
fw.write("新年快乐", 2, 2);
fw.flush(); //缓冲区写到物理节点
fw.close(); //关闭
}
}
//看来还是自己手动来关闭吧~
