标签:des android style blog http color io os java
写在前面的话
非常感谢柯元旦所赠的《Android内核剖析》一书。通过对本书的学习,让我对Android内核有了更深一层次的理解。本文是《Android内核剖析》的学习笔记。
Context是什么
一个Context意味着一个场景,一个场景就是用户和操作系统交互的一个过程。在广义上,这个所谓的过程应该包括前台界面和后台数据。
举个例子,比如当你打电话的时候,场景包括电话程序对应的界面以及隐藏在界面后的数据。
从程序的角度来看,一个Activity就是一个Context,一个Service也是一个Context。
从语义的角度来看一下Context。谷歌程序员把“场景”抽象为Context类,他们认为用户和操作系统的每一次交互都是一个场景,比如打电话,发短信。
从代码的角度来看,Activity类基于Context,而Service类也基于Context类。值得一提的是,Activity除了基于Context类外,还实现了一些其他重要接口。
从设计的角度来看,interface仅仅是某些功能的标记,而extends才是类的本质和实现。
Context相关类的继承关系
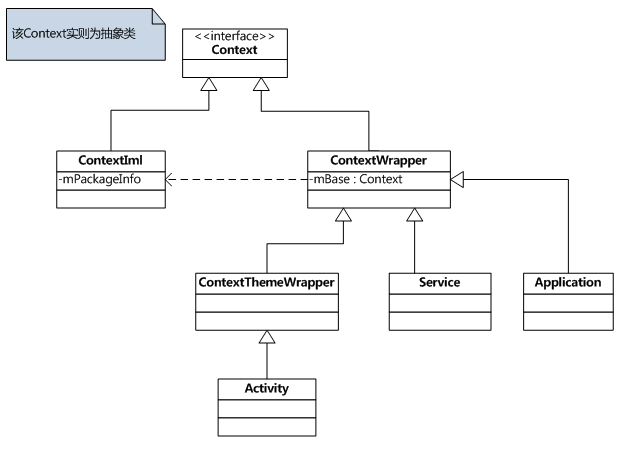
相关类介绍
Context
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/content/Context.java
抽象类,提供了一组通用的API。
/**
* Interface to global information about an application environment. This is
* an abstract class whose implementation is provided by
* the Android system. It
* allows access to application-specific resources and classes, as well as
* up-calls for application-level operations such as launching activities,
* broadcasting and receiving intents, etc.
*/
public abstract class Context { ... }ContextIml.java
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ContextImpl.java
ContextImpl是Context的具体实现类,该类实现了Context类的所有功能。注意,该函数的大部分功能都是直接调用其成员变量mPackageInfo去完成,它是一个delegate。
/**
* Common implementation of Context API, which provides the base
* context object for Activity and other application components.
*/
class ContextImpl extends Context {
private final static String TAG = "ApplicationContext";
private final static boolean DEBUG = false;
private final static boolean DEBUG_ICONS = false;
private static final Object sSync = new Object();
private static AlarmManager sAlarmManager;
private static PowerManager sPowerManager;
private static ConnectivityManager sConnectivityManager;
private static ThrottleManager sThrottleManager;
private static WifiManager sWifiManager;
private static LocationManager sLocationManager;
private static final HashMap<String, SharedPreferencesImpl> sSharedPrefs =
new HashMap<String, SharedPreferencesImpl>();
private AudioManager mAudioManager;
/*package*/ LoadedApk mPackageInfo;
private Resources mResources;
/*package*/ ActivityThread mMainThread;
private Context mOuterContext;
private IBinder mActivityToken = null;
private ApplicationContentResolver mContentResolver;
private int mThemeResource = 0;
private Resources.Theme mTheme = null;
private PackageManager mPackageManager;
private NotificationManager mNotificationManager = null;
private ActivityManager mActivityManager = null;
private WallpaperManager mWallpaperManager = null;
private Context mReceiverRestrictedContext = null;
private SearchManager mSearchManager = null;
private SensorManager mSensorManager = null;
private StorageManager mStorageManager = null;
private Vibrator mVibrator = null;
private LayoutInflater mLayoutInflater = null;
private StatusBarManager mStatusBarManager = null;
private TelephonyManager mTelephonyManager = null;
private ClipboardManager mClipboardManager = null;
private boolean mRestricted;
private AccountManager mAccountManager; // protected by mSync
private DropBoxManager mDropBoxManager = null;
private DevicePolicyManager mDevicePolicyManager = null;
private UiModeManager mUiModeManager = null;
private DownloadManager mDownloadManager = null;
private NfcManager mNfcManager = null;
private final Object mSync = new Object();
private File mDatabasesDir;
private File mPreferencesDir;
private File mFilesDir;
private File mCacheDir;
private File mExternalFilesDir;
private File mExternalCacheDir;
private static long sInstanceCount = 0;
private static final String[] EMPTY_FILE_LIST = {};
...
}
ContextWrapper类
\frameworks\base\core\java\android\content\ContextWrapper.java
该类只是对Context类的一种包装,该类的构造函数包含了一个真正的Context引用,即ContextImpl对象。
/**
* Proxying implementation of Context that simply delegates all of its calls to
* another Context. Can be subclassed to modify behavior without changing
* the original Context.
*/
public class ContextWrapper extends Context {
Context mBase;
public ContextWrapper(Context base) {
mBase = base;
}
/**
* Set the base context for this ContextWrapper. All calls will then be
* delegated to the base context. Throws
* IllegalStateException if a base context has already been set.
*
* @param base The new base context for this wrapper.
*/
protected void attachBaseContext(Context base) {
if (mBase != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Base context already set");
}
mBase = base;
}
/**
* @return the base context as set by the constructor or setBaseContext
*/
public Context getBaseContext() {
return mBase;
}
@Override
public AssetManager getAssets() {
return mBase.getAssets();
}
@Override
public Resources getResources()
{
return mBase.getResources();
}
@Override
public PackageManager getPackageManager() {
return mBase.getPackageManager();
}
@Override
public ContentResolver getContentResolver() {
return mBase.getContentResolver();
}
@Override
public Looper getMainLooper() {
return mBase.getMainLooper();
}
@Override
public Context getApplicationContext() {
return mBase.getApplicationContext();
}
@Override
public void setTheme(int resid) {
mBase.setTheme(resid);
}
...
}ContextThemeWrapper类
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ContextThemeWrapper.java
该类内部包含了主题(Theme)相关的接口,即android:theme属性指定的。只有Activity需要主题,而Service不需要主题,所以Service直接继承自ContextWrapper类。
/**
* A ContextWrapper that allows you to modify the theme from what is in the
* wrapped context.
*/
public class ContextThemeWrapper extends ContextWrapper {
private Context mBase;
private int mThemeResource;
private Resources.Theme mTheme;
private LayoutInflater mInflater;
public ContextThemeWrapper() {
super(null);
}
public ContextThemeWrapper(Context base, int themeres) {
super(base);
mBase = base;
mThemeResource = themeres;
}
@Override protected void attachBaseContext(Context newBase) {
super.attachBaseContext(newBase);
mBase = newBase;
}
@Override public void setTheme(int resid) {
mThemeResource = resid;
initializeTheme();
}
@Override public Resources.Theme getTheme() {
if (mTheme != null) {
return mTheme;
}
if (mThemeResource == 0) {
mThemeResource = com.android.internal.R.style.Theme;
}
initializeTheme();
return mTheme;
}
@Override public Object getSystemService(String name) {
if (LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE.equals(name)) {
if (mInflater == null) {
mInflater = LayoutInflater.from(mBase).cloneInContext(this);
}
return mInflater;
}
return mBase.getSystemService(name);
}
/**
* Called by {@link #setTheme} and {@link #getTheme} to apply a theme
* resource to the current Theme object. Can override to change the
* default (simple) behavior. This method will not be called in multiple
* threads simultaneously.
*
* @param theme The Theme object being modified.
* @param resid The theme style resource being applied to <var>theme</var>.
* @param first Set to true if this is the first time a style is being
* applied to <var>theme</var>.
*/
protected void onApplyThemeResource(Resources.Theme theme, int resid, boolean first) {
theme.applyStyle(resid, true);
}
private void initializeTheme() {
final boolean first = mTheme == null;
if (first) {
mTheme = getResources().newTheme();
Resources.Theme theme = mBase.getTheme();
if (theme != null) {
mTheme.setTo(theme);
}
}
onApplyThemeResource(mTheme, mThemeResource, first);
}
}究其根本,Activity、Service、Application都是Context的子类。所以,一个App中Context的数量就是Activity的数量 + Sercice的数量 + Application的数量(通常是1个)。何时创建Context
应用程序创建Context实例有如下几种情况:
1. 创建Application对象的时机
每个应用程序在第一次启动时,都会首先创建Application对象。如果对应用程序启动一个Activity(startActivity)流程比较清楚的话,创建Application的时机在创建handleBindApplication()方法中,该函数位于 ActivityThread.java类中,代码如下:
2. 创建Activity对象的时机
通过startActivity()或startActivityForResult()请求启动一个Activity时,如果系统检测需要新建一个Activity对象时,就会回调handleLaunchActivity()方法,该方法继而调用performLaunchActivity()方法,去创建一个Activity实例,并且回调onCreate(),onStart()方法等, 函数都位于 ActivityThread.java类,代码如下:
3. 创建Service对象的时机
通过startService或者bindService时,如果系统检测到需要新创建一个Service实例,就会回调handleCreateService()方法,完成相关数据操作。handleCreateService()函数位于 ActivityThread.java类,代码如下:
另外,需要注意的是,通过对ContextImp的分析可知,其方法的大多数操作都是直接调用其属性mPackageInfo(该属性类型为PackageInfo)的相关方法而来。这说明ContextImpl是一个轻量级的类,而PackageInfo才是真正重量级的类。而一个App里的所有ContextIml实例,都对应同一个packageInfo对象。
参考资料
http://blog.csdn.net/qinjuning/article/details/7310620
标签:des android style blog http color io os java
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/manoel/article/details/39431245