标签:来源 语句 限制 cti and 完成 浮点 组成 info
一. 简介
- 实体与实体之间有3种对应关系,这些关系也需要存储下来
- 在开发中需要对存储的数据进行一些处理,用到内置的一些函数
- 视图用于完成查询语句的封装
- 事务可以保证复杂的增删改操作有效
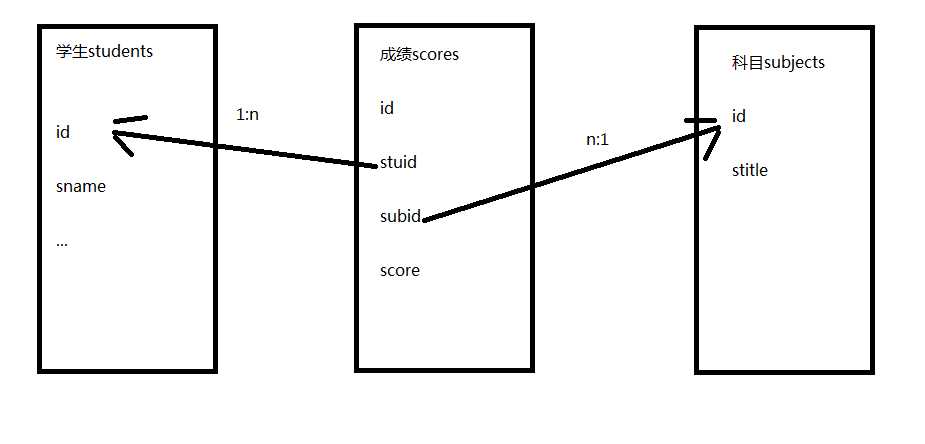
二. 关系
create table scores(
id int primary key auto_increment,
stuid int,
subid int,
score decimal(5,2)
);
外键
alter table scores add constraint stu_sco foreign key(stuid) references students(id);
create table scores(
id int primary key auto_increment,
stuid int,
subid int,
score decimal(5,2),
foreign key(stuid) references students(id),
foreign key(subid) references subjects(id)
);
外键的级联操作
alter table scores add constraint stu_sco foreign key(stuid) references students(id) on delete cascade;
三. 先看个问题
- 问:查询每个学生每个科目的分数
- 分析:学生姓名来源于students表,科目名称来源于subjects,分数来源于scores表,怎么将3个表放到一起查询,并将结果显示在同一个结果集中呢?
- 答:当查询结果来源于多张表时,需要使用连接查询
- 关键:找到表间的关系,当前的关系是
- students表的id---scores表的stuid
- subjects表的id---scores表的subid
- 则上面问题的答案是:
select students.sname,subjects.stitle,scores.score
from scores
inner join students on scores.stuid=students.id
inner join subjects on scores.subid=subjects.id;
- 结论:当需要对有关系的多张表进行查询时,需要使用连接join
连接查询
- 连接查询分类如下:
- 表A inner join 表B:表A与表B匹配的行会出现在结果中
- 表A left join 表B:表A与表B匹配的行会出现在结果中,外加表A中独有的数据,未对应的数据使用null填充
- 表A right join 表B:表A与表B匹配的行会出现在结果中,外加表B中独有的数据,未对应的数据使用null填充
- 在查询或条件中推荐使用“表名.列名”的语法
- 如果多个表中列名不重复可以省略“表名.”部分
- 如果表的名称太长,可以在表名后面使用‘ as 简写名‘或‘ 简写名‘,为表起个临时的简写名称
练习
select students.sname,avg(scores.score)
from scores
inner join students on scores.stuid=students.id
group by students.sname;
select students.sname,avg(scores.score)
from scores
inner join students on scores.stuid=students.id
where students.gender=1
group by students.sname;
select subjects.stitle,avg(scores.score)
from scores
inner join subjects on scores.subid=subjects.id
group by subjects.stitle;
select subjects.stitle,avg(scores.score),max(scores.score)
from scores
inner join subjects on scores.subid=subjects.id
where subjects.isdelete=0
group by subjects.stitle;
四. 子查询
-
查询支持嵌套使用
-
查询各学生的语文、数学、英语的成绩
select sname,
(select sco.score from scores sco inner join subjects sub on sco.subid=sub.id where sub.stitle=‘语文‘ and stuid=stu.id) as 语文,
(select sco.score from scores sco inner join subjects sub on sco.subid=sub.id where sub.stitle=‘数学‘ and stuid=stu.id) as 数学,
(select sco.score from scores sco inner join subjects sub on sco.subid=sub.id where sub.stitle=‘英语‘ and stuid=stu.id) as 英语
from students stu;
五. 内置函数
字符串函数
- 查看字符的ascii码值ascii(str),str是空串时返回0
select ascii(‘a‘);
select char(97);
- 拼接字符串concat(str1,str2...)
select concat(12,34,‘ab‘);
select length(‘abc‘);
- 截取字符串
- left(str,len)返回字符串str的左端len个字符
- right(str,len)返回字符串str的右端len个字符
- substring(str,pos,len)返回字符串str的位置pos起len个字符
select substring(‘abc123‘,2,3);
- 去除空格
- ltrim(str)返回删除了左空格的字符串str
- rtrim(str)返回删除了右空格的字符串str
- trim([方向 remstr from str)返回从某侧删除remstr后的字符串str,方向词包括both、leading、trailing,表示两侧、左、右
select trim(‘ bar ‘);
select trim(leading ‘x‘ FROM ‘xxxbarxxx‘);
select trim(both ‘x‘ FROM ‘xxxbarxxx‘);
select trim(trailing ‘x‘ FROM ‘xxxbarxxx‘);
- 返回由n个空格字符组成的一个字符串space(n)
select space(10);
- 替换字符串replace(str,from_str,to_str)
select replace(‘abc123‘,‘123‘,‘def‘);
select lower(‘aBcD‘);
数学函数
select abs(-32);
select mod(10,3);
select 10%3;
select floor(2.3);
- 天花板ceiling(n),表示不小于n的最大整数
select ceiling(2.3);
- 求四舍五入值round(n,d),n表示原数,d表示小数位置,默认为0
select round(1.6);
select pow(2,3);
select PI();
select rand();
日期时间函数
- 获取子值,语法如下
- year(date)返回date的年份(范围在1000到9999)
- month(date)返回date中的月份数值
- day(date)返回date中的日期数值
- hour(time)返回time的小时数(范围是0到23)
- minute(time)返回time的分钟数(范围是0到59)
- second(time)返回time的秒数(范围是0到59)
select year(‘2016-12-21‘);
- 日期计算,使用+-运算符,数字后面的关键字为year、month、day、hour、minute、second
select ‘2016-12-21‘+interval 1 day;
select date_format(‘2016-12-21‘,‘%Y %m %d‘);
select current_date();
select current_time();
select now();
六. 视图
- 对于复杂的查询,在多次使用后,维护是一件非常麻烦的事情
- 解决:定义视图
- 视图本质就是对查询的一个封装
- 定义视图
create view stuscore as
select students.*,scores.score from scores
inner join students on scores.stuid=students.id;
select * from stuscore;
七. 事务
- 当一个业务逻辑需要多个sql完成时,如果其中某条sql语句出错,则希望整个操作都退回
- 使用事务可以完成退回的功能,保证业务逻辑的正确性
- 事务四大特性(简称ACID)
- 原子性(Atomicity):事务中的全部操作在数据库中是不可分割的,要么全部完成,要么均不执行
- 一致性(Consistency):几个并行执行的事务,其执行结果必须与按某一顺序串行执行的结果相一致
- 隔离性(Isolation):事务的执行不受其他事务的干扰,事务执行的中间结果对其他事务必须是透明的
- 持久性(Durability):对于任意已提交事务,系统必须保证该事务对数据库的改变不被丢失,即使数据库出现故障
- 要求:表的类型必须是innodb或bdb类型,才可以对此表使用事务
- 查看表的创建语句
show create table students;
alter table ‘表名‘ engine=innodb;
开启begin;
提交commit;
回滚rollback;
示例1
- 步骤1:打开两个终端,连接mysql,使用同一个数据库,操作同一张表
终端1:
select * from students;
------------------------
终端2:
begin;
insert into students(sname) values(‘张飞‘);
终端1:
select * from students;
终端2:
commit;
------------------------
终端1:
select * from students;
示例2
- 步骤1:打开两个终端,连接mysql,使用同一个数据库,操作同一张表
终端1:
select * from students;
------------------------
终端2:
begin;
insert into students(sname) values(‘张飞‘);
终端1:
select * from students;
终端2:
rollback;
------------------------
终端1:
select * from students;
八. 总结
- 关系的存储
- 连接查询
- 自关联
- 子查询
- 常用内置函数
- 视图
- 事务
作业
- 设计班级表,与学生表关联,并进行查询
- 设计分类表,自关联,并进行查询
- 创建视图存储上面的两个
mysql高级内容
标签:来源 语句 限制 cti and 完成 浮点 组成 info
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/regit/p/8819472.html
