绪论:
本文的内容包括flume的背景、数据流模型、常见的数据流操作、flume agent启动和flume agent简单实例。参考文档为flume官网的flume1.8.0 FlumeUserGuide。
一、背景
flume是由cloudera软件公司产出的可分布式日志收集系统,2009年被捐赠给apache软件基金会,目前是apache的一个顶级项目。
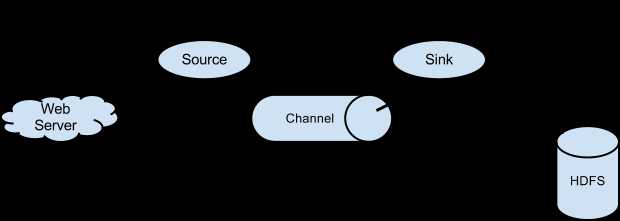
图2.1 flume数据流模型
一个flume agent的典型数据流动过程为:

图3.1 multi-agent flow
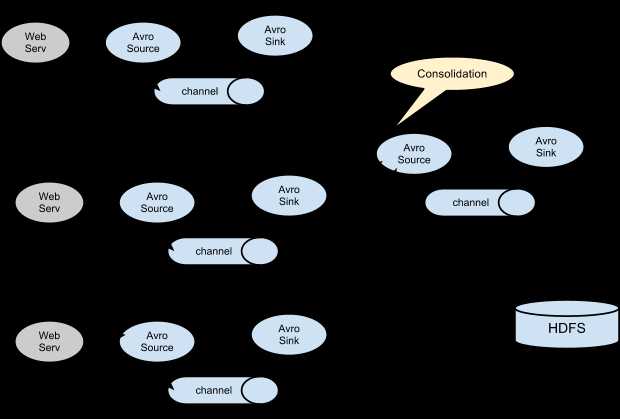
图3.2 Consolidation
3.Multiplexing the flow
通过Multiplexing,flume可以将一个event流发送到一个或多个目的地。
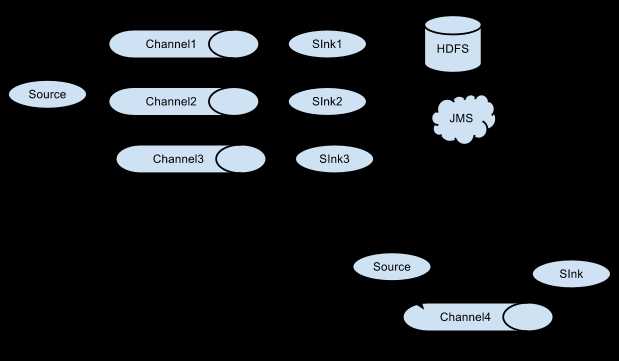
图3.3 Multiplexing the flow
四、flume agent启动
如上所述,一个flume agent可以包含多个source、channel和sink。根据flume1.8.0的FlumeUserGuide,可以通过以下命令启动一个flume agent:
$FLUME_HOME/bin/flume-ng agent -n $agent_name -c conf -f conf/flume-conf.properties.template
其中,-n参数用于指定agent名称,-c参数用于指定conf目录,-f参数用于指定配置文件。
一个flume agent的启动流程如下:
1.根据需求编写配置文件;
2.使用上述命令指定配置文件并启动flume agent。
五、flume agent实例
flume官网提供了一个flume agent的简单实例,其名称是a1,配置文件如下:
# example.conf: A single-node Flume configuration # Name the components on this agent a1.sources = r1 a1.sinks = k1 a1.channels = c1 # Describe/configure the source a1.sources.r1.type = netcat a1.sources.r1.bind = localhost a1.sources.r1.port = 44444 # Describe the sink a1.sinks.k1.type = logger # Use a channel which buffers events in memory a1.channels.c1.type = memory a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
上述配置文件配置了一个flume agent,其名称为a1,包含一个名为r1的source、名为c1的channel和名为k1的sink,数据流方向为r1-->c1-->k1。各组件的详细属性如下:
| 组件/属性 | 名称 | type | bind | port | channel | capacity | transactionCapacity |
| source | r1 | netcat | localhost | 44444 | c1 | 无 | 无 |
| channel | c1 | memory | 无 | 无 | 无 | 1000 | 100 |
| sink | k1 | logger | 无 | 无 | c1 | 无 | 无 |
在flume的安装目录执行如下命令启动该flume agent:(备注:example.conf位于flume安装目录下)
bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf --conf-file example.conf --name a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
命令参数解释:
1.--conf conf指定配置文件目录为当前目录下的conf目录;(注意:该目录下必须有flume-enx.sh文件和log4j的配置文件,否则运行失败)
2.--conf-file example.conf指定配置文件为当前目录的example.conf文件;
3.--name a1指定agent名称为a1;
4.-Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console指定日志输出级别为INFO,且输出目的地为控制台。
启动信息如下:
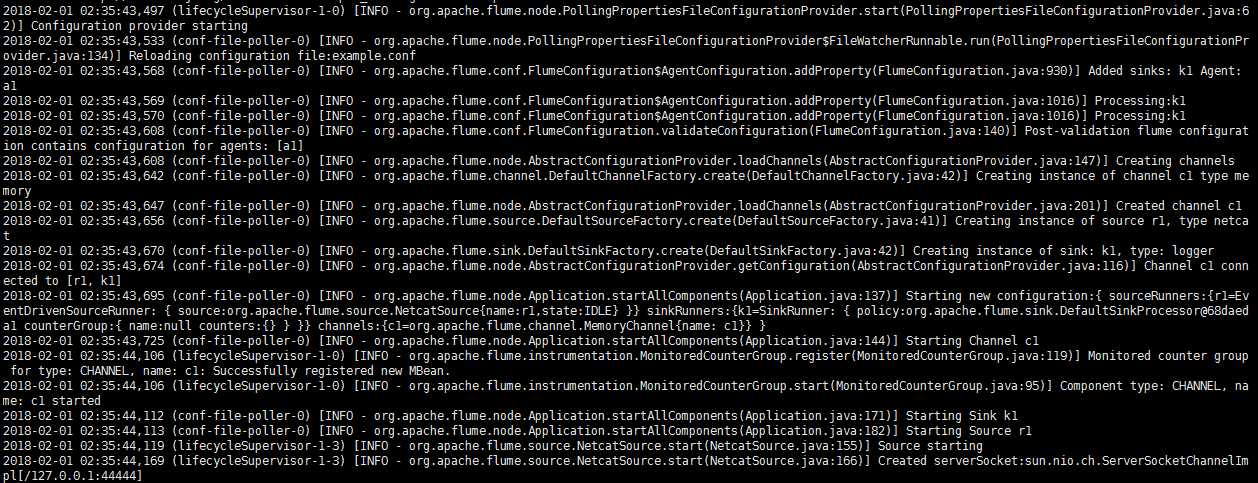
当向localhost:44444通过TCP连接发送数据时,该flume agent将会接收到发送的数据并打印在控制台:
1.通过telnet建立TCP连接并发送数据:
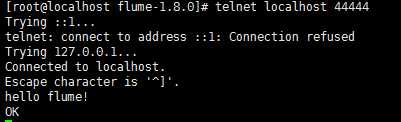
2.agent接收数据并打印在控制台:

