一、字符的操作、拼接等
1.1、字符的操作
1 #Author:W.x 2 name="wxerx {a} name is {b}" 3 names="A,B,C,D,E,F,G" 4 print(names.capitalize()) 5 print(name.capitalize()) #capitalize()首字母大写,剩余都小写 6 print(name.count("x")) #count("x")统计 7 print(name.center(4,"*")) #center(50,"_")打印50个字符,输出居中显示 8 print(name.endswith("xx")) #判断以什么结尾 输出bool值 9 print(name.find("r")) #name.find("r")取出字符的下标 10 print(name.format(a="my",b="wx")) #格式化 11 print(name.format_map({"a":"my","b":"wx"})) #.format_map()载入字典 12 print(name.index("x")) #取出索引值 13 print(name.isalnum()) #判断是否为纯阿拉伯数字或字母,输出bool值 14 print(name.isdigit()) #判断是否一个整数 15 print(‘--‘,name.isidentifier())# 判断是否一个合法的标识符 16 print(name.isnumeric()) 17 print("M B Y".istitle()) #判读是否一个标题 18 a=[1,2,3] 19 print("/".join([‘1‘,‘2‘,‘3‘])) #连接符 20 print(name.ljust(100,"*")) #ljust(100,"*") 长100,不够后边补* 21 print(name.rjust(100,"*")) #rjust(100,"*") 长100,不够前边补* 22 print("---ii".upper()) #小写变大写 23 print("MM".lower()) #大写变小写 24 print("\nxxx".lstrip()) #strip去掉空格和回车,lstrip从左边去 25 print("xxx\n".rstrip()) #去掉右边空格和回车 26 print(" xxx\n".strip()) #strip去掉空格和回车 27 print("----") 28 w_=str.maketrans("qwdxa","12@$%") 29 print("wx ed".translate(w_)) #一块儿使用,比如说密码加密 30 print(w_) 31 print("wx".replace(‘w‘,‘e‘)) #替换字符 32 print("wqwerty".rfind("y")) #查找字符,输出索引值 33 print("qwe wdd,dsdsd".split("w")) #把字符串按照空格或字符或,分割成一个列表 34 print("qwe\nsasaa".splitlines()) #按照换行符来分割 35 print("QWERT,qwert".swapcase()) #大小写替换 36 print("qwe,sdsdf,fg".title()) #变成标题 37 print("qwe".zfill(10)) #补位
1.2、字符串的拼接
1 ‘‘‘ 2 print("---请输入你的姓名和密码---") 3 username=input("username:") 4 password=input("password:") 5 print(username,password) 6 ‘‘‘ 7 #python2里的raw_input和python3里一样 8 print("---请输入员工信息employee information---") 9 name=input("name:") 10 age=int(input("age:")) 11 job=input("job:") 12 salary=int(input("salary:")) 13 #字符串的拼接‘‘‘+....+‘‘‘ 14 ‘‘‘ 15 em_information=‘‘‘ 16 em_name:‘‘‘+name+‘‘‘ 17 em_age:‘‘‘+age+‘‘‘ 18 em_job:‘‘‘+job+‘‘‘ 19 em_salary:‘‘‘+salary+‘‘‘ 20 ‘‘‘ 21 print(em_information) 22 ‘‘‘ 23 #第2种方法采用%s格式化输出 24 #eg:%s,表示格化式一个对象为字符 比如: "Hello, %s"%"world" => "Hello, world" 这个一般用在格式化输出上 25 #%f 表示格式化一个对象为浮点型 26 em_information1=‘‘‘ 27 em_name1:%s 28 em_age1:%d 29 em_job1:%s 30 em_salary:%d 31 ‘‘‘%(name,age,job,salary) 32 print(type(name,),type(age)) #打印输出变量类型 33 print("em_information1:",em_information1) 34 #第3种方法,采用format() 35 em_information2=‘‘‘ 36 em_name2={_name} 37 em_age2={_age} 38 em_job2={_job} 39 em_salary2={_salary} 40 ‘‘‘.format(_name=name, 41 _age=age, 42 _job=job, 43 _salary=salary) 44 print(em_information2) 45 #第4种方法,format()的另外一种用法 46 em_information3=‘‘‘ 47 em_name3={0} 48 em_age3={1} 49 em_job3={2} 50 em_salary3={3} 51 ‘‘‘.format(name,age,job,salary) 52 print("em_information3:",em_information3)
二、循环(for,while)
2.1、while循环
1 #Author:W.x 2 i=0 #定义一个计数变量,初始化为0 3 number=10 4 while i<3: 5 gusse=input("your gussed:") #输入值 6 if gusse.isdigit(): #判断用户输入的是否为纯数字 如果是的执行循环体 7 gusse=int(gusse) #转换成整型 8 if gusse==number: #比较 9 print("You are right!") 10 break 11 elif gusse>number: 12 print("Wrong,too big!") 13 else: 14 print("Wrong,too small!") 15 i+=1 16 else: #如果不是纯数字,提醒用户再次输入 17 print("You are not entering numbers,please enter agin") 18 else: 19 print("----Sorry!Game Over----")
2.2、for循环
1 number=10
2 for j in range(3):
3 gusse=input("your gussed:")
4 if gusse.isdigit():
5 gusse=int(gusse)
6 if gusse==number:
7 print("You are right!")
8 break
9 elif gusse>number:
10 print("Wrong,too big!")
11 else:
12 print("Wrong,too small!")
13 else:
14 print("----You are not entering numbers,please enter agin----")
15 else:
16 print("----Sorry!Game Over!----")
break和continue
break是结束循环,continue是结束本次循环,继续下一次循环
三、List列表的增删改查
3.1、dict的增删改查
1 #Author:W.x 2 names=["zhangsan","list","list","2dashan","wanger","dagou","a","b"]#元素可以重复 3 names[0]="dashan" #修改某个元素的值 4 names.remove("a")#直接删除a 5 del names[4] #删除b 两种方法 6 names.pop() #删除最后一个 7 print(names[names.index("dashan")]) 8 print(names.index("dashan")) 9 print(names.count("list")) #输出元素list出现的个数 10 ‘‘‘print(names[0],names[3]) 11 print(names[1:3]) #从第一位开始取,到第三位(不包括)结束 切片 12 #print(names[0:3])和print(names[:3])效果一样,0是可以省略掉的 13 print(names[-1]) #1直接取最后一个 从右往左-1开始数 14 print(names[-3:-1])#错误写法names[-1:-3],左边的数字必须小于右边 15 print(names[-2:]) #表示取列表最后两个值‘‘‘ 16 #names.append("laojiu")# append增加列表元素 默认放到最后一个元素 17 #names.insert(1,"xuxia")#插入元素列表指定位置 18 names_1=names.copy() 19 #names.clear() #清空 20 names_1.reverse()#元素翻转 21 names.sort()#排序 优先级是:特殊字符>数字>字母>大写>小写 22 names.extend(names_1)# 把names_1列表附加到names列表中 23 del names_1 #删除列表 24 print(names) 25 print(names_1)
1 name_2=name 2 name_3=copy.deepcopy(name) #调用import copy ,copy.deepcopy 完全独立的一份数据 深copy互不影响 3 print(name_2) 4 print(name) 5 print(name_1) 6 name.append("susan") 7 #name.insert(2,["shanghai",1]) 8 #name[4][0]="HUBEI" 9 name_1.append("yueliang") 10 name[4][0]="HUBEI" 11 print(name) 12 print(name_1) 13 print(name_3)
3.2、列表的循环
1 for i in name: 2 print(name.index(i),i) 3 for key,j in enumerate(name): 4 print(key,j)
如何复制克隆一份列表数据,分为浅copy(浅copy相当于引用根列表的元素)和深copy.deepcopy()(完全独立于根列表的一份数据,互不影响)
 浅copy
浅copy
四、元组(tuple)、字典(dict)、集合
4.1、dict的增删改查
1 #Author:W.x 2 #key:value 无序 3 info_d={"st01":"zhaosi","st02":"wanger","st03":"dagou","st04":"dashen"} 4 print(type(info_d)) 5 info_d.pop("st04","bajie") #删除元素 6 info_d["st04"]="wukong" #如果不存在就增加一个 7 del info_d["st01"] # 8 info_d.pop("st02") #删除元素 9 info_d["st01"]="--wukong" 10 print(info_d) 11 info_d["st01"]="tangseng" #修改 12 del info_d["st01"] 13 print(info_d["st03"]) 14 print(info_d.get("st01")) #查看元素,如果没有对应键位的值 输出为None 15 a="st03" in info_d #判断key对应的值是否属于dict里边 16 print("aaaaaaaaaaaaaaa",a) 17 b=info_d.values() 18 c={1:2,"qw":1,3:"rsc"} 19 print(info_d.update(c)) #字典合并 有交叉的就修改 20 print(b) 21 print(info_d.items()) #转成一个列表 22 # dict的循环嵌套 23 menu_d={"" 24 25 } 26 #dict的循环 27 info_1={"w":"q",2:1,34:23,"shengfen":["shandong","hunan","shanxi"]} 28 for i in info_1: #更加高效 29 print(i,info_1[i]) 30 for m,n in info_1.items(): #先把字典转换成列表 31 print(m,n)
4.2、
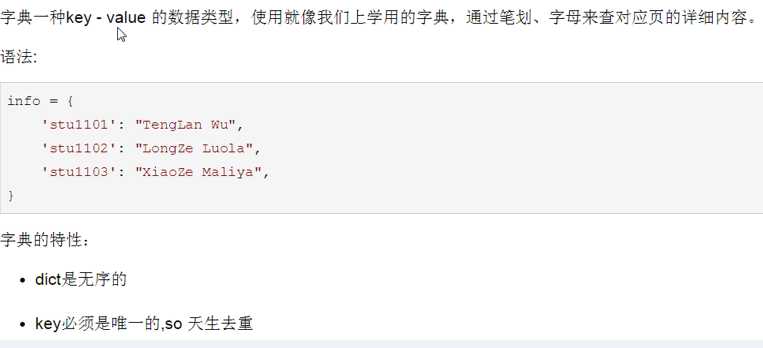
4.3、tuple的特性
tuple只能查,不能增删改
