了解.net mvc实现原理ActionResult/View
- Action的传参过程
- ActionResult
- IView / IViewEngine / ViewEngineCollection / ViewEngineResult
AuthorizationContext authContext = InvokeAuthorizationFilters(controllerContext, filterInfo.AuthorizationFilters, actionDescriptor);
ActionExecutedContext postActionContext = InvokeActionMethodWithFilters(controllerContext, filterInfo.ActionFilters, actionDescriptor, parameters);
ExceptionContext exceptionContext = InvokeExceptionFilters(controllerContext, filterInfo.ExceptionFilters, ex);
 View Code
View Code View Code
View Code View Code
View Code View Code
View Code View Code
View Code View Code
View Code View Code
View Code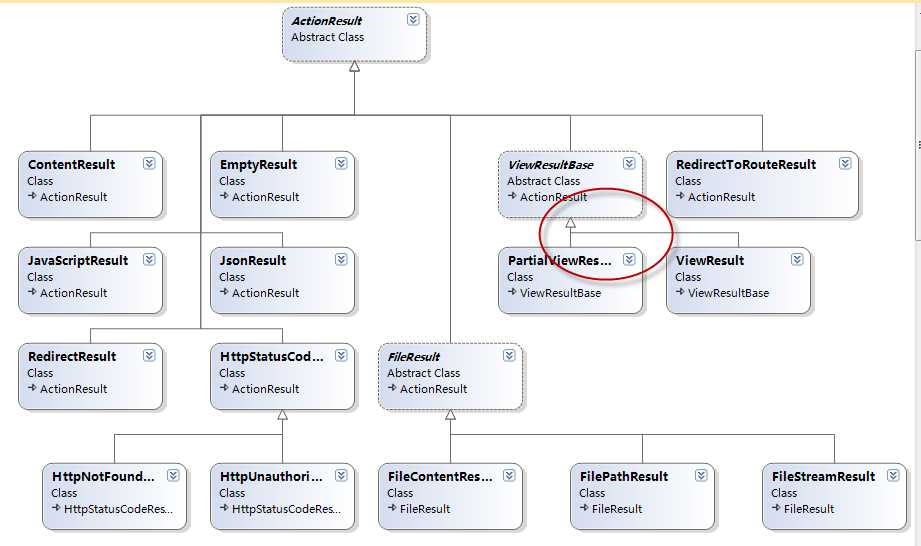
| 类名 | 抽象类 | 父类 | 功能 |
| ActionResult | abstract | Object | 顶层父类 |
| ContentResult | 根据内容的类型和编码,数据内容.通过Controller的Content方法返回 | ||
| EmptyResult | 返回空结果 | ||
| FileResult | abstract | 写入文件内容,具体的写入方式在派生类中. | |
| FileContentResult | FileResult | 通过 文件byte[] 写入Response 返回客户端,Controller的File方法 | |
| FilePathResult | FileResult | 通过 文件路径 写入Response 返回客户端,Controller的File方法 | |
| FileStreamResult | FileResult | 通过 Stream 写入Response 返回客户端,Controller的File方法 | |
| HttpUnauthorizedResult | 抛出401错误 | ||
| JavaScriptResult | 返回javascript文件 | ||
| JsonResult | 返回Json格式的数据 | ||
| RedirectResult | 使用Response.Redirect重定向页面 | ||
| RedirectToRouteResult | 根据Route规则重定向页面 | ||
| ViewResultBase | abstract | 调用IView.Render() 返回视图,两个常用属性ViewData,TempData | |
| PartialViewResult | ViewResultBase | 调用父类ViewResultBase 的ExecuteResult方法. 重写了父类的FindView方法. 寻找用户控件.ascx文件 |
|
| ViewResult | ViewResultBase |
调用父类ViewResultBase 的ExecuteResult方法. Controller的View()方法默认封装ViewResult返回结果 |
 View Code
View Code View Code
View Code View Code
View Code View Code
View Code View Code
View Code- IView 作用:展示View对象, 将页面读成流通过Writer写入Response中返回客户端,主要方法Render用来绘制DOM对象到流中。
- IViewEngine 作用:查找View对象(视图页面,例如aspx页面),但是返回结果是ViewEngineResult ,View被保存其中。主要方法FindView,FindPartialView。
- ViewEngineCollection 作用:视图引擎集合
- ViewEngineResult 作用:是IViewEngine查找View的结果
实现过程:当ViewResult执行ExecuteResult时会遍历ViewEngineCollection中所有IViewEngine 引擎,并调用每个IViewEngine 引擎的FindView,如果找到具体的View页面,则返回ViewEngineResult,ViewEngineResult包含了相关的IView信息,最后再调用IView的Render输出视图。
 View Code
View Code View Code
View Code View Code
View Code View Code
View Code书再接回上文Filter和Action的执行 ,当Action方法被执行,返回了一个ActionResult之后,紧接着就要执行ActionResult了,当然还有Filter需要执行,这些都是发生在ControllerActionInvoker的InvokeActionResultWithFilters方法之中,这里面filter的执行和action方法被执行的时候执行相应的filter是一样的,已在Filter和Action的执行 中分析过了,不再讨论。直接看ActionResult的执行:
protected virtual void InvokeActionResult(ControllerContext controllerContext, ActionResult actionResult) {
actionResult.ExecuteResult(controllerContext);
}
当然这个方法没什么好看的,这是ActionResult的一个抽象方法。先看下ASP.NET MVC 3中继承自ActionResult的类:
System.Web.Mvc.ContentResult
System.Web.Mvc.EmptyResult
System.Web.Mvc.FileResult
System.Web.Mvc.HttpStatusCodeResult
System.Web.Mvc.JavaScriptResult
System.Web.Mvc.JsonResult
System.Web.Mvc.RedirectResult
System.Web.Mvc.RedirectToRouteResult
System.Web.Mvc.ViewResultBase
其中ViewResultBase是最常用的,它还有两个继承者:
System.Web.Mvc.PartialViewResult
System.Web.Mvc.ViewResult
本文先重点看下ViewResult这个最常用的ActionResult。它的ExecuteResult方法如下:
public override void ExecuteResult(ControllerContext context) {
if (context == null) {
throw new ArgumentNullException("context");
}
if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(ViewName)) {
ViewName = context.RouteData.GetRequiredString("action");
}
ViewEngineResult result = null;
if (View == null) {
result = FindView(context);
View = result.View;
}
TextWriter writer = context.HttpContext.Response.Output;
ViewContext viewContext = new ViewContext(context, View, ViewData, TempData, writer);
View.Render(viewContext, writer);
if (result != null) {
result.ViewEngine.ReleaseView(context, View);
}
}
首先如果没有提供View的名字的话就默认是action的名字,然后调用FindView去查找对应的View:
protected override ViewEngineResult FindView(ControllerContext context) {
ViewEngineResult result = ViewEngineCollection.FindView(context, ViewName, MasterName);
if (result.View != null) {
return result;
}
// we need to generate an exception containing all the locations we searched
StringBuilder locationsText = new StringBuilder();
foreach (string location in result.SearchedLocations) {
locationsText.AppendLine();
locationsText.Append(location);
}
throw new InvalidOperationException(String.Format(CultureInfo.CurrentCulture,
MvcResources.Common_ViewNotFound, ViewName, locationsText));
}
这个方法实际上是调用了ViewEngineCollection中的对象的FindView方法,默认情况下ViewEngineCollection包括了如下对象:
new WebFormViewEngine(), new RazorViewEngine(),
先看下FindView返回的ViewEngineResult,这个类其实很简单,只是把一些对象组合在一起,一个构造函数是:
public ViewEngineResult(IView view, IViewEngine viewEngine)
表示用某个ViewEngine找到了某个IView,另一个构造函数是:
public ViewEngineResult(IEnumerable<string> searchedLocations)
表示没有找到的情况,这个时候就需要返回找过哪些地方,这些信息最终是被用于生成一个异常信息的。ViewEngineResult此处的设计似乎有一点别扭。接下来看RazorViewEngine 的FindView方法,RazorViewEngine是继承自BuildManagerViewEngine的,这个类又是继承自VirtualPathProviderViewEngine,看下VirtualPathProviderViewEngine的实现(有删节):
public virtual ViewEngineResult FindView(ControllerContext controllerContext, string viewName, string masterName, bool useCache) {
string[] viewLocationsSearched;
string[] masterLocationsSearched;
string controllerName = controllerContext.RouteData.GetRequiredString("controller");
string viewPath = GetPath(controllerContext, ViewLocationFormats, AreaViewLocationFormats, "ViewLocationFormats", viewName, controllerName, _cacheKeyPrefix_View, useCache, out viewLocationsSearched);
string masterPath = GetPath(controllerContext, MasterLocationFormats, AreaMasterLocationFormats, "MasterLocationFormats", masterName, controllerName, _cacheKeyPrefix_Master, useCache, out masterLocationsSearched);
if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(viewPath) || (String.IsNullOrEmpty(masterPath) && !String.IsNullOrEmpty(masterName))) {
return new ViewEngineResult(viewLocationsSearched.Union(masterLocationsSearched));
}
return new ViewEngineResult(CreateView(controllerContext, viewPath, masterPath), this);
}
找到View的过程本质上是找到View文件的路径,因此调用了GetPath方法来查找view的位置,看下这边的xxxLocationFormats,这是定义在RazorViewEngine的构造函数中的:
AreaViewLocationFormats = new[] {
"~/Areas/{2}/Views/{1}/{0}.cshtml",
"~/Areas/{2}/Views/{1}/{0}.vbhtml",
"~/Areas/{2}/Views/Shared/{0}.cshtml",
"~/Areas/{2}/Views/Shared/{0}.vbhtml"
};
AreaMasterLocationFormats = new[] {
"~/Areas/{2}/Views/{1}/{0}.cshtml",
"~/Areas/{2}/Views/{1}/{0}.vbhtml",
"~/Areas/{2}/Views/Shared/{0}.cshtml",
"~/Areas/{2}/Views/Shared/{0}.vbhtml"
};
AreaPartialViewLocationFormats = new[] {
"~/Areas/{2}/Views/{1}/{0}.cshtml",
"~/Areas/{2}/Views/{1}/{0}.vbhtml",
"~/Areas/{2}/Views/Shared/{0}.cshtml",
"~/Areas/{2}/Views/Shared/{0}.vbhtml"
};
ViewLocationFormats = new[] {
"~/Views/{1}/{0}.cshtml",
"~/Views/{1}/{0}.vbhtml",
"~/Views/Shared/{0}.cshtml",
"~/Views/Shared/{0}.vbhtml"
};
MasterLocationFormats = new[] {
"~/Views/{1}/{0}.cshtml",
"~/Views/{1}/{0}.vbhtml",
"~/Views/Shared/{0}.cshtml",
"~/Views/Shared/{0}.vbhtml"
};
PartialViewLocationFormats = new[] {
"~/Views/{1}/{0}.cshtml",
"~/Views/{1}/{0}.vbhtml",
"~/Views/Shared/{0}.cshtml",
"~/Views/Shared/{0}.vbhtml"
};
FileExtensions = new[] {
"cshtml",
"vbhtml",
};
这些字符串定义了一个Mvc项目文件夹的布局,RazorViewEngine将按照上面的路径依次去寻找view文件。看GetPath方法(有删节):
private string GetPath(ControllerContext controllerContext, string[] locations, string[] areaLocations, string locationsPropertyName, string name, string controllerName, string cacheKeyPrefix, bool useCache, out string[] searchedLocations) {
string areaName = AreaHelpers.GetAreaName(controllerContext.RouteData);
bool usingAreas = !String.IsNullOrEmpty(areaName);
List<ViewLocation> viewLocations = GetViewLocations(locations, (usingAreas) ? areaLocations : null);
bool nameRepresentsPath = IsSpecificPath(name);
string cacheKey = CreateCacheKey(cacheKeyPrefix, name, (nameRepresentsPath) ? String.Empty : controllerName, areaName);
if (useCache) {
return ViewLocationCache.GetViewLocation(controllerContext.HttpContext, cacheKey);
}
return (nameRepresentsPath) ?
GetPathFromSpecificName(controllerContext, name, cacheKey, ref searchedLocations) :
GetPathFromGeneralName(controllerContext, viewLocations, name, controllerName, areaName, cacheKey, ref searchedLocations);
}
首先判断当前请求是否位于一个area中,然后获得View的位置:
private static List<ViewLocation> GetViewLocations(string[] viewLocationFormats, string[] areaViewLocationFormats) {
List<ViewLocation> allLocations = new List<ViewLocation>();
if (areaViewLocationFormats != null) {
foreach (string areaViewLocationFormat in areaViewLocationFormats) {
allLocations.Add(new AreaAwareViewLocation(areaViewLocationFormat));
}
}
if (viewLocationFormats != null) {
foreach (string viewLocationFormat in viewLocationFormats) {
allLocations.Add(new ViewLocation(viewLocationFormat));
}
}
return allLocations;
}
接下来是访问缓存来找物理路径,不分析其缓存的实现,看实际获取路径的方法,首先nameRepresentsPath这个布尔量的含义:
private static bool IsSpecificPath(string name) {
char c = name[0];
return (c == ‘~‘ || c == ‘/‘);
}
其实就是看这个location是不是一个绝对路径。用razor engine的默认方式的话,这里传进来的name是view name,应该永远都是false的。另一种情况应该是路由到一个具体的文件的时候会发生(猜测,待确认)。因此,接下来会执行GetPathFromGeneralName:
private string GetPathFromGeneralName(ControllerContext controllerContext, List<ViewLocation> locations, string name, string controllerName, string areaName, string cacheKey, ref string[] searchedLocations) {
string result = String.Empty;
searchedLocations = new string[locations.Count];
for (int i = 0; i < locations.Count; i++) {
ViewLocation location = locations[i];
string virtualPath = location.Format(name, controllerName, areaName);
if (FileExists(controllerContext, virtualPath)) {
searchedLocations = _emptyLocations;
result = virtualPath;
ViewLocationCache.InsertViewLocation(controllerContext.HttpContext, cacheKey, result);
break;
}
searchedLocations[i] = virtualPath;
}
return result;
}
这个方法其实比较简单,就是依次调用刚才准备好的ViewLocation,利用Format方法将路径格式转化为真正的路径,例如ViewLocation的Format方法如下:
public virtual string Format(string viewName, string controllerName, string areaName) {
return String.Format(CultureInfo.InvariantCulture, _virtualPathFormatString, viewName, controllerName);
}
然后判断虚拟路径上的文件是否存在。这个工作最终是由BuilderManager这个类完成的。BuilderManager是ASP.NET的组成部分,其具体实现就不分析了。如果文件存在则返回。
return new ViewEngineResult(CreateView(controllerContext, viewPath, masterPath), this);
这里的CreateView方法是RazorViewEngine中定义的:
protected override IView CreateView(ControllerContext controllerContext, string viewPath, string masterPath) {
var view = new RazorView(controllerContext, viewPath,
layoutPath: masterPath, runViewStartPages: true, viewStartFileExtensions: FileExtensions, viewPageActivator: ViewPageActivator);
return view;
}
至此,RazorViewEngine的工作就完成,它找到并返回了一个IView对象:RazorView。
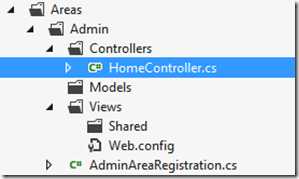
注意到在这个实现中,viewLocation实际上包括了area location和view location。也就是如果一个在area中action方法返回view之后,在查找view文件的过程中,如果在area对应的地方没有找到,那么它还会到普通view的地方去找。例如如下的文件夹结构:
在Admin中的HomeController里面直接return View(),但是在这个Area的View里并没有Index.cshtml,因此它最终找到的view是全局的View下面的Index.cshtml。个人觉得这种设计有点不符合直觉,area中的action就应该局限于area中查找view。
接下来就会调用Render方法,对于RazorView来说,这个方法是定义在它的基类BuildManagerCompiledView中的:
public void Render(ViewContext viewContext, TextWriter writer) {
if (viewContext == null) {
throw new ArgumentNullException("viewContext");
}
object instance = null;
Type type = BuildManager.GetCompiledType(ViewPath);
if (type != null) {
instance = _viewPageActivator.Create(_controllerContext, type);
}
if (instance == null) {
throw new InvalidOperationException(
String.Format(
CultureInfo.CurrentCulture,
MvcResources.CshtmlView_ViewCouldNotBeCreated,
ViewPath
)
);
}
RenderView(viewContext, writer, instance);
}
首先获得View的type,这里也是通过BuildManger来完成的,每个cshtml都会被asp.net编译成一个类。这些自动生成的类文件通常在 C:\Users\[User Name]\AppData\Local\Temp\Temporary ASP.NET Files 目录下面,这些文件都放在哈希过的目录之中,比较难找。根据这篇文档,临时文件存放在哪里是可以通过web.config配置的:
<compilation debug="true" targetFramework="4.5" tempDirectory="F:/Project/tempASP"/>
找到对应的cs文件之后,可以看到生成的类是类似:
public class _Page_Views_home_Index_cshtml : System.Web.Mvc.WebViewPage<dynamic>
这样的。如果是强类型的View,就应该是WebViewPage<T>了。找到类型后,会调用一个activator的Create方法来创建实例,这里采用了依赖注入的手法,但是在默认情况下,也只是调用反射来创建一个实例而已,在Mvc框架中,这种地方已经出现多次了。创建好了WebViewPage之后,就调用RenderView方法,这个方法是在RazorView中实现的:
protected override void RenderView(ViewContext viewContext, TextWriter writer, object instance) {
// An overriden master layout might have been specified when the ViewActionResult got returned.
// We need to hold on to it so that we can set it on the inner page once it has executed.
webViewPage.OverridenLayoutPath = LayoutPath;
webViewPage.VirtualPath = ViewPath;
webViewPage.ViewContext = viewContext;
webViewPage.ViewData = viewContext.ViewData;
webViewPage.InitHelpers();
WebPageRenderingBase startPage = null;
if (RunViewStartPages) {
startPage = StartPageLookup(webViewPage, RazorViewEngine.ViewStartFileName, ViewStartFileExtensions);
}
webViewPage.ExecutePageHierarchy(new WebPageContext(context: viewContext.HttpContext, page: null, model: null), writer, startPage);
}
渲染View仍然是一个非常复杂的过程。MVC3之中引入了viewStart页面的概念,这是一个在所有view被render之前都会被执行的页面,所以首先执行了一个StartPageLookup方法来查找viewStart页面。先看后两个参数,
internal static readonly string ViewStartFileName = "_ViewStart";
在这里定义了viewStart页面是以_ViewStart为文件名的文件。这个方法实际上是定义在StartPage类中的(有删节):
public static WebPageRenderingBase GetStartPage(WebPageRenderingBase page, string fileName, IEnumerable<string> supportedExtensions) {
// Build up a list of pages to execute, such as one of the following:
// ~/somepage.cshtml
// ~/_pageStart.cshtml --> ~/somepage.cshtml
// ~/_pageStart.cshtml --> ~/sub/_pageStart.cshtml --> ~/sub/somepage.cshtml
WebPageRenderingBase currentPage = page;
var pageDirectory = VirtualPathUtility.GetDirectory(page.VirtualPath);
// Start with the requested page‘s directory, find the init page,
// and then traverse up the hierarchy to find init pages all the
// way up to the root of the app.
while (!String.IsNullOrEmpty(pageDirectory) && pageDirectory != "/" && Util.IsWithinAppRoot(pageDirectory)) {
// Go through the list of support extensions
foreach (var extension in supportedExtensions) {
var path = VirtualPathUtility.Combine(pageDirectory, fileName + "." + extension);
if (currentPage.FileExists(path, useCache: true)) {
var factory = currentPage.GetObjectFactory(path);
var parentStartPage = (StartPage)factory();
parentStartPage.VirtualPath = path;
parentStartPage.ChildPage = currentPage;
currentPage = parentStartPage;
break;
}
}
pageDirectory = currentPage.GetDirectory(pageDirectory);
}
// At this point ‘currentPage‘ is the root-most StartPage (if there were
// any StartPages at all) or it is the requested page itself.
return currentPage;
}
结合注释,应该可以看明白这代码的查找规则,首先从当前View所在的目录开始,依次往上层搜索_ViewStart.cshtml(vbhtml)的文件,如果找到了就获得其类型,并且设置上一个找到的ViewStart页面为其ChildPage(最初的ViewStart页面的ChildPage就是当前View)。
找到了ViewStart之后,接下来就执行ExecutePageHierachy这个方法来渲染View,这个方法里面要完成相当多的工作,主要是ViewStart的执行,和Layout的执行。这里的困难之处在于对于有Layout的页面来说,Layout的内容是先输出的,然后是RenderBody内的内容,最后还是Layout的内容。如果仅仅是这样的话,只要初始化一个TextWriter,按部就班的往里面写东西就可以了,但是实际上,Layout并不能首先执行,而应该是View的代码先执行,这样的话View就有可能进行必要的初始化,供Layout使用。例如我们有如下的一个View:
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Code in View";
Layout = "_LayoutPage1.cshtml";
}
再看如下的Layout:
@{
Layout = "~/Views/Shared/_Layout.cshtml";
ViewBag.ToView = "Data from Layout";
}
<div>
Data In View: @ViewBag.Title
</div>
<div>
@RenderBody();
</div>
这样可以在页面显示Code in View字样。 但是反过来,如果试图在View中显示在Layout里面的"Data from Layout" 则是行不通的,什么也不会被显示。所以RenderBody是先于Layout中其他代码执行的,这种Layout的结构称为 Page Hierachy。在这样的代码执行顺序下,还要实现文本输出的顺序,因此asp.net mvc这里的实现中就使用了栈,这个栈是OutputStack,里面压入了TextWriter。注意到这只是一个页面的处理过程,一个页面之中还会有Partial View 和 Action等,这些的处理方式都是一样的,因此还需要一个栈来记录处理到了哪个(子)页面,因此还有一个栈,称之为TemplateStack,里面压入的是PageContext,PageContext维护了view的必要信息,比如Model之类的,当然也包括上面提到的OutputStack。有了上面的基本信息,下面看代码,先看入口点:
// This method is only used by WebPageBase to allow passing in the view context and writer.
public void ExecutePageHierarchy(WebPageContext pageContext, TextWriter writer, WebPageRenderingBase startPage) {
PushContext(pageContext, writer);
if (startPage != null) {
if (startPage != this) {
var startPageContext = Util.CreateNestedPageContext<object>(parentContext: pageContext, pageData: null, model: null, isLayoutPage: false);
startPageContext.Page = startPage;
startPage.PageContext = startPageContext;
}
startPage.ExecutePageHierarchy();
}
else {
ExecutePageHierarchy();
}
PopContext();
}
首先就是pageContext入栈:
public void PushContext(WebPageContext pageContext, TextWriter writer) {
_currentWriter = writer;
PageContext = pageContext;
pageContext.Page = this;
InitializePage();
// Create a temporary writer
_tempWriter = new StringWriter(CultureInfo.InvariantCulture);
// Render the page into it
OutputStack.Push(_tempWriter);
SectionWritersStack.Push(new Dictionary<string, SectionWriter>(StringComparer.OrdinalIgnoreCase));
// If the body is defined in the ViewData, remove it and store it on the instance
// so that it won‘t affect rendering of partial pages when they call VerifyRenderedBodyOrSections
if (PageContext.BodyAction != null) {
_body = PageContext.BodyAction;
PageContext.BodyAction = null;
}
}
然后区分了是否有ViewStart文件,如果有,就执行startPage.ExecutePageHierachy(),先看这个方法,
public override void ExecutePageHierarchy() {
// Push the current pagestart on the stack.
TemplateStack.Push(Context, this);
try {
// Execute the developer-written code of the InitPage
Execute();
// If the child page wasn‘t explicitly run by the developer of the InitPage, then run it now.
// The child page is either the next InitPage, or the final WebPage.
if (!RunPageCalled) {
RunPage();
}
}
finally {
TemplateStack.Pop(Context);
}
}
这个方法比较简单,而且这部分的代码注释都比较多,还是比较好理解的。第一步就是把当前的httpcontext压栈,然后执行_ViewStart中的代码,所以在所有的view的组成部分中,_ViewStart代码是最先执行的,然后执行RunPage:
public void RunPage() {
RunPageCalled = true;
ChildPage.ExecutePageHierarchy();
}
这就让它的“子页面”开始执行。如果页面没启用ViewStart,那么在ExecutePageHierarchy(WebPageContext pageContext, TextWriter writer, WebPageRenderingBasestartPage)中,直接就是执行的ExecutePageHierachy方法,下面来看这个方法:
public override void ExecutePageHierarchy() {
// Change the Writer so that things like Html.BeginForm work correctly
ViewContext.Writer = Output;
base.ExecutePageHierarchy();
// Overwrite LayoutPage so that returning a view with a custom master page works.
if (!String.IsNullOrEmpty(OverridenLayoutPath)) {
Layout = OverridenLayoutPath;
}
}
再看base.ExecutePageHierachy,这是一个定义在WebPageBase类中的方法(有删节):
public override void ExecutePageHierarchy() {
// Unlike InitPages, for a WebPage there is no hierarchy - it is always
// the last file to execute in the chain. There can still be layout pages
// and partial pages, but they are never part of the hierarchy.
TemplateStack.Push(Context, this);
try {
// Execute the developer-written code of the WebPage
Execute();
}
finally {
TemplateStack.Pop(Context);
}
}
这个方法就是将context压栈,然后执行相应的view的代码,然后出栈。有了这些出入栈的操作,可以保证View的代码,也就是Execute的时候的writer是正确的。Execute中的方法除去PartialView, Action之类的,最终调用的是WebPageBase中的
public override void WriteLiteral(object value) {
Output.Write(value);
}
这里的Output是:
public TextWriter Output {
get {
return OutputStack.Peek();
}
}
页面渲染的过程包括了两层的间接递归,还是比较复杂的,需要仔细体会。
至此,本系列已经分析完成了整个ASP.NET页面的生命周期。接下来还将看几个重要的部分,model验证,model template,和一些重要的html helper方法,最后还有asp.net mvc的扩展性。
https://www.cnblogs.com/yinzixin/archive/2012/12/05/2799459.html