标签:strong instance animal code 扩展 image ota cas 执行
一、基础概念
多态:
重点是对象的多态性。某一事物的多种体现形态。
多态的作用:
1.提高了代码的扩展性,后期出现的功能,可以被之前的程序所执行。
2.不能使用子类特有的功能。只能使用覆盖父类的功能。
多态的前提:
1.必须要有继承关系或者实现关系。
2.通常对方法进行重写、覆盖。
3.父类或者接口要引用指向子类对象。
多态向上转型:
1.提高程序的扩展性,隐藏了具体子类型
2.只能使用父类中的功能,不能使用子类特有的功能。功能被限定了。
多态向下转型:
1.可以使用子类型的特有功能。
2.必须面对具体的子类型。
3.为了避免运行时出现ClassCastException 问题,需要用关键字instanceof来进行判断。
二、代码实例
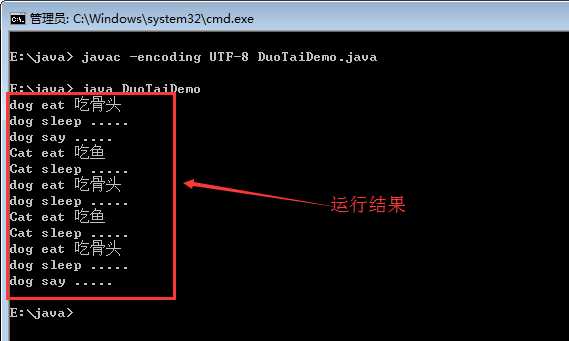
1 //父类Animal 2 abstract class Animal 3 { 4 abstract void eat(); 5 abstract void sleep(); 6 } 7 8 //Dog类继承Animal类 9 class Dog extends Animal 10 { 11 /** 12 将Animal类中的方法重写 13 */ 14 void eat() 15 { 16 System.out.println("dog eat 吃骨头"); 17 } 18 void sleep() 19 { 20 System.out.println("dog sleep ....."); 21 } 22 23 /** 24 自己特有的方法 25 */ 26 void say() 27 { 28 System.out.println("dog say ....."); 29 } 30 } 31 32 //Cat类继承Animal类 33 class Cat extends Animal 34 { 35 /** 36 将Animal类中的方法重写 37 */ 38 void eat() 39 { 40 System.out.println("Cat eat 吃鱼"); 41 } 42 void sleep() 43 { 44 System.out.println("Cat sleep ....."); 45 } 46 } 47 48 class DuoTaiDemo 49 { 50 //封装Dog类的方法 51 public static void method(Dog d) 52 { 53 d.eat(); 54 d.sleep(); 55 d.say(); 56 } 57 58 //封装Cat类的方法 59 public static void method(Cat c) 60 { 61 c.eat(); 62 c.sleep(); 63 } 64 65 //封装父类Animal的方法 66 public static void method(Animal s) 67 { 68 s.eat(); 69 s.sleep(); 70 } 71 72 public static void main(String[] args) 73 { 74 Dog d1 = new Dog(); 75 method(d1); 76 77 Cat c = new Cat(); 78 method(c); 79 80 Animal s = new Dog(); //多态性,向上转型,将Dog提升为Animal。 81 method(s); //只能使用覆盖了父类Animal的eat方法和sleep方法。不能使用Dog类中自己的say方法。 82 83 Animal a = new Cat(); //多态性,向上转型。 84 method(a); 85 86 /** 87 向下转型,为了避免运行时出现ClassCastException 问题, 88 需要用关键字instanceof来进行判断。 89 */ 90 if (s instanceof Dog) 91 { 92 Dog d2 = (Dog)s; 93 d2.eat(); 94 d2.sleep(); 95 d2.say(); 96 } 97 } 98 }
三、运行代码
标签:strong instance animal code 扩展 image ota cas 执行
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhuxr/p/8943897.html