RequestMappingHandlerMapping:这个handlerMapping是基于注解的
同样,先上类图:
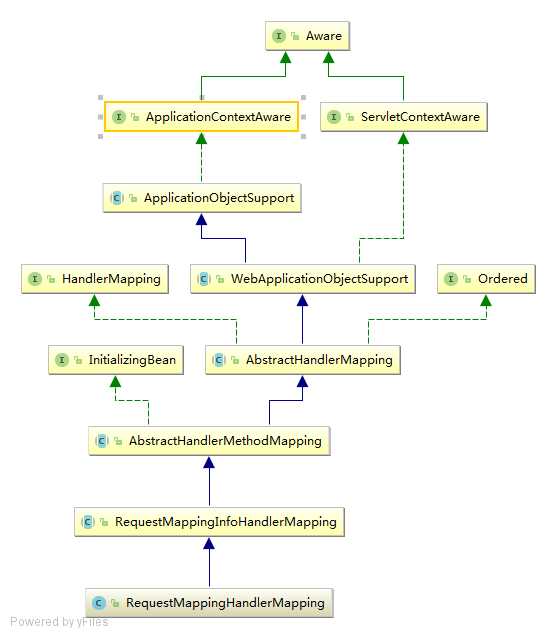
通过类图可以看到,同样是继承父类 AbstractHandlerMapping来进行拦截器的初始化工作,实际上处理自己逻辑的只有下面三个类;
需要注意的是RequestMappingHandlerMapping初始化并不是重写initApplicationContext()方法 ,而是通过实现InitializingBean接口来进行初始工作的。
备注:InitializingBean接口为bean提供了初始化方法的方式,它只包括afterPropertiesSet方法,凡是实现该接口的类,在初始化bean的时候会执行该方法。
来看AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 中关键的代码:
1 public void afterPropertiesSet() { //实现了InitializingBean接口的方法,进行初始化的入口。 2 this.initHandlerMethods(); 3 } 4 5 protected void initHandlerMethods() { 6 if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 7 this.logger.debug("Looking for request mappings in application context: " + this.getApplicationContext()); 8 } 9 //扫描应用下所有Object类 10 String[] beanNames = this.detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts ? BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(this.getApplicationContext(), Object.class) : this.getApplicationContext().getBeanNamesForType(Object.class); 11 String[] arr$ = beanNames; 12 int len$ = beanNames.length; 13 14 for(int i$ = 0; i$ < len$; ++i$) { 15 String beanName = arr$[i$]; 16 if (this.isHandler(this.getApplicationContext().getType(beanName))) { //ishandler由子类实现,是个钩子方法,让子类实现自己的逻辑 17 this.detectHandlerMethods(beanName); 18 } 19 } 20 21 this.handlerMethodsInitialized(this.getHandlerMethods());//初始化处理器对象,目前是钩子方法,但是也没有子类实现这个方法 22 }
isHandler方法是在RequestMappingHandlerMapping中实现的
1 protected boolean isHandler(Class<?> beanType) { //非常简单, 就是看这个类有没有Controller或者RequestMapping注解,有一个就行 2 return AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(beanType, Controller.class) != null || AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(beanType, RequestMapping.class) != null; 3 }
回到AbstractHandlerMethodMapping看:
1 protected void detectHandlerMethods(Object handler) { //开始注册handler 2 Class<?> handlerType = handler instanceof String ? this.getApplicationContext().getType((String)handler) : handler.getClass(); 3 final Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType);
//这块是获取handelr的所有方法,但是有一个过滤器,就是把有匹配条件的的method获取到 4 Set<Method> methods = HandlerMethodSelector.selectMethods(userType, new MethodFilter() { 5 public boolean matches(Method method) { 6 return AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.this.getMappingForMethod(method, userType) != null;//getMappingForMethod钩子方法,子类实现 7 } 8 }); 9 Iterator i$ = methods.iterator(); 10 //遍历method 进行注册。 11 while(i$.hasNext()) { 12 Method method = (Method)i$.next(); 13 T mapping = this.getMappingForMethod(method, userType); 14 this.registerHandlerMethod(handler, method, mapping); 15 } 16 17 }
来看getMappingForMethod的实现,是在RequestMappingHandlerMapping实现的
1 protected RequestMappingInfo getMappingForMethod(Method method, Class<?> handlerType) { 2 RequestMappingInfo info = null; //获取方法上的RequestMapping注解信息 3 RequestMapping methodAnnotation = (RequestMapping)AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(method, RequestMapping.class); 4 if (methodAnnotation != null) { 5 RequestCondition<?> methodCondition = this.getCustomMethodCondition(method); 6 info = this.createRequestMappingInfo(methodAnnotation, methodCondition); 构造匹配条件
// 获取类上的面RequestHandlerMapping注解信息 7 RequestMapping typeAnnotation = (RequestMapping)AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(handlerType, RequestMapping.class); 8 if (typeAnnotation != null) { 9 RequestCondition<?> typeCondition = this.getCustomTypeCondition(handlerType); 10 info = this.createRequestMappingInfo(typeAnnotation, typeCondition).combine(info); 构造匹配条件,同方法的进行合并 11 } 12 } 13 14 return info; 15 }
备注下;RequestMappingInfo 实际上是匹配条件的一个抽象对象,包含了url,method,param,header...等等
来看注册方法前,先看一下处理器是保存在哪的;
1 public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean { 2 //这块实际上是两个map保存的,泛型实际上就是RequestMappingInfo,这个就是匹配条件 HanlderMethod是封装了处理器全部信息的封装类
3 private final Map<T, HandlerMethod> handlerMethods = new LinkedHashMap(); //存的是 key:匹配条件 value: 处理器 4 private final MultiValueMap<String, T> urlMap = new LinkedMultiValueMap(); //key: url value: 匹配条件
这块讲一下MultiValueMap
public interface MultiValueMap<K, V> extends Map<K, List<V>> //实际上就是个 value是个list的map
1 protected void registerHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method, T mapping) { 2 HandlerMethod handlerMethod; 3 if (handler instanceof String) { 4 String beanName = (String)handler; 5 handlerMethod = new HandlerMethod(beanName, this.getApplicationContext(), method); 6 } else { 7 handlerMethod = new HandlerMethod(handler, method); 8 } 9 10 HandlerMethod oldHandlerMethod = (HandlerMethod)this.handlerMethods.get(mapping); 11 if (oldHandlerMethod != null && !oldHandlerMethod.equals(handlerMethod)) { //不允许存在一个mapping对应多个handlerMethod 12 throw new IllegalStateException("Ambiguous mapping found. Cannot map ‘" + handlerMethod.getBean() + "‘ bean method \n" + handlerMethod + "\nto " + mapping + ": There is already ‘" + oldHandlerMethod.getBean() + "‘ bean method\n" + oldHandlerMethod + " mapped."); 13 } else { 14 this.handlerMethods.put(mapping, handlerMethod); //存放第一个映射集合 15 if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) { 16 this.logger.info("Mapped \"" + mapping + "\" onto " + handlerMethod); 17 } 18 19 Set<String> patterns = this.getMappingPathPatterns(mapping); //获取方法的URL 20 Iterator i$ = patterns.iterator(); 21 22 while(i$.hasNext()) { 23 String pattern = (String)i$.next(); 24 if (!this.getPathMatcher().isPattern(pattern)) { //依次放入第二个映射集合 25 this.urlMap.add(pattern, mapping); 26 } 27 } 28 29 } 30 }
到此为止,RequestMappingHandlerMapping就初始化完成了。
疑问: 为什么非注解映射器都是通过重写initApplication方法,而注解映射器是通过实现iniliazingBean接口来初始化,这样的好处是什么?
欢迎探讨
