标签:effective 端到端 str 迭代 发展 效果 核心 sensor ural
3D Graph Neural Networks for RGBD Semantic Segmentation
2018-04-13 19:19:48
1. Introduction:
随着 depth sensors 的发展,RGBD 语义分割被应用于许多问题上,如:虚拟现实,机器人以及人机交互等等。与现有的2D 语义分割相比,RGBD 语义分割可以通过探索 depth information,来利用现实世界的几何信息来辅助分割。如下图所示,在常规的 2D 图像上,即子图(a),桌子会和微波炉的像素称为近邻,但是在 3D 的世界中,却没有这种 confusion,因为这些像素点在 3D point cloud 中距离很遥远。

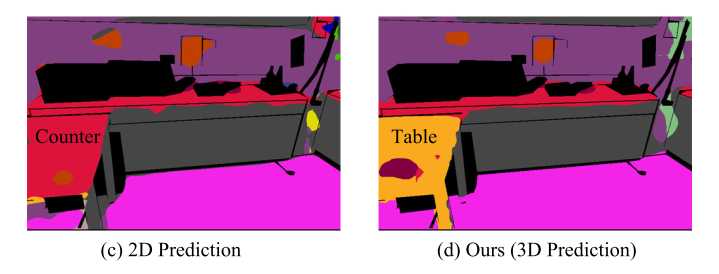
也有许多方法是将 RGBD 分割 和 2D 分割一样来做,将 depth image 当做一种 input image。用 neural network 分别对这两路图像进行特征的提取。这种做法需要两个 CNNs,使得计算量和显存使用都变成了原来的两倍。集合内容上的缺失,可能也会导致错误,如下图所示:2D 的 CNN 模型会将 table 误认为是 counter。
另一种方法是利用 3D CNN 来处理。但是也有一定的局限性:since 3D point clouds are quite sparse, effective representation learning from such data is challenging. In addition, 3D CNNs are computationally more expensive than their 2D version, thus it is difficult to scale up these systems to deal with a large number of classes.
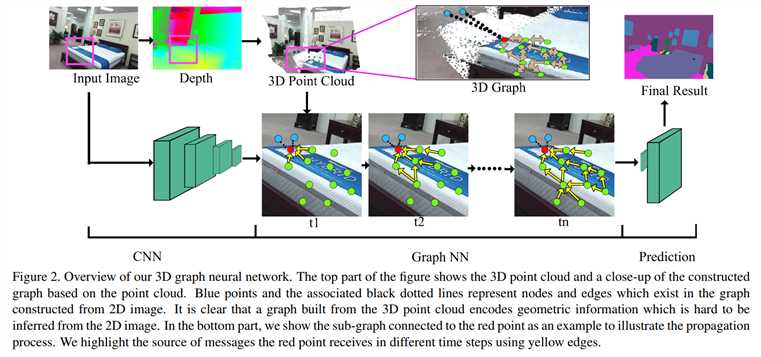
为了解决上述的挑战,我们提出一种端到端的 3D graph neural network,来直接从 3D points 中来学习其表示(directly learns its representation from 3D points)。我们首先根据 depth information 将 2D pixels 转为 3D,然后用一元特征向量将每个 3D point 连接起来,即:an output of a 2D segmentation CNN. 然后我们构建一个 graph,其 nodes 是 3D points,edges 是从 3D 中找到的最近邻。对于每一个 node,我们将图像特征向量作为初始的表达,然后用一个 recurrent function 来迭代的更新它。这个动态计算机制的核心想法是:the node state is determined by its history state and the messages sent by its neighbors, while taking both appearance and 3D information into consideration.
我们用每一个 node 的最终状态来进行每个节点的分类。我们用 BPTT 来计算 graph neural network 的梯度。我们将梯度传递给 the unary CNN 来促进 end to end training. 我们实验结果表明:在有挑战的数据集上,取得了顶尖的分割效果。
2. Related Works:
(略)
3. Graph Neural Networks:
----
论文笔记:3D Graph Neural Networks for RGBD Semantic Segmentation
标签:effective 端到端 str 迭代 发展 效果 核心 sensor ural
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/wangxiaocvpr/p/8822997.html