AStar寻路算法是一种在一个静态路网中寻找最短路径的算法,也是在游戏开发中最常用到的寻路算法之一;最近刚好需要用到寻路算法,因此把自己的实现过程记录下来。
先直接上可视化之后的效果图,图中黑色方格代表障碍物,绿色的方格代表最终路线,红色方格为关闭列表,蓝色方格为开启列表;关于这一部分我会在稍后详细叙述。(可视化的实现部分我就不讨论了,这一篇主要说一下算法的实现)



一、算法原理
在描述具体算法逻辑之前,需要先理解几个基本概念:
-
- 启发式搜索:听起来很炫酷,其实很简单;想象你在一个九宫格的中间,你现在需要走到九宫格的右上角;这个时候你的第一步有四个选择:上下左右。虽然你还不知道具体路径怎么走,但你知道左边和下边距离终点似乎更远,所以你会优先选择先往右走或者先往上走。这就是启发式搜索——优先搜索最有可能产生最佳路径的节点;通过启发式搜索,可以有效减少不必要的搜索。
- 估价函数:上面说到启发式搜索会优先搜索最有可能产生最佳路径的节点,那么估价函数的作用就是对节点与终点的距离进行预估。预估距离最短的那个节点,就是目前最有可能产生最佳路径的节点。
- 开启列表:当估价函数对一个节点估价完毕后,这个节点就会被放入开启列表中。那么开启列表中的所有节点就是下一步所有可能被搜索的节点。
- 关闭列表:当算法对开启列表中最有可能是最佳路径的节点搜索完毕后,会将这个节点放入关闭列表。那么关闭列表中的所有节点就是已经搜索完的所有路线的节点。
接下来,我用一个简单的例子来描述算法的逻辑。
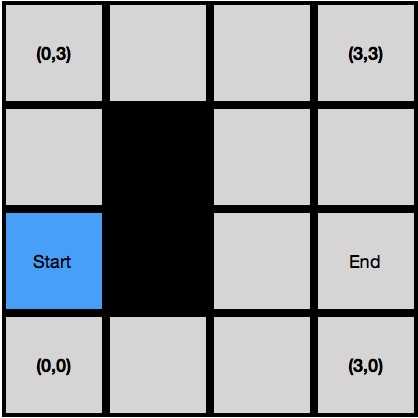
首先,假设我们有一个4*4的方格,左下角坐标(0,0),右上角坐标(3,3),黑色格子为障碍物;这个时候时候我们需要寻找点(0,1)到点(3,1)的最短路线;这个时候我们把起点加入开启列表(蓝色格子),即所有下一步可能被搜索的节点。
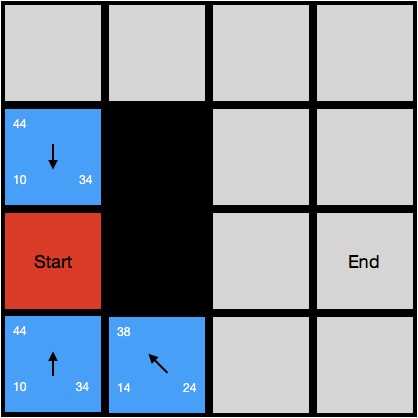
接下来我们要对开启列表进行搜索了,这个时候开启列表只有一个格子即起点,因此我们对起点进行搜索:
- 这个时候我们把起点作为当前节点(即当前正在搜索的节点),然后找出当前节点所有下一步可能的节点,把他们加入开启列表(蓝色格子),表示这些都是下一步可能被搜索的节点。
- 这个时候我们要对所有新增的节点用估价函数进行估价,估价函数的表达式为f(n)=g(n)+h(n), 其中g(h)代表节点n到起点的实际距离,h(n)即启发值,代表节点n到终点的预估距离,以节点(0,2)为例子:
- g:可以看到,(0,2)从起点往上移动了一格,假设一个格子边长为10,那么当前格子到起点的距离为10,因此g值为10,我们把它标在格子左下角。
- h:h有很多种估价的方式,在这里我们就直接取 忽略障碍物直接走到终点的距离;如图所示,该节点若要直接走到终点,它的路线为:右-右-右下,那么它的h值就是:10+10+14 = 34;我们把它标记在格子右下角。
- f:f为包含当前节点的路线的预估总距离,即g+h = 10+34 = 44,我们把它标在格子左上角。
- 父节点:父节点表示当前节点的估价是由哪个节点产生的,或者当前节点是从哪个节点走过来的;因此它的父节点为(0,1),我们用一个箭头指向(0,1),表示(0,1)是(0,2)的父节点。
- 对所有下一步可能的节点估价完毕后,我们将当前节点即起点从开启列表移动到关闭列表中(红色方格),表示我们对这个节点已经搜索完毕;结果如下图所示。
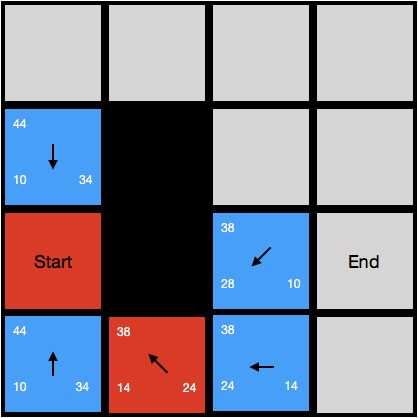
接下来我们继续对开启列表进行搜索,经过上一步后,我们的开启列表有三个节点;这个时候我们寻找f值最小的节点对它进行搜索,可以看到坐标为(1,0)的节点有着最小的f值38;因此节点(1,0)是目前最有可能产生最佳路线的节点,我们把它作为当前节点进行搜索:
- 这个时候我们重复上一步的动作,找出当前节点所有下一步可能的节点,并对它们进行估价
- 在找出节点的过程中,我们发现它左边的节点是它下一步可能的新节点(0,0)之一,但是左边的节点已经存在于开启列表中了;那我们是否让新节点覆盖旧节点呢?这个时候我们如果对新产生的节点(0,0)进行估价,我们会发现新产生的节点h值不变,g值为24,f值为24+34 = 58;我们发现新节点的f值58大于旧节点的f值44,那么我们可以知道新节点所产生的路线总距离大于老节点产生的路线的总距离,因此我们选择保留老节点。(当然如果我们发现新节点所产生的f值小于老节点所产生的f值,我们就要用新节点覆盖老节点,因为新节点所产生的路线总距离更近)
- 估价完毕后,我们对把当前节点从开启列表移动到关闭列表中(红色方格),结果如下图
这个时候我们发现最小f值的节点有两个,我们随便选一个(2,1)继续搜索,可以得到下图的结果:
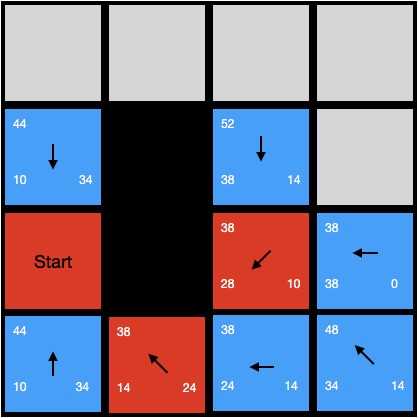
这个时候依然有两个节点f值最小,我们随便选一个(3,1),把它作为当前节点,继续搜索;这个时候我们发现当前节点位置就是终点的位置,我们按照箭头线路走到起点,于是我们终于找到了路线,如下图所示:
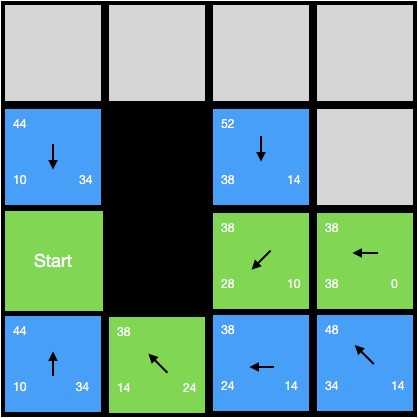
于是我们可以总结一下Astar寻路算法的算法逻辑(伪代码):
new openList;
new closeList;
openList.Add(start); //把起点加入开启列表
loop{
currentNode = lowest f cost in openList;//把开启列表中f值最低的节点作为当前节点
if (currentNode == end) return; //找到路线
foreach(neighbour in currentNode.Neighbours){ //对所有当前节点的相邻节点进行循环
if (closeList.Contains(neighbour) or neighbour == obstacle ) continue; //跳过关闭列表中的节点和障碍物节点
if( new fCost <= old fCost || !openList.Contains(neighbour) ){ //如果新节点的f值小于老节点的f值,用新节点替换老节点
neighbour.fCost = new fCost;
neighbour.parent = currentNode;
if(!openList.Contains(neighbour)) openList.Add(neighbour);//如果新节点不在开启列表,将其加入开启列表
}
}
}
二、算法实现
首先,在路径网格中每一个网格都有一个对应的坐标,因此我创建了一个Point2类用来表示网格坐标

1 //A class used to store the position information
2 public class Point2
3 {
4 public Point2(int x, int y)
5 {
6 this.x = x;
7 this.y = y;
8 }
9
10 public int x { get; set; }
11
12 public int y { get; set; }
13
14 public override bool Equals(object obj)
15 {
16 return this.x == (obj as Point2).x && this.y == (obj as Point2).y;
17 }
18
19 public override int GetHashCode()
20 {
21 return x ^ (y * 256);
22 }
23
24 public override string ToString()
25 {
26 return x + "," + y;
27 }
28
29 public static bool operator ==(Point2 a, Point2 b)
30 {
31 return a.Equals(b);
32 }
33
34 public static bool operator !=(Point2 a, Point2 b)
35 {
36 return !a.Equals(b);
37 }
38 }
接下来,我创建了一个PathNode类用来记录单个节点的信息

1 public class PathNode
2 {
3 public PathNode(bool isWall, Point2 position)
4 {
5 this.isWall = isWall;
6 this.position = position;
7 }
8
9 public readonly Point2 position;
10
11 public bool isWall { get; set; }
12
13 public PathNode parent { get; set; }
14
15 public int gCost { get; set; }
16
17 public int hCost { get; set; }
18
19 public int fCost {
20 get {
21 return gCost + hCost;
22 }
23 }
24
25 public override bool Equals(object obj)
26 {
27 PathNode node = obj as PathNode;
28 return node.isWall == this.isWall && node.gCost == this.gCost && node.hCost == this.hCost && node.parent == this.parent && this.position == node.position;
29 }
30
31 public override int GetHashCode()
32 {
33 return gCost ^ (hCost * 128) + position.GetHashCode();
34 }
35
36 public static bool operator ==(PathNode a, PathNode b)
37 {
38 return a.Equals(b);
39 }
40
41 public static bool operator !=(PathNode a, PathNode b)
42 {
43 return !a.Equals(b);
44 }
45 }
最后是我们的PathGrid类,通过创建该类的实例来创建一个网格信息,其中包含了网格大小以及所有障碍物信息。使用中输入起点信息和终点信息可以返回路径信息。关于代码部分,由于Astar算法中开销最大的部分是开启列表和关闭列表的维护以及在开启列表中寻找f值最低的部分。因此我用C#的SortedDictionary额外创建了一个开启列表用于查询f值最低的节点。当然算法还存在很大的优化空间,不过像32*32这样的小的网格中已经够用了。

1 using System.Collections.Generic;
2 using System.Linq;
3 using System;
4
5 public class PathGrid
6 {
7 private SortedDictionary<int, List<Point2>> openTree = new SortedDictionary<int, List<Point2>>();
8
9 private HashSet<Point2> openSet = new HashSet<Point2>();
10 private HashSet<Point2> closeSet = new HashSet<Point2>();
11 private Dictionary<Point2, PathNode> allNodes = new Dictionary<Point2, PathNode>();
12
13 private Point2 endPos;
14 private Point2 gridSize;
15
16 private List<Point2> currentPath;
17
18 //这一部分在实际寻路中并不需要,只是为了方便外部程序实现寻路可视化
19 public HashSet<Point2> GetCloseList()
20 {
21 return closeSet;
22 }
23
24 //这一部分在实际寻路中并不需要,只是为了方便外部程序实现寻路可视化
25 public HashSet<Point2> GetOpenList()
26 {
27 return openSet;
28 }
29
30 //这一部分在实际寻路中并不需要,只是为了方便外部程序实现寻路可视化
31 public List<Point2> GetCurrentPath()
32 {
33 return currentPath;
34 }
35
36 //新建一个PathGrid,包含了网格大小和障碍物信息
37 public PathGrid(int x, int y, List<Point2> walls)
38 {
39 gridSize = new Point2(x, y);
40 for (int i = 0; i < x; i++) {
41 for (int j = 0; j < y; j++) {
42 Point2 newPos = new Point2(i, j);
43 allNodes.Add(newPos, new PathNode(walls.Contains(newPos), newPos));
44 }
45 }
46 }
47
48 //寻路主要逻辑,通过调用该方法来获取路径信息,由一串Point2代表
49 public List<Point2> FindPath(Point2 beginPos, Point2 endPos)
50 {
51 List<Point2> result = new List<Point2>();
52
53 this.endPos = endPos;
54 Point2 currentPos = beginPos;
55 openSet.Add(currentPos);
56
57 while (!currentPos.Equals(this.endPos)) {
58 UpdatePath(currentPos);
59 if (openSet.Count == 0) return null;
60
61 currentPos = openTree.First().Value.First();
62 }
63
64 Point2 path = currentPos;
65
66 while (!path.Equals(beginPos)) {
67 result.Add(path);
68 path = allNodes[path].parent.position;
69 currentPath = result;
70 }
71
72 result.Add(beginPos);
73 return result;
74 }
75
76 //寻路
77 private void UpdatePath(Point2 currentPos)
78 {
79 closeSet.Add(currentPos);
80 RemoveOpen(currentPos, allNodes[currentPos]);
81 List<Point2> neighborNodes = FindNeighbor(currentPos);
82 foreach (Point2 nodePos in neighborNodes) {
83
84 PathNode newNode = new PathNode(false, nodePos);
85 newNode.parent = allNodes[currentPos];
86
87 int g;
88 int h;
89
90 g = currentPos.x == nodePos.x || currentPos.y == nodePos.y ? 10 : 14;
91
92 int xMoves = Math.Abs(nodePos.x - endPos.x);
93 int yMoves = Math.Abs(nodePos.y - endPos.y);
94
95 int min = Math.Min(xMoves, yMoves);
96 int max = Math.Max(xMoves, yMoves);
97 h = min * 14 + (max - min) * 10;
98
99
100 newNode.gCost = g + newNode.parent.gCost;
101 newNode.hCost = h;
102
103 PathNode originNode = allNodes[nodePos];
104
105 if (openSet.Contains(nodePos)) {
106 if (newNode.fCost < originNode.fCost) {
107 UpdateNode(newNode, originNode);
108 }
109 } else {
110 allNodes[nodePos] = newNode;
111 AddOpen(nodePos, newNode);
112 }
113 }
114 }
115
116 //将旧节点更新为新节点
117 private void UpdateNode(PathNode newNode, PathNode oldNode)
118 {
119 Point2 nodePos = newNode.position;
120 int oldCost = oldNode.fCost;
121 allNodes[nodePos] = newNode;
122 List<Point2> sameCost;
123
124 if (openTree.TryGetValue(oldCost, out sameCost)) {
125 sameCost.Remove(nodePos);
126 if (sameCost.Count == 0) openTree.Remove(oldCost);
127 }
128
129 if (openTree.TryGetValue(newNode.fCost, out sameCost)) {
130 sameCost.Add(nodePos);
131 } else {
132 sameCost = new List<Point2> { nodePos };
133 openTree.Add(newNode.fCost, sameCost);
134 }
135 }
136
137 //将目标节点移出开启列表
138 private void RemoveOpen(Point2 pos, PathNode node)
139 {
140 openSet.Remove(pos);
141 List<Point2> sameCost;
142 if (openTree.TryGetValue(node.fCost, out sameCost)) {
143 sameCost.Remove(pos);
144 if (sameCost.Count == 0) openTree.Remove(node.fCost);
145 }
146 }
147
148 //将目标节点加入开启列表
149 private void AddOpen(Point2 pos, PathNode node)
150 {
151 openSet.Add(pos);
152 List<Point2> sameCost;
153 if (openTree.TryGetValue(node.fCost, out sameCost)) {
154 sameCost.Add(pos);
155 } else {
156 sameCost = new List<Point2> { pos };
157 openTree.Add(node.fCost, sameCost);
158 }
159 }
160
161 //找到某节点的所有相邻节点
162 private List<Point2> FindNeighbor(Point2 nodePos)
163 {
164 List<Point2> result = new List<Point2>();
165
166 for (int x = -1; x < 2; x++) {
167 for (int y = -1; y < 2; y++) {
168 if (x == 0 && y == 0) continue;
169
170 Point2 currentPos = new Point2(nodePos.x + x, nodePos.y + y);
171
172 if (currentPos.x >= gridSize.x || currentPos.y >= gridSize.y || currentPos.x < 0 || currentPos.y < 0) continue; //out of bondary
173 if (closeSet.Contains(currentPos)) continue; // already in the close list
174 if (allNodes[currentPos].isWall) continue; // the node is a wall
175
176 result.Add(currentPos);
177 }
178 }
179
180 return result;
181 }
182 }

