原文地址: http://blog.csdn.net/github_37767025/article/details/67636061
1.查询一张表: select * from 表名;
2.查询指定字段:select 字段1,字段2,字段3….from 表名;
3.where条件查询:select 字段1,字段2,字段3 frome 表名 where 条件表达式;
例:select * from t_studect where id=1;
select * from t_student where age>22;
4.带in关键字查询:select 字段1,字段2 frome 表名 where 字段 [not]in(元素1,元素2);
例:select * from t_student where age in (21,23);
select * from t_student where age not in (21,23);
5.带between and的范围查询:select 字段1,字段2 frome 表名 where 字段 [not]between 取值1 and 取值2;
例:select * frome t_student where age between 21 and 29;
select * frome t_student where age not between 21 and 29;
6.带like的模糊查询:select 字段1,字段2… frome 表名 where 字段 [not] like ‘字符串’;
“%”代表任意字符;
“_”代表单个字符;
例:select * frome t_student where stuName like ‘张三”;
select * frome t_student where stuName like ‘张三%”;
select * frome t_student where stuName like ‘%张三%”;//含有张三的任意字符
select * frome t_student where stuName like ‘张三_”
7.空值查询:select 字段1,字段2…frome 表名 where 字段 is[not] null;
8.带and的多条件查询:
select 字段1,字段2…frome 表名 where 条件表达式1 and 条件表达式2 [and 条件表达式n]
例:select * frome t_student where gradeName=’一年级’ and age=23;
9.带or的多条件查询
select 字段1,字段2…frome 表名 where 条件表达式1 or 条件表达式2 [or 条件表达式n]
例:select * frome t_student where gradeName=’一年级’ or age=23;//或者,条件只要满足一个
10.distinct去重复查询:select distinct 字段名 from 表名;
11.对查询结果排序order by:select 字段1,字段2…from 表名 order by 属性名 [asc|desc]
例:select * frome t_student order by age desc;//降序,从大到小
select * frome t_student order by age asc;//升序,asc默认可以不写
12.分组查询group by
group by 属性名 [having 条件表达式][with rollup]
1.单独使用(毫无意义,不能单独使用);
2.与group_concat()函数一起使用;
例:select gradeName,group_concat(stuName) from t_student group by gradeName;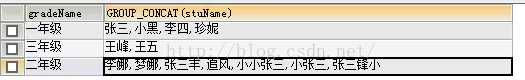
3.与聚合函数一起使用;
例:select gradeName,count(stuName) from t_student group by gradeName;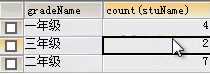
4.与having一起使用(显示输出的结果);
例:select gradeName,count(stuName) from t_student group by gradeName having count(stuName)>3;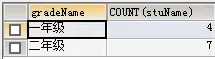
5.与with rollup 一起使用(最后加入一个总和行);
例:select gradeName,group_concat(stuName) from t_student group by gradeName with rollup;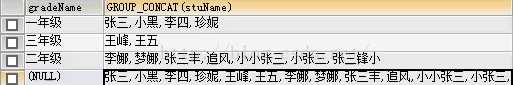
13.limit 分页查询:select 字段1,字段2,…from 表名 limit 初始位置,记录数;
例子:select * from t_student limit 0,5;多表连接查询
表一:t_book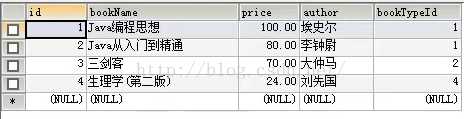
表二:t_bookType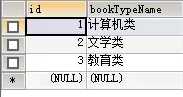
表三:t_priceLevel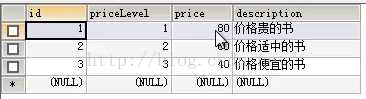
select * from t_book,t_bookType;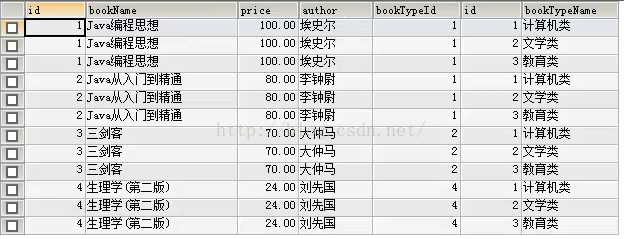1.内连接查询(两张或以上的表连接起来查询需要的数据)
根据表一的bookTypeId查询出所有bookTypeName
select * from t_book,t_bookType where t_book.bookTypeId=t_bookType.id;
查询某几个字段:
select bookNme,author from t_book,t_bookType where t_book.bookTypeId=t_bookType.id;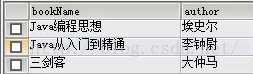
2.外连接查询(两张或以上的表连接起来查询某张表的信息)
3.左连接查询
select * from t_book left join t_bookType on t_book.bookTypeId=t_bookType.id;
如下图:表一(左边表)t_book的数据全部查出 表二没有的字段用null代替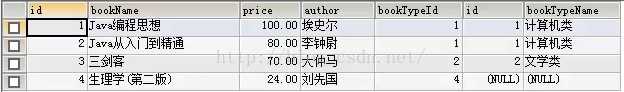
4.右连接查询
select * from t_book right join t_bookType on t_book.bookTypeId=t_bookType.id;
查出表二(右边表)的所有信息,表一没有的用null代替
5.多条件连接查询
select * from t_book,t_bookType where t_book.bookTypeId=t_bookType.id and t_book.price>70;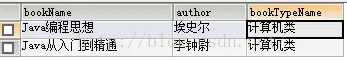
子查询
1.带in关键字的子查询(一个查询语句的条件可能落在另一个select语句的查询结果中)
select * from t_book where bookType in(select id from t_bookType);
select * from t_book where bookType not in(select id from t_bookType);
2.带比较运算符的子查询(子查询可以使用比较运算符)
select * from t_book where price>=(select price from t_priceLevel where priceLevel=1);
3.带exists关键字的子查询(加入子查询查询到记录,则进行外层查询,否则,不执行外层查询)
select * from t_book where exists(select * from t_booktype);
select * from t_book where not exists(select * from t_booktype);
4.带any关键字的子查询(any关键字表示满足其中任一条件)
select * from t_book where price>= any(select price from t_priceLevel);
5.带all关键字的子查询(all关键字表示满足所有条件)
select * from t_book where price>= all(select price from t_priceLevel);
合并查询
1.union
使用union关键字是,数据库系统会将所有的查询结果合并到一起,然后去掉相同的记录;
select id from t_book union select id from t_bookType;
2.union all
使用union all,不会去除掉重复的记录;
select id from t_book union all select id from t_bookType;