摘要
- 本文从源码层面简单讲解SpringMVC的处理器映射环节,也就是查找Controller详细过程。
SpringMVC请求流程

- Controller查找在上图中对应的步骤1至2的过程
SpringMVC初始化过程
理解初始化过程之前,先认识两个类
- RequestMappingInfo类,对RequestMapping注解封装。里面包含http请求头的相关信息。如uri、method、params、header等参数。一个对象对应一个RequestMapping注解
- HandlerMethod类,是对Controller的处理请求方法的封装。里面包含了该方法所属的bean对象、该方法对应的method对象、该方法的参数等。

上图是RequestMappingHandlerMapping的继承关系。在SpringMVC初始化的时候,首先执行RequestMappingHandlerMapping中的afterPropertiesSet方法,然后会进入AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的afterPropertiesSet方法(line:93),这个方法会进入当前类的initHandlerMethods方法(line:103)。这个方法的职责便是从applicationContext中扫描beans,然后从bean中查找并注册处理器方法,代码如下。
protected void initHandlerMethods() { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Looking for request mappings in application context: " + getApplicationContext()); } //获取applicationContext中所有的bean name String[] beanNames = (this.detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts ? BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(getApplicationContext(), Object.class) : getApplicationContext().getBeanNamesForType(Object.class)); //遍历beanName数组 for (String beanName : beanNames) { //isHandler会根据bean来判断bean定义中是否带有Controller注解或RequestMapping注解 if (isHandler(getApplicationContext().getType(beanName))){ detectHandlerMethods(beanName); } } handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods()); }isHandler方法其实很简单,如下
@Override protected boolean isHandler(Class<?> beanType) { return ((AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(beanType, Controller.class) != null) || (AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(beanType, RequestMapping.class) != null)); }就是判断当前bean定义是否带有Controlller注解或RequestMapping注解,看了这里逻辑可能会想如果只有RequestMapping会生效吗?答案是不会的,因为在这种情况下Spring初始化的时候不会把该类注册为Spring bean,遍历beanNames时不会遍历到这个类,所以这里把Controller换成Compoent注解也是可以,不过一般不会这么做。当确定bean为handlers后,便会从该bean中查找出具体的handler方法(也就是我们通常定义的Controller类下的具体定义的请求处理方法),查找代码如下
protected void detectHandlerMethods(final Object handler) { //获取到当前Controller bean的class对象 Class<?> handlerType = (handler instanceof String) ? getApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass(); //同上,也是该Controller bean的class对象 final Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType); //获取当前bean的所有handler method。这里查找的依据便是根据method定义是否带有RequestMapping注解。如果有根据注解创建RequestMappingInfo对象 Set<Method> methods = HandlerMethodSelector.selectMethods(userType, new MethodFilter() { public boolean matches(Method method) { return getMappingForMethod(method, userType) != null; } }); //遍历并注册当前bean的所有handler method for (Method method : methods) { T mapping = getMappingForMethod(method, userType); //注册handler method,进入以下方法 registerHandlerMethod(handler, method, mapping); } }以上代码有两个地方有调用了getMappingForMethod方法
protected RequestMappingInfo getMappingForMethod(Method method, Class<?> handlerType) { RequestMappingInfo info = null; //获取method的@RequestMapping注解 RequestMapping methodAnnotation = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(method, RequestMapping.class); if (methodAnnotation != null) { RequestCondition<?> methodCondition = getCustomMethodCondition(method); info = createRequestMappingInfo(methodAnnotation, methodCondition); //获取method所属bean的@RequtestMapping注解 RequestMapping typeAnnotation = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(handlerType, RequestMapping.class); if (typeAnnotation != null) { RequestCondition<?> typeCondition = getCustomTypeCondition(handlerType); //合并两个@RequestMapping注解 info = createRequestMappingInfo(typeAnnotation, typeCondition).combine(info); } } return info; }这个方法的作用就是根据handler method方法创建RequestMappingInfo对象。首先判断该mehtod是否含有RequestMpping注解。如果有则直接根据该注解的内容创建RequestMappingInfo对象。创建以后判断当前method所属的bean是否也含有RequestMapping注解。如果含有该注解则会根据该类上的注解创建一个RequestMappingInfo对象。然后在合并method上的RequestMappingInfo对象,最后返回合并后的对象。现在回过去看detectHandlerMethods方法,有两处调用了getMappingForMethod方法,个人觉得这里是可以优化的,在第一处判断method时否为handler时,创建的RequestMappingInfo对象可以保存起来,直接拿来后面使用,就少了一次创建RequestMappingInfo对象的过程。然后紧接着进入registerHandlerMehtod方法,如下
protected void registerHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method, T mapping) { //创建HandlerMethod HandlerMethod newHandlerMethod = createHandlerMethod(handler, method); HandlerMethod oldHandlerMethod = handlerMethods.get(mapping); //检查配置是否存在歧义性 if (oldHandlerMethod != null && !oldHandlerMethod.equals(newHandlerMethod)) { throw new IllegalStateException("Ambiguous mapping found. Cannot map ‘" + newHandlerMethod.getBean() + "‘ bean method \n" + newHandlerMethod + "\nto " + mapping + ": There is already ‘" + oldHandlerMethod.getBean() + "‘ bean method\n" + oldHandlerMethod + " mapped."); } this.handlerMethods.put(mapping, newHandlerMethod); if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Mapped \"" + mapping + "\" onto " + newHandlerMethod); } //获取@RequestMapping注解的value,然后添加value->RequestMappingInfo映射记录至urlMap中 Set<String> patterns = getMappingPathPatterns(mapping); for (String pattern : patterns) { if (!getPathMatcher().isPattern(pattern)) { this.urlMap.add(pattern, mapping); } } }这里T的类型是RequestMappingInfo。这个对象就是封装的具体Controller下的方法的RequestMapping注解的相关信息。一个RequestMapping注解对应一个RequestMappingInfo对象。HandlerMethod和RequestMappingInfo类似,是对Controlelr下具体处理方法的封装。先看方法的第一行,根据handler和mehthod创建HandlerMethod对象。第二行通过handlerMethods map来获取当前mapping对应的HandlerMethod。然后判断是否存在相同的RequestMapping配置。如下这种配置就会导致此处抛
Invocation of init method failed; nested exception is java.lang.IllegalStateException: Ambiguous mapping found. Cannot map...
异常@Controller @RequestMapping("/AmbiguousTest") public class AmbiguousTestController { @RequestMapping(value = "/test1") @ResponseBody public String test1(){ return "method test1"; } @RequestMapping(value = "/test1") @ResponseBody public String test2(){ return "method test2"; } }在SpingMVC启动(初始化)阶段检查RequestMapping配置是否有歧义,这是其中一处检查歧义的(后面还会提到一个在运行时检查歧义性的地方)。然后确认配置正常以后会把该RequestMappingInfo和HandlerMethod对象添加至handlerMethods(LinkedHashMap
registerHandlerMethod方法简单总结
该方法的主要有3个职责
- 检查RequestMapping注解配置是否有歧义。
- 构建RequestMappingInfo到HandlerMethod的映射map。该map便是AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的成员变量handlerMethods。LinkedHashMap
构建AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的成员变量urlMap,MultiValueMap
@Controller @RequestMapping("/UrlMap") public class UrlMapController { @RequestMapping(value = "/test1", method = RequestMethod.GET) @ResponseBody public String test1(){ return "method test1"; } @RequestMapping(value = "/test1") @ResponseBody public String test2(){ return "method test2"; } @RequestMapping(value = "/test3") @ResponseBody public String test3(){ return "method test3"; } }
- 初始化完成后,对应AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的urlMap的结构如下
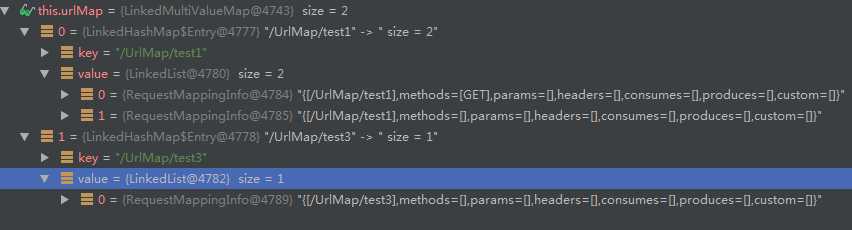
以上便是SpringMVC初始化的主要过程
查找过程
为了理解查找流程,带着一个问题来看,现有如下Controller
@Controller @RequestMapping("/LookupTest") public class LookupTestController { @RequestMapping(value = "/test1", method = RequestMethod.GET) @ResponseBody public String test1(){ return "method test1"; } @RequestMapping(value = "/test1", headers = "Referer=https://www.baidu.com") @ResponseBody public String test2(){ return "method test2"; } @RequestMapping(value = "/test1", params = "id=1") @ResponseBody public String test3(){ return "method test3"; } @RequestMapping(value = "/*") @ResponseBody public String test4(){ return "method test4"; } }- 有如下请求

- 这个请求会进入哪一个方法?
web容器(Tomcat、jetty)接收请求后,交给DispatcherServlet处理。FrameworkServlet调用对应请求方法(eg:get调用doGet),然后调用processRequest方法。进入processRequest方法后,一系列处理后,在line:936进入doService方法。然后在Line856进入doDispatch方法。在line:896获取当前请求的处理器handler。然后进入AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的lookupHandlerMethod方法。代码如下
protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<Match>(); //根据uri获取直接匹配的RequestMappingInfos List<T> directPathMatches = this.urlMap.get(lookupPath); if (directPathMatches != null) { addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request); } //不存在直接匹配的RequetMappingInfo,遍历所有RequestMappingInfo if (matches.isEmpty()) { // No choice but to go through all mappings addMatchingMappings(this.handlerMethods.keySet(), matches, request); } //获取最佳匹配的RequestMappingInfo对应的HandlerMethod if (!matches.isEmpty()) { Comparator<Match> comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request)); Collections.sort(matches, comparator); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Found " + matches.size() + " matching mapping(s) for [" + lookupPath + "] : " + matches); } //再一次检查配置的歧义性 Match bestMatch = matches.get(0); if (matches.size() > 1) { Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1); if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) { Method m1 = bestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod(); Method m2 = secondBestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod(); throw new IllegalStateException( "Ambiguous handler methods mapped for HTTP path ‘" + request.getRequestURL() + "‘: {" + m1 + ", " + m2 + "}"); } } handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request); return bestMatch.handlerMethod; } else { return handleNoMatch(handlerMethods.keySet(), lookupPath, request); } }进入lookupHandlerMethod方法,其中lookupPath="/LookupTest/test1",根据lookupPath,也就是请求的uri。直接查找urlMap,获取直接匹配的RequestMappingInfo list。这里会匹配到3个RequestMappingInfo。如下

然后进入addMatchingMappings方法
private void addMatchingMappings(Collection<T> mappings, List<Match> matches, HttpServletRequest request) { for (T mapping : mappings) { T match = getMatchingMapping(mapping, request); if (match != null) { matches.add(new Match(match, handlerMethods.get(mapping))); } } }这个方法的职责是遍历当前请求的uri和mappings中的RequestMappingInfo能否匹配上,如果能匹配上,创建一个相同的RequestMappingInfo对象。再获取RequestMappingInfo对应的handlerMethod。然后创建一个Match对象添加至matches list中。执行完addMatchingMappings方法,回到lookupHandlerMethod。这时候matches还有3个能匹配上的RequestMappingInfo对象。接下来的处理便是对matchers列表进行排序,然后获取列表的第一个元素作为最佳匹配。返回Match的HandlerMethod。这里进入RequestMappingInfo的compareTo方法,看一下具体的排序逻辑。代码如下
public int compareTo(RequestMappingInfo other, HttpServletRequest request) { int result = patternsCondition.compareTo(other.getPatternsCondition(), request); if (result != 0) { return result; } result = paramsCondition.compareTo(other.getParamsCondition(), request); if (result != 0) { return result; } result = headersCondition.compareTo(other.getHeadersCondition(), request); if (result != 0) { return result; } result = consumesCondition.compareTo(other.getConsumesCondition(), request); if (result != 0) { return result; } result = producesCondition.compareTo(other.getProducesCondition(), request); if (result != 0) { return result; } result = methodsCondition.compareTo(other.getMethodsCondition(), request); if (result != 0) { return result; } result = customConditionHolder.compareTo(other.customConditionHolder, request); if (result != 0) { return result; } return 0; }代码里可以看出,匹配的先后顺序是value>params>headers>consumes>produces>methods>custom,看到这里,前面的问题就能轻易得出答案了。在value相同的情况,params更能先匹配。所以那个请求会进入test3()方法。再回到lookupHandlerMethod,在找到HandlerMethod。SpringMVC还会这里再一次检查配置的歧义性,这里检查的原理是通过比较匹配度最高的两个RequestMappingInfo进行比较。此处可能会有疑问在初始化SpringMVC有检查配置的歧义性,这里为什么还会检查一次。假如现在Controller中有如下两个方法,以下配置是能通过初始化歧义性检查的。
@RequestMapping(value = "/test5", method = {RequestMethod.GET, RequestMethod.POST}) @ResponseBody public String test5(){ return "method test5"; } @RequestMapping(value = "/test5", method = {RequestMethod.GET, RequestMethod.DELETE}) @ResponseBody public String test6(){ return "method test6"; }现在执行 http://localhost:8080/SpringMVC-Demo/LookupTest/test5 请求,便会在lookupHandlerMethod方法中抛
java.lang.IllegalStateException: Ambiguous handler methods mapped for HTTP path ‘http://localhost:8080/SpringMVC-Demo/LookupTest/test5‘异常。这里抛该异常是因为RequestMethodsRequestCondition的compareTo方法是比较的method数。代码如下public int compareTo(RequestMethodsRequestCondition other, HttpServletRequest request) { return other.methods.size() - this.methods.size(); }什么时候匹配通配符?当通过urlMap获取不到直接匹配value的RequestMappingInfo时才会走通配符匹配进入addMatchingMappings方法。
总结
- 解析所使用代码已上传至github,https://github.com/wycm/SpringMVC-Demo
- 以上源码是基于SpringMVC 3.2.2.RELEASE版本。以上便是SpringMVC请求查找的主要过程,希望对大家有帮助。本文可能有错误,希望读者能够指出来。
