前言:这是初学时写的小项目,觉得有意思就写来玩玩,也当是巩固刚学习的知识。现在看来很不成熟,但还是记录一下做个纪念好了~
1、名称:网上网上银行及购物商城
2、项目结构:
当时刚接触python啦,哪里注意什么项目结构,就一脑子全塞到一个文件里面了
- 代码全部在bank.py里面
- admin.txt记录所有用户的名字和密码(当时还不会用数据库)
- locked.txt记录被锁定用户的帐号
- huahua.pk是记录huahua这个用户的流水和消费情况
3、效果:
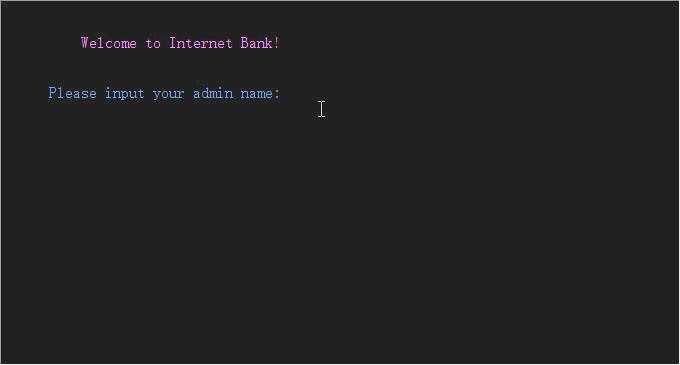
4、主要功能
1.网上银行功能:
- 能显示用户名与余额
- 输入密码三次错误就锁定
- 实现取钱,手续费3%
- 将取钱记录写入账单中
- 查看月流水
- 每月的最后一天出账单
2.购物商城功能:
- 选购商品
- 可以使用信用卡
- 查看购物车
- 购物车增加、删除商品
- 结算扣款计入月账单
5、设计过程
5.1首先设置admin.txt中的用户名和密码
5.2很骚气的设置打印出字体的颜色

# 设置打印字体的颜色 class change_color: HEADER = ‘\033[95m‘ OKBLUE = ‘\033[94m‘ OKGREEN = ‘\033[92m‘ WARNING = ‘\033[93m‘ FAIL = ‘\033[91m‘ ENDC = ‘\033[0m‘ def disable(self): self.HEADER = ‘‘ self.OKBLUE = ‘‘ self.OKGREEN = ‘‘ self.WARNING = ‘‘ self.FAIL = ‘‘ self.ENDC = ‘‘
5.3验证帐号的函数
判断帐号是否存在、锁定、密码是否正确,三次密码不正确就锁定该用户(写入lock 文件)

# 判断帐号是否存在 def admin_is_exist(user_admin): with open(admin_file, ‘rb‘) as li: for i in li.readlines(): i = i.strip().split() if user_admin in i: return True else: print ‘\n\t\t\t‘+change_color.WARNING+‘This admin is not exist! Please try again!‘+change_color.ENDC return False # 判断帐号是否被锁定 def admin_is_locked(user_admin): with open(lock_file, ‘rb‘) as lock: for i in lock.xreadlines(): i = i.strip().split() if user_admin in i: print ‘\n\t\t\t‘+change_color.WARNING+‘This admin in locked! Please try another admin!‘+change_color.ENDC return False else: return True # 判断密码是否匹配 def password_is_match(user_admin, pass_word): with open(admin_file, ‘rb‘) as admin: for i in admin.readlines(): i = i.strip().split() if user_admin in i: if pass_word == i[1]: return True else: return False # 锁定用户 def lock_user(user_admin): lock = open(lock_file, ‘ab‘) lock.write(‘\n‘ + user_admin) lock.close() print ‘\n\t\t\t‘+change_color.WARNING+‘Password do not match admin for 3 times! Admin is locked!‘+change_color.ENDC
5.4网上银行相关函数
给每个用户建立一个以该用户名为标题的账单、写入月账单、写入并读取余额、取钱、打印用户流水

# 计算提现所需的余额(包括手续费) def caculate_cash_with_fee(cash): total = cash + cash * 0.05 return total # 计算取现后的余额 def balance_caculate(cash, balance): total = balance - cash - cash * 0.05 return total # 初始化余额,如果有余额就不变,没有就初始化一个 (出错,文件为空) def create_dict_in_balance(): filename = balance_file if os.path.exists(filename): if os.path.getsize(filename): return 0 else: fw = open(filename, ‘wb‘) user_balance = {‘weiwei‘: 1520000, ‘huahua‘: 52000, ‘xiaoji‘: 100} pickle.dump(user_balance, fw) fw.close() return ‘new one‘ # 存储余额消息 # 每次初始化都替代,要改 def save_balance(user_admin, balance): fr = open(balance_file, ‘rb‘) user_balance = pickle.load(fr) user_balance[user_admin] = balance fr.close() fw = open(balance_file, ‘wb‘) pickle.dump(user_balance, fw) fw.close() # 在每个用户的流水文件中存入一个新的名字相同的列表 def create_list_in_accout(user_admin): filename = u‘%s\\%s.pk‘ % BASE_DIR, user_admin if os.path.exists(filename): # 如果文件存在 with open(filename, ‘rb‘) as f: li = pickle.load(f) if ‘accout_list‘ == li: # 列表存在,不改变 return 0 else: # 文件或列表不存在,创建 fw = open(filename, ‘wb‘) accout_list = [] pickle.dump(accout_list, fw) fw.close() return ‘new list‘ # 存储用户流水 (序列化存储多个数据时最好使用列表等方式) # 要改成‘withdraw’和‘shop’两种形式,增加一个参数 def save_current_accout(user_admin, way, cash, balance): current_accout = ‘time: %s %s: %d balance: %d‘ % (time.strftime(‘%y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S‘), way, cash, balance) fr = open(u‘%s\\%s.pk‘ % BASE_DIR, user_admin, ‘rb‘) accout_list = pickle.load(fr) accout_list.append(current_accout) # 将新的流水写入列表 fr.close() fw = open(u‘%s\\%s.pk‘ % BASE_DIR, user_admin, ‘wb‘) pickle.dump(accout_list, fw) fw.close() return current_accout # 打印用户流水 def print_user_accout(user_admin): f = open(u‘%s\\%s.pk‘ % BASE_DIR, user_admin, ‘rb‘) accout_list = pickle.load(f) f.close() for i in accout_list: print i # 读出某用户文档中的余额 def read_balance(user_admin): f = open(balance_file, ‘rb‘) user_balance = pickle.load(f) f.close() return user_balance[user_admin] # 读出余额的字典 def read_balance_dict(): f = open(balance_file, ‘rb‘) user_balance = pickle.load(f) f.close() return user_balance
5.5主函数
购物这个功能是之后加的,所以直接在注函数实现,这样会让主函数十分冗余,不推荐。
主函数就是一些基本的逻辑判断啊,人机交互之类的

# (全局变量)用户余额信息 shopping = {‘orange‘: 30, ‘milk‘: 50, ‘bike‘: 200, ‘lipstick‘: 350, ‘bag‘: 3000, ‘car‘: 100000, ‘house‘: 1200000} # 主程序 if __name__ == ‘__main__‘: print ‘\n\t\t\t\t‘+change_color.HEADER+‘Welcome to Internet Bank!‘+change_color.ENDC # 欢迎界面 login = 1 # 为0表示已经登录进去了,为1表示尚未登录成功 while login: # 登录主程序 user_admin = raw_input(‘\n\t\t\t‘+change_color.OKBLUE+‘Please input your admin name:‘+change_color.ENDC) # 输入帐号 if admin_is_locked(user_admin): #判断帐号是否被锁定 if admin_is_exist(user_admin): #判断帐号是否存在 times = 3 while times:# 可以输入密码三次 pass_word = raw_input(‘\n\t\t\t‘+change_color.OKBLUE+‘Please input your password:‘+change_color.ENDC) # 输入密码 if password_is_match(user_admin, pass_word): # 密码正确,打印账户资料 print ‘\n\t\t\t\t‘+change_color.HEADER+‘Welcome!‘+change_color.ENDC login = 0 break else: times -= 1 print ‘\n\t\t\t‘+change_color.WARNING+"Password do not match! You still have "+str(times)+" times to try!" + change_color.ENDC if times == 0: # 输入密码三次不正确,锁定用户 lock_user(user_admin) print ‘\n\t\t\t‘+change_color.WARNING+"%s is locked " %user_admin + change_color.ENDC sys.exit() # 网上银行界面 if login == 0: create_list_in_accout(user_admin) create_dict_in_balance() user_interface = 1 while user_interface: print ‘\n\t\t\t‘+change_color.OKBLUE+‘‘‘ ################################################# user name: %s user balance: %s Operation: 1.withdraw cash 2.shopping 3.month account 4.exit ################################################# ‘‘‘ % (user_admin, read_balance(user_admin)) + change_color.ENDC # 用户选择要进行的操作 operation = input(‘\n\t\t\t‘+change_color.OKBLUE+‘Please input the number of operation(1/2/3/4):‘+change_color.ENDC) if operation == 1: # 提现操作 cash_interface = 1 while cash_interface: cash = input(‘\n\t\t\t‘+change_color.OKBLUE+‘Please input cash you want:‘+change_color.ENDC) user_balance = read_balance_dict() if user_balance[user_admin] >= caculate_cash_with_fee(cash): # 提现的钱不超过余额 if cash <= 15000: # 小于额度 balance = balance_caculate(cash, user_balance[user_admin]) # 计算新的余额 print ‘\n\t\t\t‘+change_color.OKGREEN+‘You can take your cash! Your card still have %s:‘ % balance + change_color.ENDC # 将余额写入文档 save_balance(user_admin, balance) # 将流水写入文档(做成函数) save_current_accout(user_admin, ‘withdraw cash‘, cash, balance) else: print ‘\n\t\t\t‘+change_color.WARNING+‘You can not take more than 15000!‘+change_color.ENDC else: print ‘\n\t\t\t‘+change_color.WARNING+‘You balance is not enough!‘+change_color.ENDC # 选择是否继续 choice = raw_input(‘\n\t\t\t‘+change_color.OKBLUE+‘Do you want to continue?(y/n):‘+change_color.ENDC) if choice == ‘y‘: # 继续提现 continue else: # 返回主界面 cash_interface = 0 if operation == 2: # 购物车系统 buy_count = {} # 存放已经买的东西的种类 buy_counts = [] # 所有东西都直接加到购物车中 buy_balance = read_balance(user_admin) can_buy = 1 while can_buy: print ‘\n\t\t\t\t‘+change_color.OKBLUE+‘Welcome for shopping!‘+change_color.ENDC print print ‘\n\t\t\t\t‘+change_color.OKBLUE+‘****************************************‘+change_color.ENDC for i in enumerate(sorted(shopping.items(), key = lambda item:item[1]), 1): # 将字典中的元素转换成元组排序,编号并输出 print ‘\t\t\t\t‘+change_color.OKBLUE+‘%d %s %d‘% (i[0], i[1][0], i[1][1]) + change_color.ENDC print ‘\t\t\t\t‘+change_color.OKBLUE+‘****************************************‘+change_color.ENDC # 读取用户余额 print ‘\n\t\t\t‘+change_color.OKBLUE+‘You balance: %d‘ % buy_balance +change_color.ENDC # 用户选择要进行的操作 buy = input(‘\n\t\t\t‘+change_color.OKBLUE+‘Please input the number of goods you want to buy(1/2/3/4/...):‘+change_color.ENDC) shopping_list = sorted(shopping.items(), key=lambda item: item[1]) if buy_balance > shopping_list[buy - 1][1]: # 工资卡里的钱可以购买这样东西 # 把东西放到购物车里 buy_counts.append(shopping_list[buy - 1][0]) print ‘\n\t\t\t‘+change_color.OKGREEN+‘%s is added into you shopping car‘ % shopping_list[buy - 1][0] +change_color.ENDC # 计算新的余额 buy_balance -= shopping_list[buy - 1][1] else: # 钱不够, 使用信用额度 credit = raw_input( ‘\n\t\t\t‘+change_color.WARNING+‘Balance is not enough! Using credit(y/n)?‘+change_color.ENDC) if credit ==‘y‘: # 把东西放到购物车里 buy_counts.append(shopping_list[buy - 1][0]) print ‘\n\t\t\t‘+change_color.OKGREEN+‘%s is added into you shopping car‘ % shopping_list[buy - 1][0] +change_color.ENDC # 计算新的余额 buy_balance -= shopping_list[buy - 1][1] choice = raw_input(‘\n\t\t\t‘+change_color.OKBLUE+‘Continue?(y/n)‘+change_color.ENDC) # 是否继续 if choice == ‘y‘: continue if choice == ‘n‘: finish = 1 while finish: print ‘\n\t\t\t‘+change_color.OKBLUE+‘‘‘ ################################################# Operation: 1.watch shopping car 2.add 3.reduce 4.accout 5.exit to user interface 6.exit system ################################################# ‘‘‘ + change_color.ENDC # 用户选择要进行的操作 buy_operation = input(‘\n\t\t\t‘+change_color.OKBLUE+‘Please input the number of operation(1/2/3/4/5):‘+change_color.ENDC) if buy_operation == 1: # 查看购物车 # 购物车列表转换为集合去重 buy_count = set(buy_counts) buy_list = list(buy_count) print ‘\n\t\t\t\t‘+change_color.OKBLUE+‘number name price amount‘ + change_color.ENDC # 打印选购的商品价格和数量 for i in enumerate(buy_list, 1): print ‘\t\t\t\t‘+change_color.OKBLUE+‘%s %s %d %d‘ % (i[0], i[1], shopping[i[1]], buy_counts.count(i)) + change_color.ENDC print ‘\n\t\t\t‘+change_color.OKGREEN+‘All above is: %d‘ % (read_balance(user_admin) - buy_balance) +change_color.ENDC # 打印总价 print ‘\n\t\t\t‘+change_color.WARNING+ ‘10s later will come back to shopping operate interface‘ +change_color.ENDC time.sleep(10) if buy_operation == 2: # 增加购物车里的东西 finish = 0 if buy_operation == 3: # 减去购物车里的东西 undo_finish = 1 while undo_finish: # 读取用户余额 print ‘\n\t\t\t‘+change_color.OKBLUE+‘You balance: %d‘ % buy_balance +change_color.ENDC # 打印购物车 buy_count = set(buy_counts) buy_list = list(buy_count) print ‘\n\t\t\t\t‘+change_color.OKBLUE+‘number name price amount‘ + change_color.ENDC # 打印选购的商品价格和数量 for i in enumerate(buy_list, 1): print ‘\t\t\t\t‘+change_color.OKBLUE+‘%s %s %d %d‘ % (i[0], i[1], shopping[i[1]], buy_counts.count(i)) + change_color.ENDC print ‘\n\t\t\t‘+change_color.OKGREEN+‘All above is: %d‘ % (read_balance(user_admin) - buy_balance) +change_color.ENDC # 打印总价 # 用户选择要进行的操作 undo = input(‘\n\t\t\t‘+change_color.OKBLUE+‘Please input the number of goods you want to reduce(1/2/...):‘+change_color.ENDC) if buy_list[undo - 1] in buy_counts: # 如果商品在购物车中,删除 buy_counts.remove(buy_list[undo - 1]) print ‘\n\t\t\t‘+change_color.OKGREEN+‘%s is delete from you shopping car‘ % shopping_list[undo - 1][0] +change_color.ENDC # 计算新的余额 buy_balance += shopping[buy_list[undo - 1]] else: # 购物车里没有该物品 print ‘\n\t\t\t‘+change_color.WARNING+‘%s is not in you shopping car‘ % buy_list[undo - 1]+change_color.ENDC undo_choice = raw_input(‘\n\t\t\t‘+change_color.OKBLUE+‘Continue?(y/n)‘+change_color.ENDC) # 是否继续 if undo_choice == ‘y‘: continue if undo_choice == ‘n‘: undo_finish = 0 if buy_operation == 4: # 结算 buy_count = set(buy_counts) buy_list = list(buy_count) print ‘\n\t\t\t\t‘+change_color.OKBLUE+‘name price amount‘ + change_color.ENDC # 打印选购的商品价格和数量 for i in buy_list: print ‘\t\t\t\t‘+change_color.OKBLUE+‘%s %d %d‘% (i, shopping[i], buy_counts.count(i)) + change_color.ENDC total = read_balance(user_admin) - buy_balance print ‘\n\t\t\t‘+change_color.OKGREEN+‘All above is: %d‘ % total +change_color.ENDC # 打印总价 pay = raw_input(‘\n\t\t\t‘+change_color.OKGREEN+‘Do you want to pay(y/n)?‘+change_color.ENDC) if pay == ‘y‘: # 确认付款,将流水和余额写入文件 # 余额 save_balance(user_admin, buy_balance) print ‘\n\t\t\t‘+change_color.OKGREEN+‘Successful payment!‘+change_color.ENDC print ‘\n\t\t\t‘+change_color.OKBLUE+‘You balance: %d‘ % buy_balance +change_color.ENDC # 流水写入文件 save_current_accout(user_admin, ‘shopping‘, total, buy_balance) finish = 0 # 返回主界面 can_buy = 0 time.sleep(3) if pay == ‘n‘: # 如果不付款,返回商品操作界面 can_buy = 0 if buy_operation == 5: # 退回主界面 print ‘\n\t\t\t\t‘+change_color.HEADER+‘Thanks for Internet shopping!‘+change_color.ENDC finish = 0 can_buy = 0 if buy_operation == 6: # 退出 print ‘\n\t\t\t\t‘+change_color.HEADER+‘Thanks for Internet shopping!‘+change_color.ENDC sys.exit() if not (buy_operation == 1 or buy_operation == 2 or buy_operation == 3 or buy_operation == 4 or buy_operation == 5 or buy_operation == 6): print ‘\n\t\t\t‘+change_color.WARNING+‘You have to input number as(1/2/3/...)‘+change_color.ENDC time.sleep(3) if operation == 3: # 查看流水账操作 #‘dict‘ object has no attribute ‘readline print_user_accout(user_admin) print ‘\n\t\t\t‘+change_color.WARNING+‘10s later will come back to user interface‘+change_color.ENDC time.sleep(10) if operation == 4: # 退出系统 print ‘\n\t\t\t\t‘+change_color.HEADER+‘Thanks for using Internet Bank!‘+change_color.ENDC sys.exit() if not (operation == 1 or operation == 2 or operation == 3 or operation == 4): print ‘\n\t\t\t‘+change_color.WARNING+‘You have to input number as(1/2/3/...)‘+change_color.ENDC time.sleep(3)
整个系统的逻辑其实很简单,说一下我在这个过程中遇到的问题吧。
由于我刚刚接触这个语言,代码写的非常不整洁,冗余部分很多(我的主函数太长了,长到我自己都有点懵),其实可以把很多部分单独拎出来作为一个函数,这样整个项目的可读性比较好。还有很多不足之处,一时也说不上来,等我回去想想~
我会把整个项目贴在我的github上,欢迎大家来提供意见~
完整项目代码 :https://github.com/huahua462/bank-sopping

