var num = 1; var str = ‘1‘; var test = 1; test == num //true 相同类型 相同值 test === num //true 相同类型 相同值 test !== num //false test与num类型相同,其值也相同, 非运算肯定是false num == str //true 把str转换为数字,检查其是否相等。 num != str //false == 的 非运算 num === str //false 类型不同,直接返回false num !== str //true num 与 str类型不同 意味着其两者不等 非运算自然是true啦== 和 != 比较若类型不同,先偿试转换类型,再作值比较,最后返回值比较结果 。
而
=== 和 !== 只有在相同类型下,才会比较其值。(值和类型都相同的情况下比较)
==, 两边值类型不同的时候,要先进行类型转换,再比较。
===,不做类型转换,类型不同的一定不等。
JS中Null与Undefined的区别
Undefined:当声明的变量还未被初始化时,变量的默认值为undefined。
null类型也只有一个值,即null。null用来表示尚未存在的对象,常用来表示函数企图返回一个不存在的对象。
var re;
typeof(re) ; //返回 结果为undefined
typeof(null); //返回结果为object
null的数据类型是Object对象,那么JS的五大数据类型是String,Boolean,Number,Null,Undefine
用法:
null表示"没有对象",即该处不应该有值。典型用法是:
(1) 作为函数的参数,表示该函数的参数不是对象。
(2) 作为对象原型链的终点。
举例:
Object.getPrototypeOf(Object.prototype)
// null
undefined表示"缺少值",就是此处应该有一个值,但是还没有定义。典型用法是:
(1)变量被声明了,但没有赋值时,就等于undefined。
(2) 调用函数时,应该提供的参数没有提供,该参数等于undefined。
(3)对象没有赋值的属性,该属性的值为undefined。
(4)函数没有返回值时,默认返回undefined。
举例:
var i;
i // undefined
function f(x){console.log(x)}
f() // undefined
var o = new Object();
o.p // undefined
var x = f();
x // undefined 读取XML文件
XmlDocument xmlDoc = new XmlDocument();
string filePath = Path.Combine(AppContext.BaseDirectory, "Configuration", sDir, string.Format("{0}.xml", sXmlName));
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
using (FileStream fs = File.Open(filePath, FileMode.OpenOrCreate))
{
using (StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(fs, Encoding.UTF8))
{
builder.Append(sr.ReadToEnd());
}
}
if (builder.Length > 0)
xmlDoc.LoadXml(builder.ToString()); //
return xmlDoc;
注意:
xmldoc.load可以加载文件,比如:xmldoc.load("c:\\a.xml");
而xmldoc.loadXML是加载xml格式的字符串,比如:xmldoc.loadXML("<aab>aaa</aab>")
-----------------------
举例说明
1: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
2: <bookstore>
4: <book Type="必修课" ISBN="7-111-19149-2">
5: <title>数据结构</title>
6: <author>严蔚敏</author>
7: <price>30.00</price>
8: </book>
9: <book Type="必修课" ISBN="7-111-19149-3">
10: <title>路由型与交换型互联网基础</title>
11: <author>程庆梅</author>
12: <price>27.00</price>
13: </book>
34: </bookstore>
1: // 得到根节点bookstore
2: XmlNode xn = xmlDoc.SelectSingleNode("bookstore");
5: // 得到根节点的所有子节点
6: XmlNodeList xnl = xn.ChildNodes;
8: foreach (XmlNode xn1 in xnl)
9: {
11: // 将节点转换为元素,便于得到节点的属性值
12: XmlElement xe = (XmlElement)xn1;
13: // 得到Type和ISBN两个属性的属性值
14: bookModel.BookISBN = xe.GetAttribute("ISBN").ToString();
15: bookModel.BookType = xe.GetAttribute("Type").ToString();
16: // 得到Book节点的所有子节点
17: XmlNodeList xnl0 = xe.ChildNodes;
18: bookModel.BookName=xnl0.Item(0).InnerText;
19: bookModel.BookAuthor=xnl0.Item(1).InnerText;
20: bookModel.BookPrice=Convert.ToDouble(xnl0.Item(2).InnerText);
21: bookModeList.Add(bookModel);
22: }
//获取根节点
XmlDocument doc = new XmlDocument();
doc.Load(filePath);
XmlElement root = doc.DocumentElement;
//获取子节点集合
//XmlNodeList xnl = root.ChildNodes;
XmlNodeList personNodes = root.GetElementsByTagName("book"); //两个table
方法一:SelectNodes
xml样式:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<TableLists>
<Columns Name="A01" >
<Item Id="ID1" Filed="Name" MappingName="姓名" Code="Value" />
<Item Id="ID2" Filed="Name" MappingName="年龄" Code="Value"/>
<Item Id="ID3" Filed="Name" MappingName="性别" Code="Value"/>
<Item Id="ID4" Filed="Name" MappingName="部门" Code="Value"/>
</Columns>
<Columns Name="A02" >
<Item Id="ID21" Filed="Name" MappingName="姓名" Code="Value" />
<Item Id="ID22" Filed="Name" MappingName="年龄" Code="Value"/>
<Item Id="ID23" Filed="Name" MappingName="性别" Code="Value"/>
<Item Id="ID24" Filed="Name" MappingName="部门" Code="Value"/>
</Columns>
</TableLists>
XmlDocument doc = new XmlDocument();
doc.Load(fileRelationPath);
XmlNodeList a01Nodes = doc.SelectNodes("TableLists/Columns"); //2个columns
XmlNodeList a01Node = doc.SelectNodes("//Columns"); //2个columns
XmlNodeList a01Nodes = doc.SelectNodes("TableLists/Columns/Item"); //8个Item
XmlNodeList a01Node = doc.SelectNodes("//Item"); //8个Item
foreach (XmlNode xnode in a01Nodes)
{
//获取表名字
XmlElement xe = (XmlElement)xnode;
string tableName = xe.GetAttribute("Name").ToString(); //表名字
}
doc.ChildNodes[1].ChildNodes[0].ChildNodes
说明:
doc.ChildNodes的值[0] <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
[1] TableLists 根元素节点
获取路径的方式
static void Main(string[] args)
4 {
5
string str = System.AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory; //获取程序的基目录
string filePath = System.IO.Path.Combine(str, "Files", "MyPerson.xml");
6 //获取当前运行程序的目录
7 string fileDir = Environment.CurrentDirectory;
8 Console.WriteLine("当前程序目录:"+fileDir);
9
10 //一个文件目录
11 string filePath = "C:\\JiYF\\BenXH\\BenXHCMS.xml";
12 Console.WriteLine("该文件的目录:"+filePath);
13
14 string str = "获取文件的全路径:" + Path.GetFullPath(filePath); //-->C:\JiYF\BenXH\BenXHCMS.xml
15 Console.WriteLine(str);
16 str = "获取文件所在的目录:" + Path.GetDirectoryName(filePath); //-->C:\JiYF\BenXH
17 Console.WriteLine(str);
18 str = "获取文件的名称含有后缀:" + Path.GetFileName(filePath); //-->BenXHCMS.xml
19 Console.WriteLine(str);
20 str = "获取文件的名称没有后缀:" + Path.GetFileNameWithoutExtension(filePath); //-->BenXHCMS
21 Console.WriteLine(str);
22 str = "获取路径的后缀扩展名称:" + Path.GetExtension(filePath); //-->.xml
23 Console.WriteLine(str);
24 str = "获取路径的根目录:" + Path.GetPathRoot(filePath); //-->C:25 Console.WriteLine(str);
26 Console.ReadKey();
27
28 }
或者
string str = System.AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory;
string filePath = System.IO.Path.Combine(str, "Files", "Lists.xml");

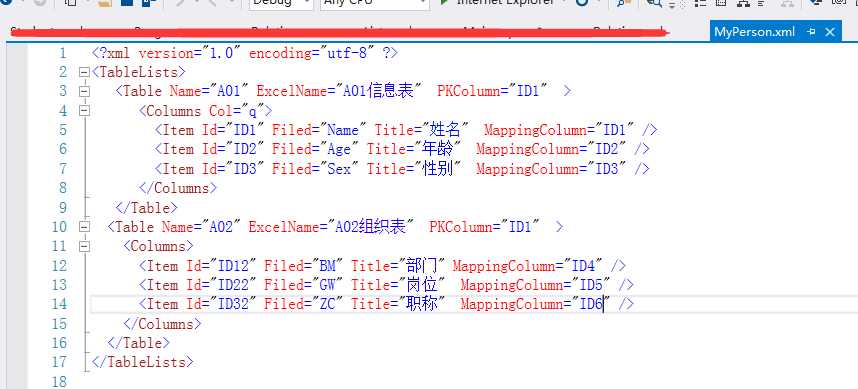
//加载根目录下XML文件
string filePath = System.IO.Path.Combine(str, "Files", "MyPerson.xml");
doc.Load(filePath);
//获取根节点
XmlElement root = doc.DocumentElement;
//获取子节点集合
//XmlNodeList xnl = root.ChildNodes;
XmlNodeList personNodes = root.GetElementsByTagName("Table");
foreach (XmlNode node in personNodes)
{
//XmlNodeList y= node.ChildNodes[0].ChildNodes; //得到是Columns的子节点集合(3个Item)
XmlElement xe = (XmlElement)node;
string tableName = xe.GetAttribute("Name").ToString(); //表名字
XmlElement xeChild = (XmlElement)xe.ChildNodes[0]; //获取的是Columns
string namee = xeChild.GetAttribute("Col").ToString(); //Columns的属性名Item
XmlNodeList x = xeChild.ChildNodes; // 得到Columns节点的所有子节点Item
foreach (XmlNode oo in x)
{
XmlElement xeChildd = (XmlElement)oo;
string sID = xeChildd.GetAttribute("Id").ToString(); //Item的属性名
string sFiled = xeChildd.GetAttribute("Filed").ToString(); //Item的属性名
string sName = xeChildd.GetAttribute("Name").ToString(); //Item的属性名
}
}
C#中Cookie,Session,Application的用法与区别?
1.Application 储存在服务端,没有时间限制,服务器关闭即销毁(前提是自己没写销毁方法)
2.Session 储存在服务端,客户端(浏览器)关闭即销毁(若长时间不使用 且 浏览器未关闭的情况下, 默认自动销毁时间为20分钟)
3.Cookie 储存在客户端,由用户自己销毁
application:
程序全局变量对象,对每个用户每个页面都有效
session:
用户全局变量,对于该用户的所有操作过程都有效
cookie:
客户端信息存放对象,可以把用户的信息保存在用户的本地,
不必总是访问服务器
Application用于保存所有用户共用的数据信息,如果被保存的数据在应用程序生存期内根本不会改变或很少改变,用它。但是在asp.net中有个web.config,可能更好点。如果要使用application,一个需要考虑的问题是任何写操作都有要在application_onstart事件中(Global.asax)中完成。尽管使用application.lock和application.unlock方法来避免操作的同步,但是它串行化了对application的请求,当网站访问量大时会造成性能瓶颈。因此最好不要用它存取大的数据集。
使用方法:
//存放信息
Application["test"] = "100";
//读取
String test = Application["test"].ToString();
Session 用于保存每个用户的专用信息,它的生存期是用户持续请求时间再加上一段时间(可以在web.config中设置,默认是20分钟)。Session中的信息保存在服务器的内存中,当然你也可以设置它的保存方法(如存在SQL数据库中)。由于用户停止使用程序后它仍然在内存中保持一段时间,因此使用Session对象保存用户数据的方法效率很低。对于小量的数据。使用Session还是一个不错的选择。
//存
Session["user"] = "majcms";
//取
String username = Session["user"].ToString();
在web.config中进行如下配置
<system.web>
<sessionState mode="InProc" timeout="30"/>
</system.web>
Cookie用于保存客户浏览器请求服务器页面的请求信息,程序员也可以用它保存非敏感性的内容。保存时间可以根据需要设置。如果没有设置Cookie失效时间,它仅保存至浏览器关闭。如果将Cookie设置为Min Value,则表示它永不过期。Cookie存储量受到很大限制,一般浏览器支持最大容量为4096字节。因此不能用来存储大量数据。由于并非所有浏览器都支持Cookie,并且它是以明文方式保存的,所以最好不要保存敏感性的内容。否则会影响网络安全。
//创建、写入Cookie
HttpCookie cookie = Request.Cookies["MWS_User"];
if (cookie == null)
{
cookie = new HttpCookie("MWS_User");
}
cookie.Values.Set("UserID", strUserID);
Response.SetCookie(cookie);
二、读取cookie:
HttpCookie cookie = Request.Cookies["MWS_User"];
if (cookie != null && cookie["UserID"].ToString() != "")
{
Response.Write("cookie=" + cookie["UserID"].ToString());
}
//存
Response.Cookies["name"].Value = "majcms";
//取
String username = Response.Cookies["name"].Value;
---------------------------------------------------------------------
//写入
protected void Button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
HttpCookie cookie=new HttpCookie("MyCook");//初使化并设置Cookie的名称
DateTime dt=DateTime.Now;
TimeSpan ts = new TimeSpan(0, 0, 1,0,0);//过期时间为1分钟
cookie.Expires = dt.Add(ts);//设置过期时间
cookie.Values.Add("userid", "userid_value");
cookie.Values.Add("userid2","userid2_value2");
Response.AppendCookie(cookie);
//输出该Cookie的所有内容
//Response.Write(cookie.Value);//输出为:userid=userid_value&userid2=userid2_value2
}
//读取
protected void Button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// HttpCookie cokie = new HttpCookie("MyCook");//初使化
if (Request.Cookies["MyCook"]!=null)
{
//Response.Write("Cookie中键值为userid的值:" + Request.Cookies["MyCook"]["userid"]);//整行
//Response.Write("Cookie中键值为userid2的值" + Request.Cookies["MyCook"]["userid2"]);
Response.Write(Request.Cookies["MyCook"].Value);//输出全部的值
}
}
//修改Cookie
protected void Button3_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//获取客户端的Cookie对象
HttpCookie cok = Request.Cookies["MyCook"];
if (cok != null)
{
//修改Cookie的两种方法
cok.Values["userid"] = "alter-value";
cok.Values.Set("userid", "alter-value");
//往Cookie里加入新的内容
cok.Values.Set("newid", "newValue");
Response.AppendCookie(cok);
}
}
//删除Cookie
protected void Button4_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
HttpCookie cok = Request.Cookies["MyCook"];
if (cok != null)
{
if (!CheckBox1.Checked)
{
cok.Values.Remove("userid");//移除键值为userid的值 } else { TimeSpan ts = new TimeSpan(-1, 0, 0, 0); cok.Expires = DateTime.Now.Add(ts);//删除整个Cookie,只要把过期时间设置为现在 } Response.AppendCookie(cok);
}
}
session: 该对象是HttpSession 类型的对象,描述一个客户端与服务器之间的一次通话时
段,该段时间内包含客户端的若干次请求和服务器的相应响应,整个时间段session 对象都
存在。常用来实现购物车之类的存储当前用户的数据。不同用户有各自的不同session 对象。
application: 该对象是ServletContext 类型的对象,描述的是本身Web 程序。该对象在
Web 程序部署到tomcat 服务器时由容器产生,其生命周期至Web 程序从tomcat
服务器卸载出去时消失。是所有客户端能共享的一个
全局对象,整个系统只有一份。
Cookie以文件的形式保存的请求信息
c#反射
反射的定义:审查元数据并收集关於它的类型信息的能力,元数据(编辑后的基本数据单元)就是一大堆表,编译器会创建一个类定义表,一个字段定义表,一个方法定义表等,System.Reflection命名空间包含的几个类,允许你反射(解析)这些元数据的代码。
简单来理解:就是编译器在编译反射相关的代码时,会将所有的类、方法、属性等分别创建一个表,而每个表的元素都对应着一部分元数据中的代码。当我们利用类名称字符串去创建这个类中,程序会在保存类中表中找到我们提供的这个类名称,然后再找到对应的构造函数,并执行。
反射中的类型
MemberInfo-反射类的成员
ConstructorInfo-反射类的构造函数
FieldInfo-反射类的字段
MethodInfo-反射类的构造函数的方法
PropertyInfo-反射类的构造函数的属性
EventInfo-反射类的构造函数的事件
代码
using ReflectionInjection.Helper;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Reflection;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Reflection
{
class Program
{
static void Main1(string[] args)
{
Assembly assembly = Assembly.Load("TestClass"); //TestClass程序集dll文件
Type[] types = assembly.GetTypes();
Type type = types[0];
string className = "Reflection." + "Student";
string className2 = "Reflection." + "Person"; //Person代表的是这个程序集里面要查找的类;Reflection 代表的是程序集
// string className3 = "ReflectionInjection.Helper." + "MacButtonn";
Student stu= Assembly.Load("Reflection").CreateInstance(className) as Student;
Person person = Assembly.Load("Reflection").CreateInstance(className2) as Person;
// MacButtonn macButton = Assembly.Load("ReflectionInjection").CreateInstance(className3) as MacButtonn;
Console.ReadKey();
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Assembly assembly = Assembly.Load("TestClass");
Type[] types = assembly.GetTypes(); //获取数据集中所有的数据类型(即我们在dll中定义的类)
Type type = types[0];
object obj1 = Activator.CreateInstance(type);
FieldInfo[] listFinfo = type.GetFields(); //字段
foreach (FieldInfo finfo in listFinfo)
{
var name = finfo.GetValue(obj1); //字段的值
Console.WriteLine("字段的名字 " + finfo.Name+"字段的值"+name);
}
PropertyInfo[] listPropertyInfo = type.GetProperties(); //属性
foreach (PropertyInfo propertyInfo in listPropertyInfo) {
var name = propertyInfo.GetValue(obj1, null); //属性的值
Console.WriteLine("属性的名字 " + propertyInfo.Name);
}
MethodInfo[] minfos = type.GetMethods(); //方法
foreach (MethodInfo me in minfos)
{
if (me.Name == "Run")
{
object o=me.Invoke(obj1, null); //调用方法
string ss = "nihao";
}
}
Console.WriteLine(type.FullName);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
public class Student
{
public string _name = "dsc";
public string Name
{
get
{
return _name;
}
set
{
_name = value;
}
}
public string Run()
{
return "Hello World";
}
}
}
namespace TestClass
{
class Person
{
public string _name = "dsc";
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
public string Run()
{
return "你好,我是测试类";
}
}
}
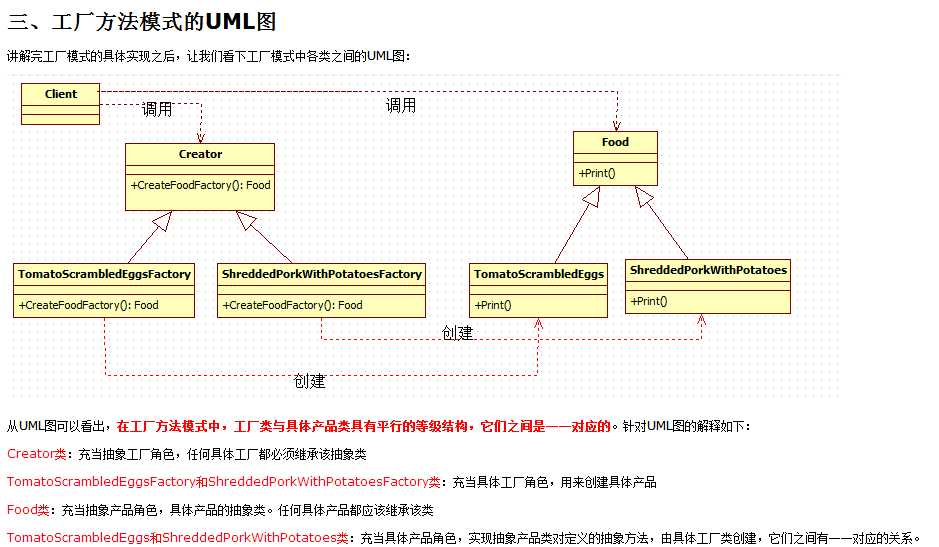
抽象工厂
工厂方法模式之所以可以解决简单工厂的模式,是因为它的实现把具体产品的创建推迟到子类中,此时工厂类不再负责所有产品的创建,而只是给出具体工厂必须实现的接口,这样工厂方法模式就可以允许系统不修改工厂类逻辑的情况下来添加新产品,这样也就克服了简单工厂模式中缺点。下面看下工厂模式的具体实现代码(这里还是以简单工厂模式中点菜的例子来实现):
namespace 设计模式之工厂方法模式
{
/// <summary>
/// 菜抽象类
/// </summary>
public abstract class Food
{
// 输出点了什么菜
public abstract void Print();
}
/// <summary>
/// 西红柿炒鸡蛋这道菜
/// </summary>
public class TomatoScrambledEggs : Food
{
public override void Print()
{
Console.WriteLine("西红柿炒蛋好了!");
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 土豆肉丝这道菜
/// </summary>
public class ShreddedPorkWithPotatoes : Food
{
public override void Print()
{
Console.WriteLine("土豆肉丝好了");
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 抽象工厂类
/// </summary>
public abstract class Creator
{
// 工厂方法
public abstract Food CreateFoddFactory();
}
/// <summary>
/// 西红柿炒蛋工厂类
/// </summary>
public class TomatoScrambledEggsFactory:Creator
{
/// <summary>
/// 负责创建西红柿炒蛋这道菜
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public override Food CreateFoddFactory()
{
return new TomatoScrambledEggs();
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 土豆肉丝工厂类
/// </summary>
public class ShreddedPorkWithPotatoesFactory:Creator
{
/// <summary>
/// 负责创建土豆肉丝这道菜
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public override Food CreateFoddFactory()
{
return new ShreddedPorkWithPotatoes();
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 客户端调用
/// </summary>
class Client
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 初始化做菜的两个工厂()
Creator shreddedPorkWithPotatoesFactory = new ShreddedPorkWithPotatoesFactory();
Creator tomatoScrambledEggsFactory = new TomatoScrambledEggsFactory();
// 开始做西红柿炒蛋
Food tomatoScrambleEggs = tomatoScrambledEggsFactory.CreateFoddFactory();
tomatoScrambleEggs.Print();
//开始做土豆肉丝
Food shreddedPorkWithPotatoes = shreddedPorkWithPotatoesFactory.CreateFoddFactory();
shreddedPorkWithPotatoes.Print();
Console.Read();
}
}
}