整体思路:
- 创建一个需要扩展的组件
- 定义一个XSD文件,描述组件内容
- 创建一个java类,实现BeanDefinitionParser接口,用来解析XSD文件中的定义和组件定义
- 创建一个Handler类,扩展子NameSpaceHandlerSupport,目的是将组件注册到容器。
- 编写(添加)Spring.handlers和Spring.schemas文件。
解析流程:通过Spring.schemas找到对应的XSD文件,校验xml格式;通过Spring.handlers找到对应的NamespaceHandler类作为解析自定义标签的类,通过init方法中的参数BeanDefinition实现类,根据解析的值生成BeanDefinition,
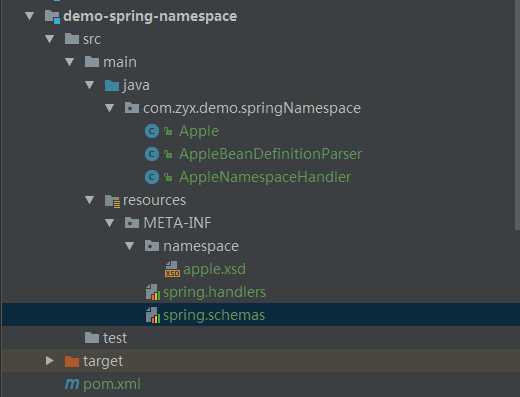
目录结构
创建模型类
public class Apple { private String name; private String appleColor; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getAppleColor() { return appleColor; } public void setAppleColor(String appleColor) { this.appleColor = appleColor; } }
创建xsd文件
对于该类标签的定义,spring中有着相应的XSD定义文档
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
对于XSD,简单的说是xml的一个标签的定义,在这里就不对XSD过多的解释了,祥见
http://www.w3school.com.cn/schema/schema_example.asp
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <xsd:schema xmlns="http://www.zyx.com/schema/apple" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:beans="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" targetNamespace="http://www.zyx.com/schema/apple" elementFormDefault="qualified" attributeFormDefault="unqualified"> <xsd:import namespace="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd" /> <xsd:element name="apple"> <xsd:complexType> <xsd:all> <xsd:element ref="apple-color" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1"/> </xsd:all> <xsd:attribute name="id" type="xsd:string" /> <xsd:attribute name="name" type="xsd:string" use="required"/> </xsd:complexType> </xsd:element> <xsd:element name="apple-color"> <xsd:complexType> <xsd:attribute name="color" type="xsd:string" use="required"/> </xsd:complexType> </xsd:element> </xsd:schema>
type是用来定义该属性的格式,例如
xsd:string 表示是一个字符串,对格式没什么要求
xsd:id 表示该属性的值是一个id,有格式要求(例如不能以数字开头)。
xsd:IDREF 表示该属性的值与某xsd:id属性的值对应
其他还有很多,例如number,double,datetime等等。
编写spring.schemas
改配置文件主要是用一个url来映射我们第一步配置好的文件,形式如下
http\://www.zyx.com/schema/apple.xsd=META-INF/namespace/apple.xsd
编写BeanDefinition,解析xml
public class AppleBeanDefinitionParser extends AbstractSingleBeanDefinitionParser { protected Class getBeanClass(Element element) { return Apple.class; } protected void doParse(Element element, BeanDefinitionBuilder bean) { String name = element.getAttribute("name"); String color = parseAppleColor(element); if (StringUtils.hasText(name)) { bean.addPropertyValue("name", name); } if (StringUtils.hasText(color)) { bean.addPropertyValue("appleColor", color); } } private String parseAppleColor(Element element) { Element colorElement = DomUtils.getChildElementByTagName(element, "apple-color"); return colorElement.getAttribute("color"); } }
编写NamespaceHandlerSupport
我们配置了com.zyx.demo.springNamespace.AppleNamespaceHandler类作为解析自定义标签的类,所以namespace为apple的标签,都会用这里注册的标签解析器来解析
public class AppleNamespaceHandler extends NamespaceHandlerSupport { public void init() { registerBeanDefinitionParser("apple",new AppleBeanDefinitionParser()); } }
编写spring.handlers
这个配置文件用来配置解析我们apple标签,然后生成一些BeanDefinition进行注册
http\://www.zyx.com/schema/apple=com.zyx.demo.springNamespace.AppleNamespaceHandler
到这里就写完了,下面是测试
测试:创建spring.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:myname="http://www.zyx.com/schema/apple" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd http://www.zyx.com/schema/apple http://www.zyx.com/schema/apple.xsd" default-autowire="byName"> <myname:apple id="xxx" name="hongfushi"> <myname:apple-color color="red"></myname:apple-color> </myname:apple> </beans>
测试代码
@Controller @RequestMapping("/test") public class TestSpringNamespace { @ResponseBody @RequestMapping("spring/namespace") public String test(){ Apple apple = SpringUtils.getBean(Apple.class); System.out.println(apple.toString()); return apple.toString(); } }
