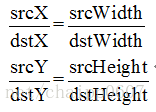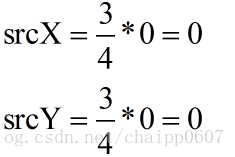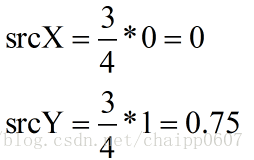图像几何变换(缩放、旋转)中的常用的插值算法
在图像几何变换的过程中,常用的插值方法有最邻近插值(近邻取样法)、双线性内插值和三次卷积法。
最邻近插值:
这是一种最为简单的插值方法,在图像中最小的单位就是单个像素,但是在旋转个缩放的过程中如果出现了小数,那么就对这个浮点坐标进行简单的取整,得到一个整数型坐标,这个整数型坐标对应的像素值就是目标像素的像素值。取整的方式就是:取浮点坐标最邻近的左上角的整数点。
举个例子:
3*3的灰度图像,其每一个像素点的灰度如下所示
我们要通过缩放,将它变成一个4*4的图像,那么其实相当于放大了4/3倍,从这个倍数我们可以得到这样的比例关系:
根据公式可以计算出目标图像中的(0,0)坐标与原图像中对应的坐标为(0,0)
(由于分母不能为0,所以我们将公式改写)
然后我们就可以确定出目标图像中(0,0)坐标的像素灰度了,就是234。
然后我们在确定目标图像中的(0,1)坐标与原图像中对应的坐标,同样套用公式:
我们发现,这里出现了小数,也就是说它对应的原图像的坐标是(0,0.75),显示这是错误的,如果我们不考虑亚像素情况,那么一个像素单位就是图像中最小的单位了,那么按照最临近插值算法,我们找到距离0.75最近的最近的整数,也就是1,那么对应的原图的坐标也就是(0,1),像素灰度为67。
双线性内插值:
对于一个目的像素,设置坐标通过反向变换得到的浮点坐标为(i+u,j+v),其中i、j均为非负整数,u、v为[0,1)区间的浮点数,则这个像素得值 f(i+u,j+v) 可由原图像中坐标为 (i,j)、(i+1,j)、(i,j+1)、(i+1,j+1)所对应的周围四个像素的值决定,即:
f(i+u,j+v) = (1-u)(1-v)f(i,j) + (1-u)vf(i,j+1) + u(1-v)f(i+1,j) + uvf(i+1,j+1)
其中f(i,j)表示源图像(i,j)处的的像素值。
那么还是上面的例子,目标图像中(0,1)对应的原图像浮点坐标是(0,0.75),套用上面的公式这个坐标可以写成(0+0,0+0.75),其中i=0,j=0,u=0,v=0.75
我们套用公式看一下它最后的灰度
f(i+u,j+v) = 0.25*f(0,0)+0.75*f(0,1)=0.25*234+0.75*67
约等于108
这就是双线性内插值法。双线性内插值法计算量大,但缩放后图像质量高,不会出现像素值不连续的的情况。由于双线性插值具有低通滤波器的性质,使高频分量受损,所以可能会使图像轮廓在一定程度上变得模糊。
三次卷积法:
其实这个方法在好像有很多叫法,它在OpenCV中被命名为INTER_CUBIC,就是立方(三次)的意思,现在我把它和三次卷积法认为是同一种算法,引用一个帖子里面的话:
全称双立方(三次)卷积插值。
代码或许有不同写法,实现方式就一种
该算法是对函数 sin x / x 的一种近似,也就是说 原图像对目标图像的影响
等于 目标点对应于原图像点周围 x距离的点,按照 sin x / x 比例 的加权平均 。
这里x代表,周围得点跟目标点, x或者 y 轴 对应于原图的相对位置。
sin x / x 是归一化了的,实际应用的是近似公式
f(i+u,j+v) = [A] * [B] * [C]
[A]=[ S(u + 1) S(u + 0) S(u - 1) S(u - 2) ]
┏ f(i-1, j-1) f(i-1, j+0) f(i-1, j+1) f(i-1, j+2) ┓
[B]=┃ f(i+0, j-1) f(i+0, j+0) f(i+0, j+1) f(i+0, j+2) ┃
┃ f(i+1, j-1) f(i+1, j+0) f(i+1, j+1) f(i+1, j+2) ┃
┗ f(i+2, j-1) f(i+2, j+0) f(i+2, j+1) f(i+2, j+2) ┛
┏ S(v + 1) ┓
[C]=┃ S(v + 0) ┃
┃ S(v - 1) ┃
┗ S(v - 2) ┛
┏ 1-2*Abs(x)^2+Abs(x)^3 , 0<=Abs(x)<1 ┓
S(x)={ 4-8*Abs(x)+5*Abs(x)^2-Abs(x)^3 , 1<=Abs(x)<2 ┃
┗ 0 , Abs(x)>=2 ┛
S(x)是对 Sin(x*Pi)/x 的逼近(Pi是圆周率——π)
private void zoom_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { if (curBitmap != null) { zoom zoomForm = new zoom(); if (zoomForm.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK) { Rectangle rect = new Rectangle(0, 0, curBitmap.Width, curBitmap.Height); BitmapData bmpData = curBitmap.LockBits(rect, ImageLockMode.ReadWrite, curBitmap.PixelFormat); IntPtr ptr = bmpData.Scan0; int bytes = curBitmap.Width * curBitmap.Height; byte[] grayValues = new byte[bytes]; Marshal.Copy(ptr, grayValues, 0, bytes); //得到横向和纵向缩放量 double x = Convert.ToDouble(zoomForm.GetXZoom); double y = Convert.ToDouble(zoomForm.GetYZoom); //图像的几何中心 int halfWidth = (int)(curBitmap.Width / 2); int halfHeight = (int)(curBitmap.Height / 2); int xz = 0; int yz = 0; int tempWidth = 0; int tempHeight = 0; byte[] tempArray = new byte[bytes]; if (zoomForm.GetNearOrBil == true) { //最近邻插值法 for (int i = 0; i < curBitmap.Height; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < curBitmap.Width; j++) { //以图像的几何中心为坐标原点进行坐标变换 //按逆向映射得到输入图像的坐标 tempHeight = i - halfHeight; tempWidth = j - halfWidth;//以图像的几何中心为坐标原点的横坐标 //在不同象限进行四舍五入处理 if (tempWidth > 0) { //进行缩放 xz = (int)(tempWidth / x + 0.5); } else {//tempWidth < 0 ,则-0.5才能四舍五入 xz = (int)(tempWidth / x - 0.5); } if (tempHeight > 0) { yz = (int)(tempHeight / y + 0.5); } else { yz = (int)(tempHeight / y - 0.5); } //坐标逆变换(坐标原点变回原来的(0,0)点了) //经过缩放的坐标,映射到原来以(0,0)点为坐标原点的坐标系上 tempWidth = xz + halfWidth; tempHeight = yz + halfHeight; //得到输出图像像素值 if (tempWidth < 0 || tempWidth >= curBitmap.Width || tempHeight < 0 || tempHeight >= curBitmap.Height) { //缩放后留下的空白部分用白色像素代替 tempArray[i * curBitmap.Width + j] = 255; } else { //tempArray[i * curBitmap.Width + j]是缩放后的坐标 //grayValues[tempHeight * curBitmap.Width + tempWidth]是缩放后对应的原图像素坐标 tempArray[i * curBitmap.Width + j] = grayValues[tempHeight * curBitmap.Width + tempWidth]; } } } } else { //双线性插值法 double tempX, tempY, p, q; for (int i = 0; i < curBitmap.Height; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < curBitmap.Width; j++) { //以图像的几何中心为坐标原点进行坐标变换 //按逆向映射得到输入图像的坐标 tempHeight = i - halfHeight; tempWidth = j - halfWidth; tempX = tempWidth / x; tempY = tempHeight / y; //在不同象限进行四舍五入处理 if (tempWidth > 0) { //进行缩放 xz = (int)tempX; } else { xz = (int)(tempX - 1); } if (tempHeight > 0) { yz = (int)tempY; } else { yz = (int)(tempY - 1); } //f(i+p,j+q)=(1-p)(1-q)f(i,j)+(1-p)qf(i,j+1)+p(1-q)f(i+1,j)+pqf(i+1, j + 1) //得到公式中的p和q p = tempX - xz; q = tempY - yz; //坐标逆变换 tempWidth = xz + halfWidth; tempHeight = yz + halfHeight; if (tempWidth < 0 || (tempWidth + 1) >= curBitmap.Width || tempHeight < 0 || (tempHeight + 1) >= curBitmap.Height) { //缩放后留下的空白部分用白色像素代替 tempArray[i * curBitmap.Width + j] = 255; } else { //应用公式得到双线性插值 tempArray[i * curBitmap.Width + j] = (byte)((1.0 - q) * ((1.0 - p) * grayValues[tempHeight * curBitmap.Width + tempWidth] + p * grayValues[tempHeight * curBitmap.Width + tempWidth + 1]) + q * ((1.0 - p) * grayValues[(tempHeight + 1) * curBitmap.Width + tempWidth] + p * grayValues[(tempHeight + 1) * curBitmap.Width + 1 + tempWidth])); } } } } grayValues = (byte[])tempArray.Clone(); Marshal.Copy(grayValues, 0, ptr, bytes); curBitmap.UnlockBits(bmpData); } Invalidate(); } }