下篇介绍DispatcherServlet的逻辑处理。
我们知道在HttpServlet类中分别提供了相应的服务方法,它们是doDelete(),doGet(),doOptions(),doPost(),doPut()和doTrace(),它会根据请求的不同形式将程序引导至对应的函数进行处理。这几个函数中最常用的函数无非就是doGet()和doPost(),那么先看看DispatcherServlet中对这两个函数的逻辑实现。
FrameworkServlet类中
/** * Delegate GET requests to processRequest/doService. * <p>Will also be invoked by HttpServlet‘s default implementation of {@code doHead}, * with a {@code NoBodyResponse} that just captures the content length. * @see #doService * @see #doHead */ @Override protected final void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { processRequest(request, response); } /** * Delegate POST requests to {@link #processRequest}. * @see #doService */ @Override protected final void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { processRequest(request, response); }
对于不同的方法,Spring并没有做特殊处理,而是统一将程序再一次地引导至processRequest(request, response)中。FrameworkServlet类中processRequest方法如下:
/** * Process this request, publishing an event regardless of the outcome. * <p>The actual event handling is performed by the abstract * {@link #doService} template method. */ protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); Throwable failureCause = null; LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext(); LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request); RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes(); ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes); WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor()); initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes); try { doService(request, response); } catch (ServletException ex) { failureCause = ex; throw ex; } catch (IOException ex) { failureCause = ex; throw ex; } catch (Throwable ex) { failureCause = ex; throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", ex); } finally { resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes); if (requestAttributes != null) { requestAttributes.requestCompleted(); } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { if (failureCause != null) { this.logger.debug("Could not complete request", failureCause); } else { if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { logger.debug("Leaving response open for concurrent processing"); } else { this.logger.debug("Successfully completed request"); } } } publishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, failureCause); } }
函数中已经开始了对请求的处理,虽然把细节转移到了doService函数中实现,但是我们不难看出处理请求前后所做的准备与处理工作。
- 为了保证当前线程的LocaleContext以及RequestAttributes可以在当前请求后还能恢复,提取当前线程的两个属性。
- 根据当前request创建对应的LocaleContext和RequestAttributes,并绑定到当前线程。
- 委托给doService方法进一步处理。
- 请求处理结束后恢复线程到原始状态。
- 请求处理结束后无论成功与否发布事件通知。
继续查看DispatcherServlet类中的doService方法。
/** * Exposes the DispatcherServlet-specific request attributes and delegates to {@link #doDispatch} * for the actual dispatching. */ @Override protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { String resumed = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).hasConcurrentResult() ? " resumed" : ""; logger.debug("DispatcherServlet with name ‘" + getServletName() + "‘" + resumed + " processing " + request.getMethod() + " request for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "]"); } // Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include, // to be able to restore the original attributes after the include. Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null; if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) { attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<String, Object>(); Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames(); while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) { String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement(); if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith("org.springframework.web.servlet")) { attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName)); } } } // Make framework objects available to handlers and view objects. request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext()); request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver); request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver); request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource()); FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response); if (inputFlashMap != null) { request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap)); } request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap()); request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager); try { doDispatch(request, response); } finally { if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { // Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include. if (attributesSnapshot != null) { restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot); } } } }
在该方法中同样是一些准备工作,但是这些准备工作却是必不可少的。Spring将已经初始化的功能辅助工具变量,比如WebApplicationContext,LocaleResolver,ThemeResolver等设置在request属性中。下面看看DispatcherServlet类中的doDispatch方法:
/** * Process the actual dispatching to the handler. * <p>The handler will be obtained by applying the servlet‘s HandlerMappings in order. * The HandlerAdapter will be obtained by querying the servlet‘s installed HandlerAdapters * to find the first that supports the handler class. * <p>All HTTP methods are handled by this method. It‘s up to HandlerAdapters or handlers * themselves to decide which methods are acceptable. * @param request current HTTP request * @param response current HTTP response * @throws Exception in case of any kind of processing failure */ protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request; HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null; boolean multipartRequestParsed = false; WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); try { ModelAndView mv = null; Exception dispatchException = null; try { processedRequest = checkMultipart(request); multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request); // Determine handler for the current request. mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest); if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) { noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response); return; } // Determine handler adapter for the current request. HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()); // Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler. String method = request.getMethod(); boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method); if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) { long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified); } if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) { return; } } if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) { return; } // Actually invoke the handler. mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { return; } applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv); mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv); } catch (Exception ex) { dispatchException = ex; } catch (Throwable err) { // As of 4.3, we‘re processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well, // making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios. dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err); } processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException); } catch (Exception ex) { triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex); } catch (Throwable err) { triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err)); } finally { if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { // Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion if (mappedHandler != null) { mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response); } } else { // Clean up any resources used by a multipart request. if (multipartRequestParsed) { cleanupMultipart(processedRequest); } } } }
doDispatch函数中展示了Spring请求处理所涉及的主要逻辑,而我们之前设置在request中的各种辅助属性也都有被派上用场了。下面回顾一下逻辑处理的全过程。
一:MultipartContent类型的request处理
对于请求的处理,Spring首先考虑的是对于Multipart的处理,如果是MultipartContent类型的request,则转换request为MultipartHttpServletRequest类型的request。
/** * Convert the request into a multipart request, and make multipart resolver available. * <p>If no multipart resolver is set, simply use the existing request. * @param request current HTTP request * @return the processed request (multipart wrapper if necessary) * @see MultipartResolver#resolveMultipart */ protected HttpServletRequest checkMultipart(HttpServletRequest request) throws MultipartException { if (this.multipartResolver != null && this.multipartResolver.isMultipart(request)) {
//原始请求是否是MultipartHttpServletRequest类型 if (WebUtils.getNativeRequest(request, MultipartHttpServletRequest.class) != null) { logger.debug("Request is already a MultipartHttpServletRequest - if not in a forward, " + "this typically results from an additional MultipartFilter in web.xml"); } else if (hasMultipartException(request) ) { logger.debug("Multipart resolution failed for current request before - " + "skipping re-resolution for undisturbed error rendering"); } else { try { return this.multipartResolver.resolveMultipart(request); } catch (MultipartException ex) { if (request.getAttribute(WebUtils.ERROR_EXCEPTION_ATTRIBUTE) != null) { logger.debug("Multipart resolution failed for error dispatch", ex); // Keep processing error dispatch with regular request handle below } else { throw ex; } } } } // If not returned before: return original request. return request; }
/** * Return an appropriate request object of the specified type, if available, * unwrapping the given request as far as necessary. * @param request the servlet request to introspect * @param requiredType the desired type of request object * @return the matching request object, or {@code null} if none * of that type is available */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public static <T> T getNativeRequest(ServletRequest request, Class<T> requiredType) { if (requiredType != null) { if (requiredType.isInstance(request)) { return (T) request; } else if (request instanceof ServletRequestWrapper) { return getNativeRequest(((ServletRequestWrapper) request).getRequest(), requiredType); } } return null; }
二:根据request信息寻找对应的Handler

在Spring加载的过程中,Spring会将类型为SimpleUrlHandlerMapping的实例加载到this.handlerMappings中。
/** * Return the HandlerExecutionChain for this request. * <p>Tries all handler mappings in order. * @param request current HTTP request * @return the HandlerExecutionChain, or {@code null} if no handler could be found */ protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { for (HandlerMapping hm : this.handlerMappings) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace( "Testing handler map [" + hm + "] in DispatcherServlet with name ‘" + getServletName() + "‘"); } HandlerExecutionChain handler = hm.getHandler(request); if (handler != null) { return handler; } } return null; }
在系统启动时Spring会将所有的映射类型的bean注册到this.handlerMappings变量中,所以此函数的目的就是遍历所有的HandlerMapping,并调用其getHandler方法进行封装处理。以SimpleUrlHandlerMapping为例,查看其继承关系和getHandler方法:
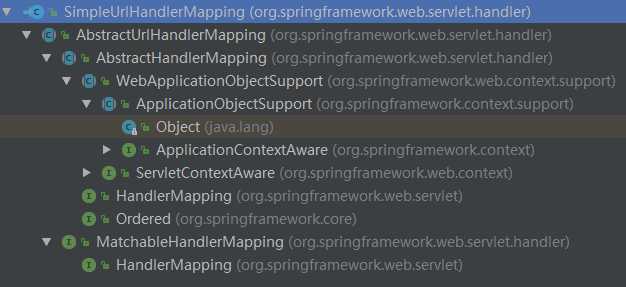
(1)根据request查找对应的Handler
在AbstractHandlerMapping类中
/** * Look up a handler for the given request, falling back to the default * handler if no specific one is found. * @param request current HTTP request * @return the corresponding handler instance, or the default handler * @see #getHandlerInternal */ @Override public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request); if (handler == null) { handler = getDefaultHandler(); } if (handler == null) { return null; } // Bean name or resolved handler? if (handler instanceof String) { String handlerName = (String) handler; handler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName); } HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request); if (CorsUtils.isCorsRequest(request)) { CorsConfiguration globalConfig = this.corsConfigSource.getCorsConfiguration(request); CorsConfiguration handlerConfig = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request); CorsConfiguration config = (globalConfig != null ? globalConfig.combine(handlerConfig) : handlerConfig); executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config); } return executionChain; }
下面再介绍两个接口:
public interface HandlerMapping { /** * Name of the {@link HttpServletRequest} attribute that contains the path * within the handler mapping, in case of a pattern match, or the full * relevant URI (typically within the DispatcherServlet‘s mapping) else. * <p>Note: This attribute is not required to be supported by all * HandlerMapping implementations. URL-based HandlerMappings will * typically support it, but handlers should not necessarily expect * this request attribute to be present in all scenarios. */ String PATH_WITHIN_HANDLER_MAPPING_ATTRIBUTE = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".pathWithinHandlerMapping"; /** * Name of the {@link HttpServletRequest} attribute that contains the * best matching pattern within the handler mapping. * <p>Note: This attribute is not required to be supported by all * HandlerMapping implementations. URL-based HandlerMappings will * typically support it, but handlers should not necessarily expect * this request attribute to be present in all scenarios. */ String BEST_MATCHING_PATTERN_ATTRIBUTE = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".bestMatchingPattern"; /** * Name of the boolean {@link HttpServletRequest} attribute that indicates * whether type-level mappings should be inspected. * <p>Note: This attribute is not required to be supported by all * HandlerMapping implementations. */ String INTROSPECT_TYPE_LEVEL_MAPPING = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".introspectTypeLevelMapping"; /** * Name of the {@link HttpServletRequest} attribute that contains the URI * templates map, mapping variable names to values. * <p>Note: This attribute is not required to be supported by all * HandlerMapping implementations. URL-based HandlerMappings will * typically support it, but handlers should not necessarily expect * this request attribute to be present in all scenarios. */ String URI_TEMPLATE_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".uriTemplateVariables"; /** * Name of the {@link HttpServletRequest} attribute that contains a map with * URI matrix variables. * <p>Note: This attribute is not required to be supported by all * HandlerMapping implementations and may also not be present depending on * whether the HandlerMapping is configured to keep matrix variable content * in the request URI. */ String MATRIX_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".matrixVariables"; /** * Name of the {@link HttpServletRequest} attribute that contains the set of * producible MediaTypes applicable to the mapped handler. * <p>Note: This attribute is not required to be supported by all * HandlerMapping implementations. Handlers should not necessarily expect * this request attribute to be present in all scenarios. */ String PRODUCIBLE_MEDIA_TYPES_ATTRIBUTE = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".producibleMediaTypes"; /** * Return a handler and any interceptors for this request. The choice may be made * on request URL, session state, or any factor the implementing class chooses. * <p>The returned HandlerExecutionChain contains a handler Object, rather than * even a tag interface, so that handlers are not constrained in any way. * For example, a HandlerAdapter could be written to allow another framework‘s * handler objects to be used. * <p>Returns {@code null} if no match was found. This is not an error. * The DispatcherServlet will query all registered HandlerMapping beans to find * a match, and only decide there is an error if none can find a handler. * @param request current HTTP request * @return a HandlerExecutionChain instance containing handler object and * any interceptors, or {@code null} if no mapping found * @throws Exception if there is an internal error */ HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception; }
public interface MatchableHandlerMapping extends HandlerMapping { /** * Determine whether the given request matches the request criteria. * @param request the current request * @param pattern the pattern to match * @return the result from request matching, or {@code null} if none */ RequestMatchResult match(HttpServletRequest request, String pattern); }
在getHandler方法中调用了getHandlerInternal(request)方法,在AbstractUrlHandlerMapping类中实现了该抽象方法
/** * Look up a handler for the URL path of the given request. * @param request current HTTP request * @return the handler instance, or {@code null} if none found */ @Override protected Object getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
//截取用于匹配的url有效路径 String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request);
//根据路径寻找Handler Object handler = lookupHandler(lookupPath, request); if (handler == null) { // We need to care for the default handler directly, since we need to // expose the PATH_WITHIN_HANDLER_MAPPING_ATTRIBUTE for it as well. Object rawHandler = null; if ("/".equals(lookupPath)) { rawHandler = getRootHandler(); } if (rawHandler == null) { rawHandler = getDefaultHandler(); } if (rawHandler != null) { // Bean name or resolved handler? if (rawHandler instanceof String) { String handlerName = (String) rawHandler; rawHandler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName); } validateHandler(rawHandler, request); handler = buildPathExposingHandler(rawHandler, lookupPath, lookupPath, null); } } if (handler != null && logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Mapping [" + lookupPath + "] to " + handler); } else if (handler == null && logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("No handler mapping found for [" + lookupPath + "]"); } return handler; }
函数中首先会使用getHandlerInternal方法根据request信息获取对应的Handler,如果以SimpleUrlHandlerMapping为例分析,那么我们推断此步骤提供的功能很可能就是根据URL找到匹配的Controller并返回,当然如果没有找到对应的Controller处理器那么程序会尝试去查找配置中的默认处理器,当查找的controller为String类型时,那就意味着返回的是配置的bean名称,需要根据bean名称查找对应的bean。最后,还要根据getHandlerExecutionChain方法对返回的Handler进行封装,以保证满足返回类型的匹配。
AbstractUrlHandlerMapping类中lookupHandler方法
/** * Look up a handler instance for the given URL path. * <p>Supports direct matches, e.g. a registered "/test" matches "/test", * and various Ant-style pattern matches, e.g. a registered "/t*" matches * both "/test" and "/team". For details, see the AntPathMatcher class. * <p>Looks for the most exact pattern, where most exact is defined as * the longest path pattern. * @param urlPath URL the bean is mapped to * @param request current HTTP request (to expose the path within the mapping to) * @return the associated handler instance, or {@code null} if not found * @see #exposePathWithinMapping * @see org.springframework.util.AntPathMatcher */ protected Object lookupHandler(String urlPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { // Direct match?
//直接匹配情况的处理 Object handler = this.handlerMap.get(urlPath); if (handler != null) { // Bean name or resolved handler? if (handler instanceof String) { String handlerName = (String) handler; handler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName); } validateHandler(handler, request); return buildPathExposingHandler(handler, urlPath, urlPath, null); } // Pattern match?
//通配符匹配的处理 List<String> matchingPatterns = new ArrayList<String>(); for (String registeredPattern : this.handlerMap.keySet()) { if (getPathMatcher().match(registeredPattern, urlPath)) { matchingPatterns.add(registeredPattern); } else if (useTrailingSlashMatch()) { if (!registeredPattern.endsWith("/") && getPathMatcher().match(registeredPattern + "/", urlPath)) { matchingPatterns.add(registeredPattern +"/"); } } } String bestMatch = null; Comparator<String> patternComparator = getPathMatcher().getPatternComparator(urlPath); if (!matchingPatterns.isEmpty()) { Collections.sort(matchingPatterns, patternComparator); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Matching patterns for request [" + urlPath + "] are " + matchingPatterns); } bestMatch = matchingPatterns.get(0); } if (bestMatch != null) { handler = this.handlerMap.get(bestMatch); if (handler == null) { if (bestMatch.endsWith("/")) { handler = this.handlerMap.get(bestMatch.substring(0, bestMatch.length() - 1)); } if (handler == null) { throw new IllegalStateException( "Could not find handler for best pattern match [" + bestMatch + "]"); } } // Bean name or resolved handler? if (handler instanceof String) { String handlerName = (String) handler; handler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName); } validateHandler(handler, request); String pathWithinMapping = getPathMatcher().extractPathWithinPattern(bestMatch, urlPath); // There might be multiple ‘best patterns‘, let‘s make sure we have the correct URI template variables // for all of them Map<String, String> uriTemplateVariables = new LinkedHashMap<String, String>(); for (String matchingPattern : matchingPatterns) { if (patternComparator.compare(bestMatch, matchingPattern) == 0) { Map<String, String> vars = getPathMatcher().extractUriTemplateVariables(matchingPattern, urlPath); Map<String, String> decodedVars = getUrlPathHelper().decodePathVariables(request, vars); uriTemplateVariables.putAll(decodedVars); } } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("URI Template variables for request [" + urlPath + "] are " + uriTemplateVariables); } return buildPathExposingHandler(handler, bestMatch, pathWithinMapping, uriTemplateVariables); } // No handler found... return null; }
根据URL获取对应Handler的匹配规则代码实现起来虽然很长,但是不难理解,考虑了直接匹配与通配符两种情况。其中,buildPathExposingHandler函数将Handler封装成了HandlerExecutionChain类型。
AbstractUrlHandlerMapping类中
/** * Build a handler object for the given raw handler, exposing the actual * handler, the {@link #PATH_WITHIN_HANDLER_MAPPING_ATTRIBUTE}, as well as * the {@link #URI_TEMPLATE_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE} before executing the handler. * <p>The default implementation builds a {@link HandlerExecutionChain} * with a special interceptor that exposes the path attribute and uri template variables * @param rawHandler the raw handler to expose * @param pathWithinMapping the path to expose before executing the handler * @param uriTemplateVariables the URI template variables, can be {@code null} if no variables found * @return the final handler object */ protected Object buildPathExposingHandler(Object rawHandler, String bestMatchingPattern, String pathWithinMapping, Map<String, String> uriTemplateVariables) { HandlerExecutionChain chain = new HandlerExecutionChain(rawHandler); chain.addInterceptor(new PathExposingHandlerInterceptor(bestMatchingPattern, pathWithinMapping)); if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(uriTemplateVariables)) { chain.addInterceptor(new UriTemplateVariablesHandlerInterceptor(uriTemplateVariables)); } return chain; }
在函数中我们看到了通过将Handler以参数形式传入,并构建HandlerExecutionChain类型实例,加入了两个拦截器。
(2)加入拦截器到执行链
getHandlerExecutionChain函数最主要的目的是将配置中的对应拦截器加入到执行链中,以保证这些拦截器可以有效地作用于目标对象。
AbstractHandlerMapping类中
/** * Build a {@link HandlerExecutionChain} for the given handler, including * applicable interceptors. * <p>The default implementation builds a standard {@link HandlerExecutionChain} * with the given handler, the handler mapping‘s common interceptors, and any * {@link MappedInterceptor}s matching to the current request URL. Interceptors * are added in the order they were registered. Subclasses may override this * in order to extend/rearrange the list of interceptors. * <p><b>NOTE:</b> The passed-in handler object may be a raw handler or a * pre-built {@link HandlerExecutionChain}. This method should handle those * two cases explicitly, either building a new {@link HandlerExecutionChain} * or extending the existing chain. * <p>For simply adding an interceptor in a custom subclass, consider calling * {@code super.getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request)} and invoking * {@link HandlerExecutionChain#addInterceptor} on the returned chain object. * @param handler the resolved handler instance (never {@code null}) * @param request current HTTP request * @return the HandlerExecutionChain (never {@code null}) * @see #getAdaptedInterceptors() */ protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) { HandlerExecutionChain chain = (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain ? (HandlerExecutionChain) handler : new HandlerExecutionChain(handler)); String lookupPath = this.urlPathHelper.getLookupPathForRequest(request); for (HandlerInterceptor interceptor : this.adaptedInterceptors) { if (interceptor instanceof MappedInterceptor) { MappedInterceptor mappedInterceptor = (MappedInterceptor) interceptor; if (mappedInterceptor.matches(lookupPath, this.pathMatcher)) { chain.addInterceptor(mappedInterceptor.getInterceptor()); } } else { chain.addInterceptor(interceptor); } } return chain; }
三:没找到对应的Handler的错误处理
每个请求都应该对应着一个Handler,因为每个请求都会在后台有相应的逻辑对应,而逻辑的实现就是在Handler中,所以一旦没有找到Handler的情况(正常情况下如果没有URL匹配的Handler,开发人员可以设置默认的Handler来处理请求,但是如果默认请求也未设置就会出现Handler为空的情况),就只能通过response向用户返回错误信息。
DispatcherServlet类中
/** * No handler found -> set appropriate HTTP response status. * @param request current HTTP request * @param response current HTTP response * @throws Exception if preparing the response failed */ protected void noHandlerFound(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { if (pageNotFoundLogger.isWarnEnabled()) { pageNotFoundLogger.warn("No mapping found for HTTP request with URI [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] in DispatcherServlet with name ‘" + getServletName() + "‘"); }
//this.throwExceptionIfNoHandlerFound默认为false if (this.throwExceptionIfNoHandlerFound) { throw new NoHandlerFoundException(request.getMethod(), getRequestUri(request), new ServletServerHttpRequest(request).getHeaders()); } else { response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND); } }
四:根据当前Handler寻找对应的HandlerAdapter
在WebApplicationContext的初始化过程中我们讨论了HandlerAdapters的初始化,了解了在默认情况下普通的Web请求会交给SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter去处理。下面我们以SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter为例来分析获取适配器的逻辑。
DispatcherServlet类中
/** * Return the HandlerAdapter for this handler object. * @param handler the handler object to find an adapter for * @throws ServletException if no HandlerAdapter can be found for the handler. This is a fatal error. */ protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException { for (HandlerAdapter ha : this.handlerAdapters) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Testing handler adapter [" + ha + "]"); } if (ha.supports(handler)) { return ha; } } throw new ServletException("No adapter for handler [" + handler + "]: The DispatcherServlet configuration needs to include a HandlerAdapter that supports this handler"); }
SimpleControllerHandlerApapter类
public class SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter implements HandlerAdapter { @Override public boolean supports(Object handler) { return (handler instanceof Controller); } @Override public ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { return ((Controller) handler).handleRequest(request, response); } @Override public long getLastModified(HttpServletRequest request, Object handler) { if (handler instanceof LastModified) { return ((LastModified) handler).getLastModified(request); } return -1L; } }
对应SpringMVC来说,我们会把逻辑封装至Controller的子类中。
HandlerAdapter接口
public interface HandlerAdapter { /** * Given a handler instance, return whether or not this {@code HandlerAdapter} * can support it. Typical HandlerAdapters will base the decision on the handler * type. HandlerAdapters will usually only support one handler type each. * <p>A typical implementation: * <p>{@code * return (handler instanceof MyHandler); * } * @param handler handler object to check * @return whether or not this object can use the given handler */ boolean supports(Object handler); /** * Use the given handler to handle this request. * The workflow that is required may vary widely. * @param request current HTTP request * @param response current HTTP response * @param handler handler to use. This object must have previously been passed * to the {@code supports} method of this interface, which must have * returned {@code true}. * @throws Exception in case of errors * @return ModelAndView object with the name of the view and the required * model data, or {@code null} if the request has been handled directly */ ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception; /** * Same contract as for HttpServlet‘s {@code getLastModified} method. * Can simply return -1 if there‘s no support in the handler class. * @param request current HTTP request * @param handler handler to use * @return the lastModified value for the given handler * @see javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet#getLastModified * @see org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.LastModified#getLastModified */ long getLastModified(HttpServletRequest request, Object handler); }
五:HandlerInterceptor的处理
Servlet API定义的servlet过滤器可以在servlet处理每个Web请求的前后分别对它进行前置处理和后置处理。有些时候,你可能只想处理由某些SpringMVC处理程序处理的Web请求,并在这些处理程序返回的模型属性被传递到视图之前,对它们进行一些操作。
SpringMVC允许你通过处理拦截Web请求,进行前置和后置处理。每个处理拦截都必须实现HandlerInterceptor接口,它包含三个需要你实现的回调方法:preHandle(),postHandle()和afterCompletion()。第一个和第二个方法分别是在处理程序处理请求之前和之后被调用的。第二个方法还允许访问返回的ModelAndView对象,因此可以在它里面操作模型属性。最后一个是在所有请求处理完成之后被调用的(如视图呈现之后)。
六:逻辑处理
对于逻辑处理其实是通过适配器中转调用Handler并返回视图的,对应代码:
// Actually invoke the handler. mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
对于普通的Web请求,Spring默认使用SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter类进行处理,我们进入该类的handle方法:
@Override public ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { return ((Controller) handler).handleRequest(request, response); }
下面再看看Controller接口:
public interface Controller { /** * Process the request and return a ModelAndView object which the DispatcherServlet * will render. A {@code null} return value is not an error: it indicates that * this object completed request processing itself and that there is therefore no * ModelAndView to render. * @param request current HTTP request * @param response current HTTP response * @return a ModelAndView to render, or {@code null} if handled directly * @throws Exception in case of errors */ ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception; }
再看看AbstractController类:
public abstract class AbstractController extends WebContentGenerator implements Controller { private boolean synchronizeOnSession = false; /** * Create a new AbstractController which supports * HTTP methods GET, HEAD and POST by default. */ public AbstractController() { this(true); } /** * Create a new AbstractController. * @param restrictDefaultSupportedMethods {@code true} if this * controller should support HTTP methods GET, HEAD and POST by default, * or {@code false} if it should be unrestricted * @since 4.3 */ public AbstractController(boolean restrictDefaultSupportedMethods) { super(restrictDefaultSupportedMethods); } /** * Set if controller execution should be synchronized on the session, * to serialize parallel invocations from the same client. * <p>More specifically, the execution of the {@code handleRequestInternal} * method will get synchronized if this flag is "true". The best available * session mutex will be used for the synchronization; ideally, this will * be a mutex exposed by HttpSessionMutexListener. * <p>The session mutex is guaranteed to be the same object during * the entire lifetime of the session, available under the key defined * by the {@code SESSION_MUTEX_ATTRIBUTE} constant. It serves as a * safe reference to synchronize on for locking on the current session. * <p>In many cases, the HttpSession reference itself is a safe mutex * as well, since it will always be the same object reference for the * same active logical session. However, this is not guaranteed across * different servlet containers; the only 100% safe way is a session mutex. * @see AbstractController#handleRequestInternal * @see org.springframework.web.util.HttpSessionMutexListener * @see org.springframework.web.util.WebUtils#getSessionMutex(javax.servlet.http.HttpSession) */ public final void setSynchronizeOnSession(boolean synchronizeOnSession) { this.synchronizeOnSession = synchronizeOnSession; } /** * Return whether controller execution should be synchronized on the session. */ public final boolean isSynchronizeOnSession() { return this.synchronizeOnSession; } @Override public ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { if (HttpMethod.OPTIONS.matches(request.getMethod())) { response.setHeader("Allow", getAllowHeader()); return null; } // Delegate to WebContentGenerator for checking and preparing. checkRequest(request); prepareResponse(response); // Execute handleRequestInternal in synchronized block if required. if (this.synchronizeOnSession) { HttpSession session = request.getSession(false); if (session != null) { Object mutex = WebUtils.getSessionMutex(session); synchronized (mutex) { return handleRequestInternal(request, response); } } } return handleRequestInternal(request, response); } /** * Template method. Subclasses must implement this. * The contract is the same as for {@code handleRequest}. * @see #handleRequest */ protected abstract ModelAndView handleRequestInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception; }
我们可以继承自AbstractController并实现handleRequestInternal来实现逻辑部分完成相应的逻辑处理。
七:异常视图的处理
在doDispatch函数中对最后结果进行了统一处理
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
/** * Handle the result of handler selection and handler invocation, which is * either a ModelAndView or an Exception to be resolved to a ModelAndView. */ private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, ModelAndView mv, Exception exception) throws Exception { boolean errorView = false; if (exception != null) { if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException) { logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", exception); mv = ((ModelAndViewDefiningException) exception).getModelAndView(); } else { Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null); mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception); errorView = (mv != null); } } // Did the handler return a view to render? if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) { render(mv, request, response); if (errorView) { WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request); } } else { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Null ModelAndView returned to DispatcherServlet with name ‘" + getServletName() + "‘: assuming HandlerAdapter completed request handling"); } } if (WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { // Concurrent handling started during a forward return; } if (mappedHandler != null) { mappedHandler.triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null); } }
异常处理:
/** * Determine an error ModelAndView via the registered HandlerExceptionResolvers. * @param request current HTTP request * @param response current HTTP response * @param handler the executed handler, or {@code null} if none chosen at the time of the exception * (for example, if multipart resolution failed) * @param ex the exception that got thrown during handler execution * @return a corresponding ModelAndView to forward to * @throws Exception if no error ModelAndView found */ protected ModelAndView processHandlerException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception { // Check registered HandlerExceptionResolvers... ModelAndView exMv = null; for (HandlerExceptionResolver handlerExceptionResolver : this.handlerExceptionResolvers) { exMv = handlerExceptionResolver.resolveException(request, response, handler, ex); if (exMv != null) { break; } } if (exMv != null) { if (exMv.isEmpty()) { request.setAttribute(EXCEPTION_ATTRIBUTE, ex); return null; } // We might still need view name translation for a plain error model... if (!exMv.hasView()) { exMv.setViewName(getDefaultViewName(request)); } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Handler execution resulted in exception - forwarding to resolved error view: " + exMv, ex); } WebUtils.exposeErrorRequestAttributes(request, ex, getServletName()); return exMv; } throw ex; }
其中,HandlerExceptionResolver接口如下:
public interface HandlerExceptionResolver { /** * Try to resolve the given exception that got thrown during handler execution, * returning a {@link ModelAndView} that represents a specific error page if appropriate. * <p>The returned {@code ModelAndView} may be {@linkplain ModelAndView#isEmpty() empty} * to indicate that the exception has been resolved successfully but that no view * should be rendered, for instance by setting a status code. * @param request current HTTP request * @param response current HTTP response * @param handler the executed handler, or {@code null} if none chosen at the * time of the exception (for example, if multipart resolution failed) * @param ex the exception that got thrown during handler execution * @return a corresponding {@code ModelAndView} to forward to, or {@code null} * for default processing */ ModelAndView resolveException( HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex); }
如果异常解析器解析后返回的ModelAndView为null,则会抛出该异常。
八:根据视图跳转页面
在processDispatchResult函数中,若逻辑处理正常,会调用render函数进行视图跳转的逻辑处理。
DispatcherServlet类中
/** * Render the given ModelAndView. * <p>This is the last stage in handling a request. It may involve resolving the view by name. * @param mv the ModelAndView to render * @param request current HTTP servlet request * @param response current HTTP servlet response * @throws ServletException if view is missing or cannot be resolved * @throws Exception if there‘s a problem rendering the view */ protected void render(ModelAndView mv, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { // Determine locale for request and apply it to the response. Locale locale = this.localeResolver.resolveLocale(request); response.setLocale(locale); View view; if (mv.isReference()) { // We need to resolve the view name. view = resolveViewName(mv.getViewName(), mv.getModelInternal(), locale, request); if (view == null) { throw new ServletException("Could not resolve view with name ‘" + mv.getViewName() + "‘ in servlet with name ‘" + getServletName() + "‘"); } } else { // No need to lookup: the ModelAndView object contains the actual View object. view = mv.getView(); if (view == null) { throw new ServletException("ModelAndView [" + mv + "] neither contains a view name nor a " + "View object in servlet with name ‘" + getServletName() + "‘"); } } // Delegate to the View object for rendering. if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Rendering view [" + view + "] in DispatcherServlet with name ‘" + getServletName() + "‘"); } try { if (mv.getStatus() != null) { response.setStatus(mv.getStatus().value()); } view.render(mv.getModelInternal(), request, response); } catch (Exception ex) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Error rendering view [" + view + "] in DispatcherServlet with name ‘" + getServletName() + "‘", ex); } throw ex; } }
(8.1)解析视图名称
DispatcherServlet会根据ModelAndView选择合适的视图类进行渲染,而这一功能是在DispatcherServlet类的resolveViewName函数中完成的。
/** * Resolve the given view name into a View object (to be rendered). * <p>The default implementations asks all ViewResolvers of this dispatcher. * Can be overridden for custom resolution strategies, potentially based on * specific model attributes or request parameters. * @param viewName the name of the view to resolve * @param model the model to be passed to the view * @param locale the current locale * @param request current HTTP servlet request * @return the View object, or {@code null} if none found * @throws Exception if the view cannot be resolved * (typically in case of problems creating an actual View object) * @see ViewResolver#resolveViewName */ protected View resolveViewName(String viewName, Map<String, Object> model, Locale locale, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { for (ViewResolver viewResolver : this.viewResolvers) { View view = viewResolver.resolveViewName(viewName, locale); if (view != null) { return view; } } return null; }
我们以org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver为例来分析ViewResolver逻辑的解析过程,,其中resolveViewName函数的实现是在其父类AbstractCachingViewResolver中完成的。
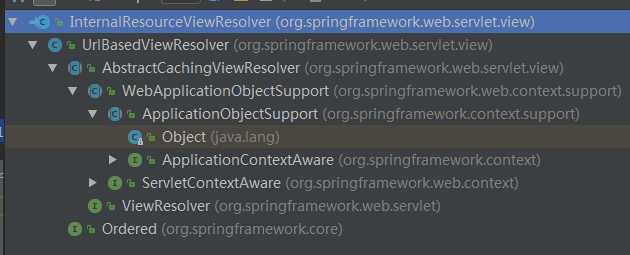
@Override public View resolveViewName(String viewName, Locale locale) throws Exception { if (!isCache()) { return createView(viewName, locale); } else { Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(viewName, locale); View view = this.viewAccessCache.get(cacheKey); if (view == null) { synchronized (this.viewCreationCache) { view = this.viewCreationCache.get(cacheKey); if (view == null) { // Ask the subclass to create the View object. view = createView(viewName, locale); if (view == null && this.cacheUnresolved) { view = UNRESOLVED_VIEW; } if (view != null) { this.viewAccessCache.put(cacheKey, view); this.viewCreationCache.put(cacheKey, view); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Cached view [" + cacheKey + "]"); } } } } } return (view != UNRESOLVED_VIEW ? view : null); } }
/** * Return if caching is enabled. */ public boolean isCache() { return (this.cacheLimit > 0); }
/** Dummy marker object for unresolved views in the cache Maps */ private static final View UNRESOLVED_VIEW = new View() { @Override public String getContentType() { return null; } @Override public void render(Map<String, ?> model, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) { } };
如果首次访问没有相应的视图,也会被缓存下来。
在父类UrlBasedViewResolver中重写了createView函数。
/** * Overridden to implement check for "redirect:" prefix. * <p>Not possible in {@code loadView}, since overridden * {@code loadView} versions in subclasses might rely on the * superclass always creating instances of the required view class. * @see #loadView * @see #requiredViewClass */ @Override protected View createView(String viewName, Locale locale) throws Exception { // If this resolver is not supposed to handle the given view, // return null to pass on to the next resolver in the chain. if (!canHandle(viewName, locale)) { return null; } // Check for special "redirect:" prefix. if (viewName.startsWith(REDIRECT_URL_PREFIX)) { String redirectUrl = viewName.substring(REDIRECT_URL_PREFIX.length()); RedirectView view = new RedirectView(redirectUrl, isRedirectContextRelative(), isRedirectHttp10Compatible()); view.setHosts(getRedirectHosts()); return applyLifecycleMethods(viewName, view); } // Check for special "forward:" prefix. if (viewName.startsWith(FORWARD_URL_PREFIX)) { String forwardUrl = viewName.substring(FORWARD_URL_PREFIX.length()); return new InternalResourceView(forwardUrl); } // Else fall back to superclass implementation: calling loadView. return super.createView(viewName, locale); }
AbstractCachingViewResolver类中
/** * Create the actual View object. * <p>The default implementation delegates to {@link #loadView}. * This can be overridden to resolve certain view names in a special fashion, * before delegating to the actual {@code loadView} implementation * provided by the subclass. * @param viewName the name of the view to retrieve * @param locale the Locale to retrieve the view for * @return the View instance, or {@code null} if not found * (optional, to allow for ViewResolver chaining) * @throws Exception if the view couldn‘t be resolved * @see #loadView */ protected View createView(String viewName, Locale locale) throws Exception { return loadView(viewName, locale); }
UrlBasedViewResolver类中
/** * Delegates to {@code buildView} for creating a new instance of the * specified view class, and applies the following Spring lifecycle methods * (as supported by the generic Spring bean factory): * <ul> * <li>ApplicationContextAware‘s {@code setApplicationContext} * <li>InitializingBean‘s {@code afterPropertiesSet} * </ul> * @param viewName the name of the view to retrieve * @return the View instance * @throws Exception if the view couldn‘t be resolved * @see #buildView(String) * @see org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware#setApplicationContext * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet */ @Override protected View loadView(String viewName, Locale locale) throws Exception { AbstractUrlBasedView view = buildView(viewName); View result = applyLifecycleMethods(viewName, view); return (view.checkResource(locale) ? result : null); }
/** * Creates a new View instance of the specified view class and configures it. * Does <i>not</i> perform any lookup for pre-defined View instances. * <p>Spring lifecycle methods as defined by the bean container do not have to * be called here; those will be applied by the {@code loadView} method * after this method returns. * <p>Subclasses will typically call {@code super.buildView(viewName)} * first, before setting further properties themselves. {@code loadView} * will then apply Spring lifecycle methods at the end of this process. * @param viewName the name of the view to build * @return the View instance * @throws Exception if the view couldn‘t be resolved * @see #loadView(String, java.util.Locale) */ protected AbstractUrlBasedView buildView(String viewName) throws Exception { AbstractUrlBasedView view = (AbstractUrlBasedView) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(getViewClass()); view.setUrl(getPrefix() + viewName + getSuffix()); String contentType = getContentType(); if (contentType != null) { view.setContentType(contentType); } view.setRequestContextAttribute(getRequestContextAttribute()); view.setAttributesMap(getAttributesMap()); Boolean exposePathVariables = getExposePathVariables(); if (exposePathVariables != null) { view.setExposePathVariables(exposePathVariables); } Boolean exposeContextBeansAsAttributes = getExposeContextBeansAsAttributes(); if (exposeContextBeansAsAttributes != null) { view.setExposeContextBeansAsAttributes(exposeContextBeansAsAttributes); } String[] exposedContextBeanNames = getExposedContextBeanNames(); if (exposedContextBeanNames != null) { view.setExposedContextBeanNames(exposedContextBeanNames); } return view; }
InternalResourceViewResolver类中重写了buildView并调用父类 UrlBasedViewResolver类中buildView
@Override protected AbstractUrlBasedView buildView(String viewName) throws Exception { InternalResourceView view = (InternalResourceView) super.buildView(viewName); if (this.alwaysInclude != null) { view.setAlwaysInclude(this.alwaysInclude); } view.setPreventDispatchLoop(true); return view; }

(8.2)页面跳转
在DispatcherServlet类中render函数中,首先解析视图,最后调用了视图的render方法
public interface View { /** * Name of the {@link HttpServletRequest} attribute that contains the response status code. * <p>Note: This attribute is not required to be supported by all View implementations. */ String RESPONSE_STATUS_ATTRIBUTE = View.class.getName() + ".responseStatus"; /** * Name of the {@link HttpServletRequest} attribute that contains a Map with path variables. * The map consists of String-based URI template variable names as keys and their corresponding * Object-based values -- extracted from segments of the URL and type converted. * * <p>Note: This attribute is not required to be supported by all View implementations. */ String PATH_VARIABLES = View.class.getName() + ".pathVariables"; /** * The {@link MediaType} selected during content negotiation, which may be * more specific than the one the View is configured with. For example: * "application/vnd.example-v1+xml" vs "application/*+xml". */ String SELECTED_CONTENT_TYPE = View.class.getName() + ".selectedContentType"; /** * Return the content type of the view, if predetermined. * <p>Can be used to check the content type upfront, * before the actual rendering process. * @return the content type String (optionally including a character set), * or {@code null} if not predetermined. */ String getContentType(); /** * Render the view given the specified model. * <p>The first step will be preparing the request: In the JSP case, * this would mean setting model objects as request attributes. * The second step will be the actual rendering of the view, * for example including the JSP via a RequestDispatcher. * @param model Map with name Strings as keys and corresponding model * objects as values (Map can also be {@code null} in case of empty model) * @param request current HTTP request * @param response HTTP response we are building * @throws Exception if rendering failed */ void render(Map<String, ?> model, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception; }
上面bulidView中的创建的视图是InternalResourceView
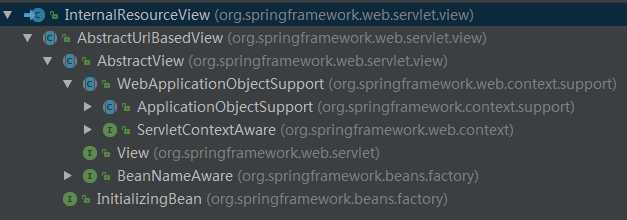
AbstractView类中render方法和 createMergedOutputModel 方法
/** * Prepares the view given the specified model, merging it with static * attributes and a RequestContext attribute, if necessary. * Delegates to renderMergedOutputModel for the actual rendering. * @see #renderMergedOutputModel */ @Override public void render(Map<String, ?> model, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Rendering view with name ‘" + this.beanName + "‘ with model " + model + " and static attributes " + this.staticAttributes); } Map<String, Object> mergedModel = createMergedOutputModel(model, request, response); prepareResponse(request, response); renderMergedOutputModel(mergedModel, getRequestToExpose(request), response); }
将要使用到的属性放入request中,以便在其他地方可以直接调用,而解析这些属性的工作就是在createMergedOutputModel函数中完成的。
/** * Creates a combined output Map (never {@code null}) that includes dynamic values and static attributes. * Dynamic values take precedence over static attributes. */ protected Map<String, Object> createMergedOutputModel(Map<String, ?> model, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Map<String, Object> pathVars = (this.exposePathVariables ? (Map<String, Object>) request.getAttribute(View.PATH_VARIABLES) : null); // Consolidate static and dynamic model attributes. int size = this.staticAttributes.size(); size += (model != null ? model.size() : 0); size += (pathVars != null ? pathVars.size() : 0); Map<String, Object> mergedModel = new LinkedHashMap<String, Object>(size); mergedModel.putAll(this.staticAttributes); if (pathVars != null) { mergedModel.putAll(pathVars); } if (model != null) { mergedModel.putAll(model); } // Expose RequestContext? if (this.requestContextAttribute != null) { mergedModel.put(this.requestContextAttribute, createRequestContext(request, response, mergedModel)); } return mergedModel; }
InternalResourceView类中重写了 renderMergedOutputModel 方法,该方法用来处理页面跳转
/** * Render the internal resource given the specified model. * This includes setting the model as request attributes. */ @Override protected void renderMergedOutputModel( Map<String, Object> model, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { // Expose the model object as request attributes. //将model中的数据以属性的方式设置到request中
exposeModelAsRequestAttributes(model, request); // Expose helpers as request attributes, if any. exposeHelpers(request); // Determine the path for the request dispatcher. String dispatcherPath = prepareForRendering(request, response); // Obtain a RequestDispatcher for the target resource (typically a JSP). RequestDispatcher rd = getRequestDispatcher(request, dispatcherPath); if (rd == null) { throw new ServletException("Could not get RequestDispatcher for [" + getUrl() + "]: Check that the corresponding file exists within your web application archive!"); } // If already included or response already committed, perform include, else forward. if (useInclude(request, response)) { response.setContentType(getContentType()); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Including resource [" + getUrl() + "] in InternalResourceView ‘" + getBeanName() + "‘"); } rd.include(request, response); } else { // Note: The forwarded resource is supposed to determine the content type itself. if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Forwarding to resource [" + getUrl() + "] in InternalResourceView ‘" + getBeanName() + "‘"); } rd.forward(request, response); } }
