文件/目录管理命令:
cd命令主要是改变目录的功能
cd ~ 返回登录目录
cd / 返回系统根目录
cd ../ 或者cd .. 返回上一级目录
cd - 返回上一次访问的目录
pwd命令用于显示用户当前所在的路径、目录
文件内容查看:
cat song.log : 查看song.log文件内容
head s.log :查看s.log文件内容的前10行
head -n 20 s.log :查看s.log文件内容的前20行
tail s.log :查看s.log文件内容的后10行
tail -n 20 s.log :查看s.log文件内容的后20行
more s.log :以翻页的形式查看s.log的内容(按空格键下翻,不能上翻)
less s.log : 以翻页的形式查看s.log的内容(按上下键进行上下翻页,按q退出)
查看文件:
基本语法: find 查找位置 查找参数
find . -name *java* 在当前位置下查找文件名包含java字符的文件
find . -perm 777 在当前位置下查找权限为777 的文件
find / -user ouyang 在系统中查找用户为ouyang的文件
find . -type d 在当前位置下查看找类型为文件夹的文件
查找参数:
-name -perm -user -group -ctime -type -size
新建:
mkdir [option] dir
mkdir a :创建目录文件夹a
mkdir -p a/b/c/d : 当前目录下创建多个目录
touch [option] filename
touch a.txt : 创建文件a.txt
[songshichao@song ~]$ cd dir1 [songshichao@song dir1]$ mkdir dir_1 dir_2 dir_3 #创建目录 [songshichao@song dir1]$ touch file_1 file_2 #创建文件 [songshichao@song dir1]$ touch -d ‘4/4/18 00:00‘ file_3 #创建文件并改变时间戳 [songshichao@song dir1]$ ll 总用量 0 drwxrwxr-x. 2 songshichao songshichao 6 4月 5 21:32 dir_1 drwxrwxr-x. 3 songshichao songshichao 18 4月 5 21:22 dir2 drwxrwxr-x. 2 songshichao songshichao 6 4月 5 21:32 dir_2 drwxrwxr-x. 2 songshichao songshichao 6 4月 5 21:32 dir_3 -rw-rw-r--. 1 songshichao songshichao 0 4月 5 21:33 file_1 -rw-rw-r--. 1 songshichao songshichao 0 4月 5 21:33 file_2 -rw-rw-r--. 1 songshichao songshichao 0 4月 4 00:00 file_3
重命名:
rename aaa bbb
删除:
rm [option] file
r:删除目录时将目录中的所有内容一并删除
f:忽略删除的目录中不存在的子目录,并且删除时不提示用户
[songshichao@song dir1]$ rm file_1
[songshichao@song dir1]$ rmdir dir_2 #删除空白目录 [songshichao@song dir1]$ rm dir_3 #目录含有其他的目录或文件 rm: 无法删除"dir_3": 是一个目录 [songshichao@song dir1]$ rm -rf dir_3 #删除目录及目录中的所有文件和子目录,要配合选项r和f [songshichao@song dir1]$ ll 总用量 0 drwxrwxr-x. 2 songshichao songshichao 6 4月 5 21:32 dir_1 drwxrwxr-x. 3 songshichao songshichao 18 4月 5 21:22 dir2-rw-rw-r--. 1 songshichao songshichao 0 4月 5 21:33 file_2 -rw-rw-r--. 1 songshichao songshichao 0 4月 4 00:00 file_3
移动:
mv filename dir
filename:需要移动的文件或目录名
dir:移动后的位置和文件名,若该参数指定的文件已经存在,则覆盖已经存在的文件,如果不存在,则移动文件并重命名。
[songshichao@song dir1]$ mv dir_1 dir2/ [songshichao@song dir1]$ cd dir2 [songshichao@song dir2]$ ll 总用量 0 drwxrwxr-x. 2 songshichao songshichao 6 4月 5 21:32 dir_1 drwxrwxr-x. 2 songshichao songshichao 6 4月 5 21:22 dir3
[songshichao@song dir1]$ mkdir dir3
[songshichao@song dir1]$ mv -i dir3 dir2/ #覆盖文件
mv:是否覆盖"dir2/dir3"? y
[songshichao@song dir1]$ cd dir2
[songshichao@song dir2]$ ll
总用量 0
drwxrwxr-x. 2 songshichao songshichao 6 4月 5 21:32 dir_1
drwxrwxr-x. 2 songshichao songshichao 6 4月 5 21:58 dir3
复制:
cp [option] filename Directory
filename:要复制的源文件
Directory:复制文件的新位置,如果此参数是一个新目录名,则将文件复制 到新位置时重命名文件
[songshichao@song dir2]$ cp /home/songshichao/dir1/file_2 ./#复制到当前目录下 [songshichao@song dir2]$ cp /home/songshichao/dir1/file_2 ./file_2_1 #复制并重命名 [songshichao@song dir2]$ ll 总用量 0 drwxrwxr-x. 2 songshichao songshichao 6 4月 5 21:32 dir_1 drwxrwxr-x. 2 songshichao songshichao 6 4月 5 21:58 dir3 -rw-rw-r--. 1 songshichao songshichao 0 4月 5 22:07 file_2 -rw-rw-r--. 1 songshichao songshichao 0 4月 5 22:08 file_2_1 [songshichao@song dir1]$ cp -r /home/songshichao/dir1/dir2 /home/songshichao/dir1/dir_2_1 #复制目录dir2到dir1,包括子目录与文件 [songshichao@song dir1]$ ll 总用量 0 drwxrwxr-x. 4 songshichao songshichao 61 4月 5 22:08 dir2 drwxrwxr-x. 4 songshichao songshichao 61 4月 5 22:14 dir_2_1 -rw-rw-r--. 1 songshichao songshichao 0 4月 5 21:33 file_2 -rw-rw-r--. 1 songshichao songshichao 0 4月 4 00:00 file_3
修改文件属性:
chgrp 修改文件属组
chgrp users l.log 修改文件l.log的所属用户组为users
chown 修改属主
chown bin install.log 修改install.log的所有者为bin
chmod 修改权限
Linux文件的基本权限有9个,分别是owenr、group、others三种身份各自有自己的r、w和x。假如文件的权限字符为:“-rwxrwxrwx”,这9个权限是三个三个一组的,我们可以使用数字表示权限:
r->4
w->2
x->1
所以,当文件权限为“-rwxrwx---”时,分数是:
owner->4+2+1=7
group->4+2+1=7
others->0+0+0=0
此时文件的权限数字就是770.
假如有一文件bashrc,权限字符为“-rwxrwxrwx”,我们需要修改为“-rwxr-xr--”,计算得权限数字为754,所以,执行命令:
- # chmod 754 bashrc
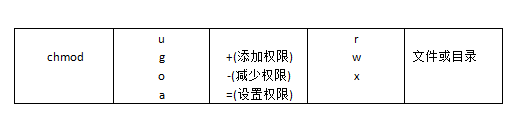
还有一个改变权限的办法。我们知道文件有9个基本权限,分别是owner、group和others三种身份各自的三个权限,我们用u、g、o代表三种身份,用a(all)代表所有身份,得到下表:
例如,我们可以这样设置文件bashrc的权限:
- # chmod u=rwx,go=rx bashrc
即user权限为rwx,group和others的权限均为rx。
如果我们想让每个人都可对文件bashrc写入,则可以:
- # chmod a+w bashrc
而如果要将权限去掉,则用-。例如我们去掉全部人的执行权限:
- # chmod a-x bashrc