1. 从网上找到一张归并排序的图解,如下:
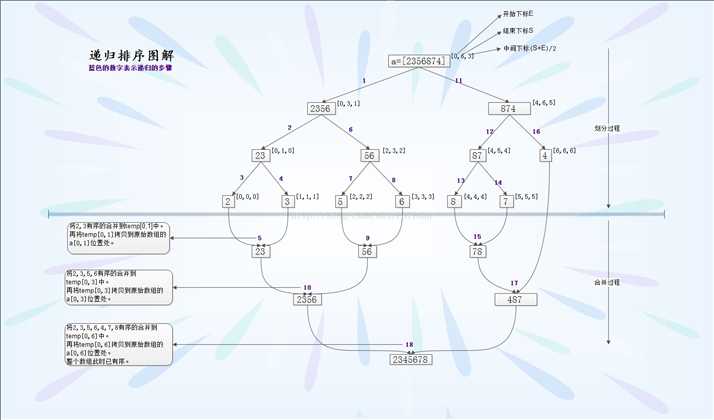
可以看出,归并排序主要运用分治的思想,将要排序的数组由大化小,分别排序后再进行合并。时间复杂度是 O(nlogn)。
2. 归并排序的特点:
优点:稳定
缺点:需要线性的额外空间
3. JAVA代码如下:
public class GB { //将两个有序数组合并成一个数组,此处是将一个数组分为两个有序,再合并 private void Merge(int []a,int first,int mid, int last, int [] temp) { int i = first; int m = mid; int j = mid+1; int n = last; int k = 0; while( i<=m && j<=n) { if(a[i]<=a[j]) temp[k++] = a[i++]; else temp[k++] = a[j++]; } while(i <= m) temp[k++] = a[i++]; while(j <= n) temp[k++] = a[j++]; for(int z=0;z<k;z++) { a[first+z] = temp[z]; } } private void sort(int [] a, int first, int last, int [] temp) { if(first < last) { int mid = (first+last)/2; //分的过程: this.sort(a,first,mid,temp); this.sort(a,mid+1,last,temp); //治的过程: this.Merge(a,first,mid,last,temp); } } public void Sort(int [] a) { int [] temp = new int[a.length]; this.sort(a, 0, a.length-1, temp); } public void print(int [] a) { for(int i : a) System.out.print(i+" "); System.out.println(); } public static void main(String[] args) { int [] a = {2,5,1,2,8,5,9,10,4}; GB gb = new GB(); gb.print(a); gb.Sort(a); gb.print(a); } }
