类与对象
类相当于一个模板,而对象就是依据类这个模板打造出来的可以使用的工具。类是对象的抽象,对象是类的具体化。
构造函数与析构函数
- 构造函数用来初始化一个对象,构造和默认构造两种。
构造函数与析构函数的调用对等
矩形
#include<iostream> using namespace std; class Rectangle{ double length,width; public : Rectangle(); Rectangle(double l,double w); Rectangle(const Rectangle &); ~Rectangle(); double getArea(); void setData(double ,double); }; Rectangle::Rectangle(double l,double w):length(l),width(w){ cout<<"构造一个Rectangle对象"<<endl; } Rectangle::Rectangle():Rectangle(1.0,2.0){ } Rectangle::Rectangle(const Rectangle &r) { length=r.length; width=r.width; cout<<"复制构造一个Rectangle对象"<<endl; } Rectangle::~Rectangle() { cout<<"析构一个Rectangle对象"<<endl; } double Rectangle::getArea() { return length*width; } void Rectangle::setData(double l,double w) { length=l; width=w; } int main() { Rectangle r1; Rectangle r2(5.0,6.0); cout<<"r1的面积是:"<<r1.getArea()<<endl; cout<<"r2的面积是:"<<r2.getArea()<<endl; cout<<"重新设置r1的长和宽。"<<endl; double l,w; cin>>l>>w; r1.setData(l,w); cout<<"修改后r1的面积为:"<<r1.getArea()<<endl; return 0; }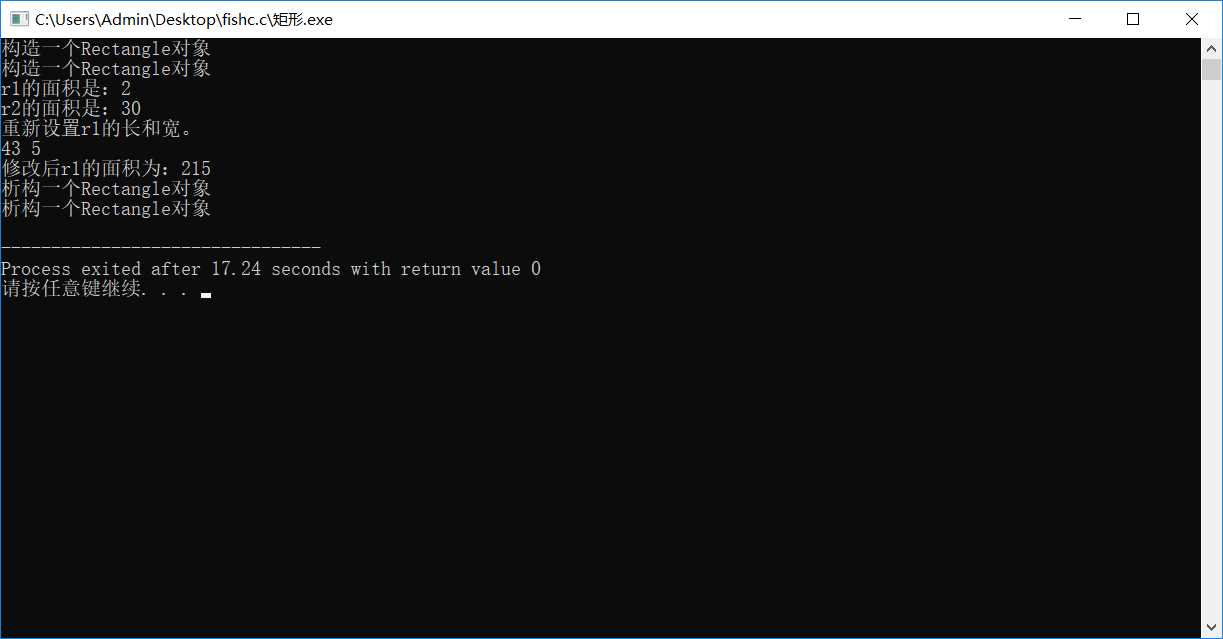
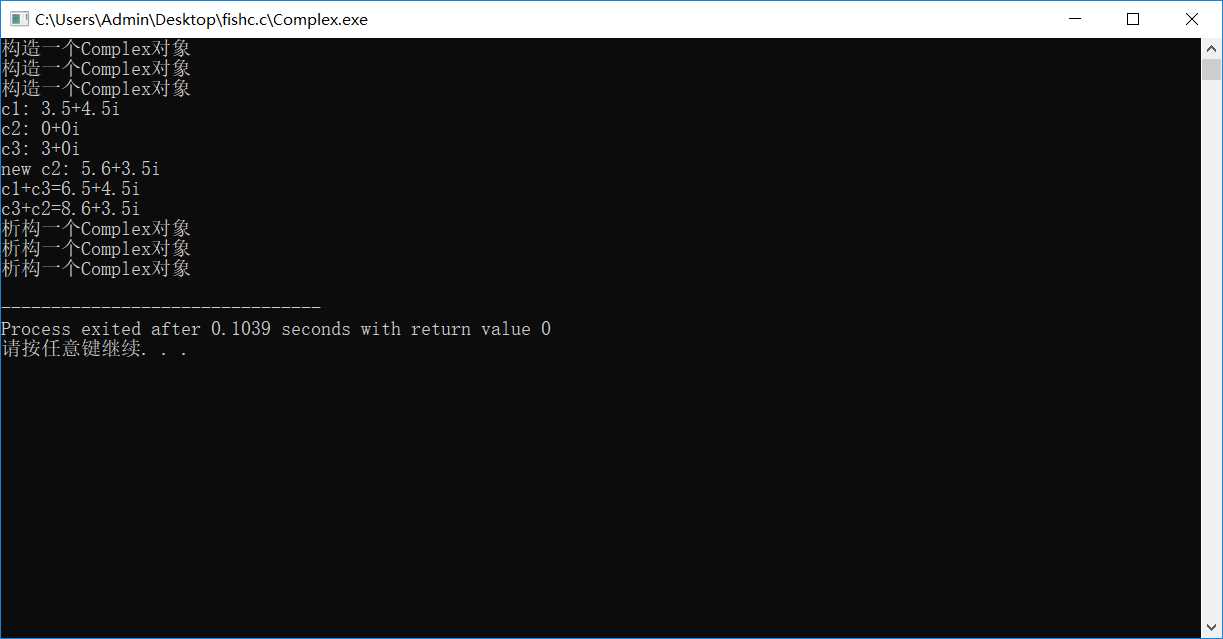
Complex
#include<iostream> using namespace std; class Complex{ double real,imaginary; public : Complex(double r,double i); Complex(double r); Complex(); Complex(const Complex &c); ~Complex(); void set(double r,double i); void add(const Complex &c); void show(); }; Complex::Complex(double r,double i):real(r),imaginary(i){ cout<<"构造一个Complex对象"<<endl; } Complex::Complex(double r):real(r),imaginary(0){ cout<<"构造一个Complex对象"<<endl; } Complex::Complex():Complex(0,0){ } Complex::Complex(const Complex &c) { real=c.real; imaginary=c.imaginary; cout<<"复制构造一个Complex对象"<<endl; } Complex::~Complex() { cout<<"析构一个Complex对象"<<endl; } void Complex::set(double r,double i) { real=r; imaginary=i; } void Complex::add(const Complex &c) { real+=c.real; imaginary+=c.imaginary; } void Complex::show() { cout<<real<<"+"<<imaginary<<"i"<<endl; } int main() { Complex c1(3.5,4.5); Complex c2; Complex c3=3; cout<<"c1: "; c1.show(); cout<<"c2: "; c2.show(); cout<<"c3: "; c3.show(); c2.set(5.6,3.5); cout<<"new c2: "; c2.show(); c1.add(c3); cout<<"c1+c3="; c1.show(); c3.add(c2); cout<<"c3+c2="; c3.show(); return 0; }