---恢复内容开始---
d定义:
pandas是一个强大的Python数据分析的工具包。
pandas是基于NumPy构建的。
安装方法:
pip install pandas
import pandas as pd
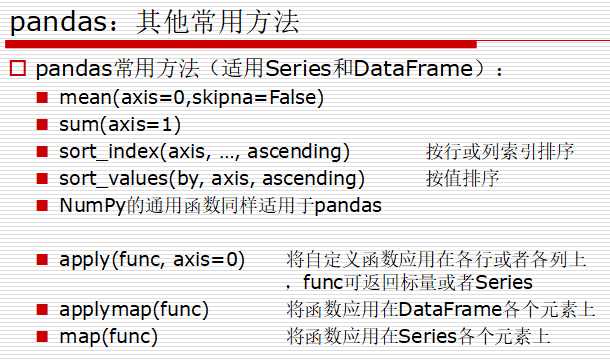
pandas的主要功能
具备对其功能的数据结构DataFrame、Series
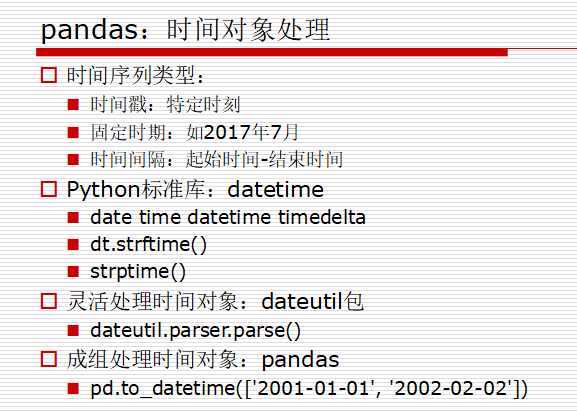
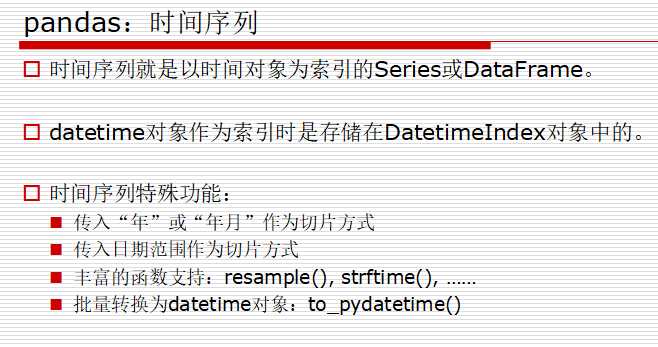
集成时间序列功能
提供丰富的数学运算和操作
灵活处理缺失数据
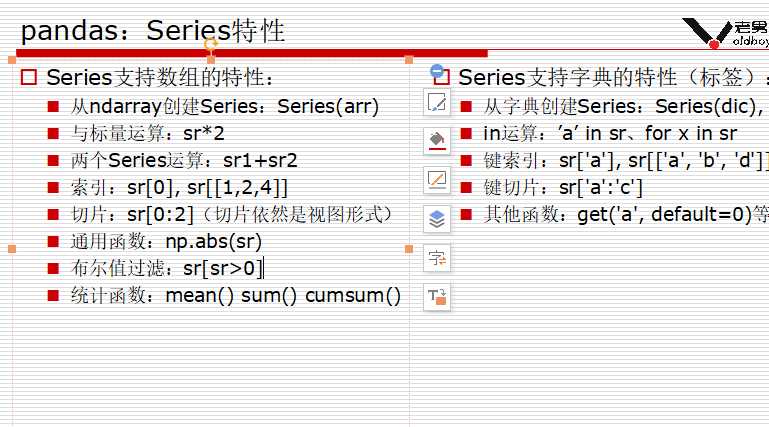
Series
定义:Series是一种类似于一位数组的对象,由一组数据和一组与之相关的数据标签(索引)组成。
创建方式:
创建方式: pd.Series([4,7,-5,3]) pd.Series([4,7,-5,3],index=[‘a‘,‘b‘,‘c‘,‘d‘]) pd.Series({‘a‘:1, ‘b‘:2}) pd.Series(0, index=[‘a‘,‘b‘,‘c‘,‘d’])
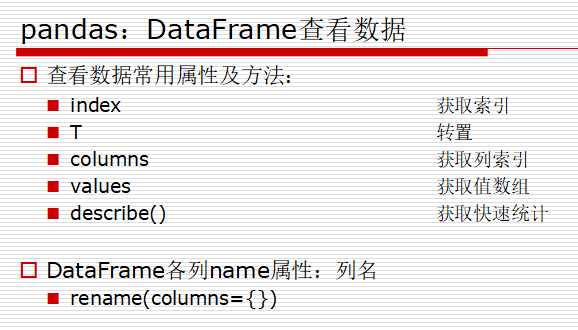
获取值数组和索引数组:values属性和index属性
Series比较像列表(数组)和字典的结合体。







实例:

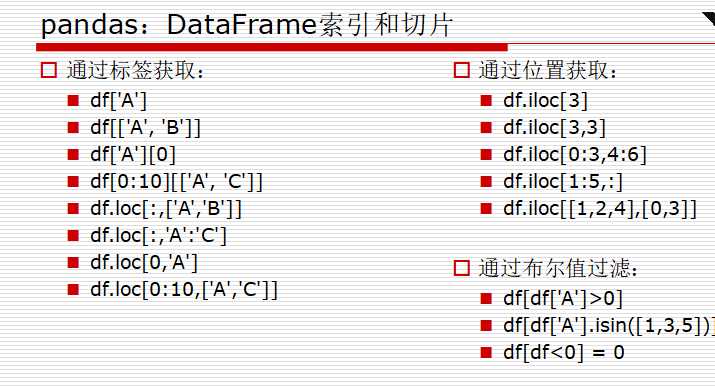
sr=pd.Series([1,2,3,4],index=[‘a‘,‘b‘,‘c‘,‘d‘]) sr[‘a‘:‘c‘] ==> a -4 b 3 c 5 dtype: int64 sr[[‘a‘,‘d‘]] == a -4 d 6 dtype: int64 判断 条件是键不是值 ‘b‘ in sr == true 1 in sr == flase 取值: 取值的方法和字典相类似 sr.get(‘a‘,0)

sr=pd.Series([1,2,3,4],index=[‘b‘,‘c‘,‘d‘,‘a‘]) b 1 c 2 d 3 a 4 dtype: int64 sr.iloc[1] #取索引为1 == 2 sr.ilc[2] #取索引为2 == 3

sr=pd.Series([1,2,3,4],index=[‘b‘,‘c‘,‘d‘,‘a‘]) sr1=pd.Series([5,6,7,8,9],index=[‘a‘,‘b‘,‘c‘,‘d‘,‘e‘]) sr2=pd.Series([5,6,7,8,9,10],index=[‘a‘,‘b‘,‘c‘,‘d‘,‘e‘,‘f‘]) sr+sr1 == a 9.0 b 7.0 c 9.0 d 11.0 e NaN dtype: float64 PS:多出来的值只是NAN add方法 sr3=sr.add(sr2,fill_value=0) sr3: == a 9.0 b 7.0 c 9.0 d 11.0 e 9.0 f 10.0 dtype: float64 用add方法:没有就加上,不会出现Nan

sr4 a 9.0 b 7.0 c 9.0 d 11.0 e NaN dtype: float64 sr4.notnull() a True b True c True d True e False dtype: bool sr4[sr4.notnull()] #把是NAN的去掉 a 9.0 b 7.0 c 9.0 d 11.0 sr4.dropna() #也是直接去掉为nan的 a 9.0 b 7.0 c 9.0 d 11.0 dtype: float64
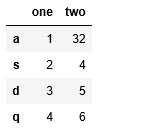
sr=pd.DataFrame({‘one‘:[1,2,3,4],‘two‘:[32,4,5,6]},index=[‘a‘,‘s‘,‘d‘,‘q‘])

import random li = [random.uniform(10,20) for _ in range(1000)] ratio = 6.3 list(map(lambda x:x*ratio, li))
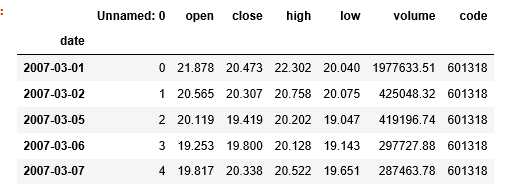
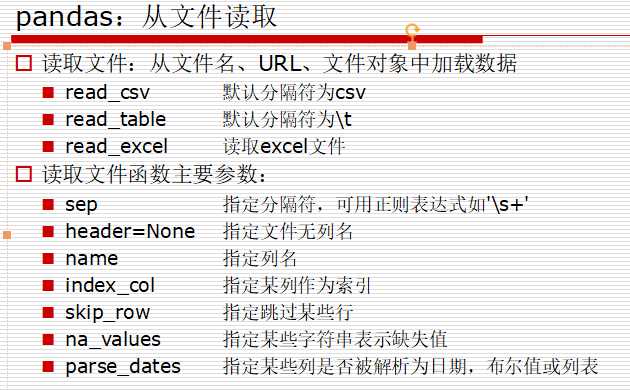
df = pd.read_csv(‘601318.csv‘, header=None, names=list(‘asdfghjk‘))
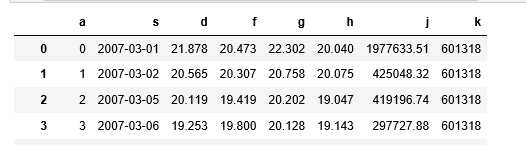
df = pd.read_csv(‘601318.csv‘,index_col=1, parse_dates=[‘date‘]) df
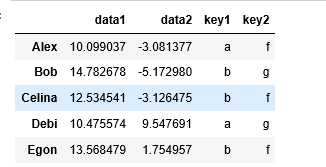
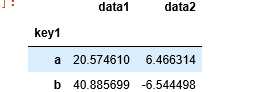
df.groupby(‘key1‘).sum()
---恢复内容结束---