spring:
application:
name: foo
cloud:
config:
uri: ${SPRING_CONFIG_URI:http://localhost:8888}
标签:classname foo 禁用 结果 ebean lte shu ref close
tips:我希望通过这篇文章来给对于bootstrap还不理解的朋友带来帮助。当然这篇文章不仅仅是讲解知识,我更希望给广大朋友带来学习与理解官方文档的一种思路。阅读本文前,建议大家对SpringBoot的启动机制与Environment的作用有大致的了解。关于SpringBoot的启动机制我们可以参考:SpringBoot学习之启动探究
SpringCloud为我们提供了bootstrap.properties的属性文件,我们可以在该属性文件里做我们的服务配置。可是,我们知道SpringBoot已经为我们提供了做服务配置的属性文件application.properties,那么这两个配置文件有什么区别呢?在SpringCloud里是否能用bootstrap代替application做服务的配置?要解决这个问题,我们必须先讨论一下SpringCloud的引导。
ConfigurableApplicationContext是ApplicationContext的子接口,这里面有一个方法叫setParent(), 该方法就的作用是设置它的父级ApplicationContext ,注意一旦设置了它的父上下文,后面就不能再次调用setParent方法了。究竟调用这个方法会产生什么效果呢?下面我们来看一下源代码:
AbstractApplicationContext的setParent:

/** * Set the parent of this application context. * <p>The parent {@linkplain ApplicationContext#getEnvironment() environment} is * {@linkplain ConfigurableEnvironment#merge(ConfigurableEnvironment) merged} with * this (child) application context environment if the parent is non-{@code null} and * its environment is an instance of {@link ConfigurableEnvironment}. * @see ConfigurableEnvironment#merge(ConfigurableEnvironment) */ @Override public void setParent(ApplicationContext parent) { this.parent = parent; if (parent != null) { Environment parentEnvironment = parent.getEnvironment(); if (parentEnvironment instanceof ConfigurableEnvironment) { getEnvironment().merge((ConfigurableEnvironment) parentEnvironment); } } }
我们可以通过源代码得知:一旦设置设置父上下文,当前的Environment会合并父上下文的Environment。
GenericApplicationContext:

//....... /** * Create a new GenericApplicationContext with the given parent. * @param parent the parent application context * @see #registerBeanDefinition * @see #refresh */ public GenericApplicationContext(ApplicationContext parent) { this(); setParent(parent); } // ..... /** * Set the parent of this application context, also setting * the parent of the internal BeanFactory accordingly. * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableBeanFactory#setParentBeanFactory */ @Override public void setParent(ApplicationContext parent) { super.setParent(parent); this.beanFactory.setParentBeanFactory(getInternalParentBeanFactory()); }
通过源代码得知:该类不仅会合并Environment还会把父上下文的BeanFactory"借用过来" ,我们常用的ClasspathXmlApplicationContext是AbstractApplicationContext的子类,而AnnotationConfigApplicationContext是GenericApplicationContext的子类
首先我们先建一个属性文件application.properties,在属性文件里配置:
jdbc.user=root
然后我们按照如下目录建立好相关文件:
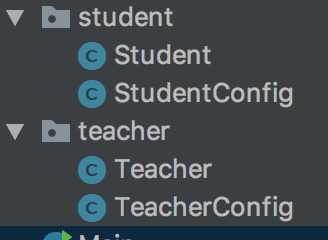
StudentConfig:

package org.hzgj.spring.study.student; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource; @Configuration @ComponentScan @PropertySource("application.properties") public class StudentConfig { }
TeacherConfig:

package org.hzgj.spring.study.teacher; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration @ComponentScan public class TeacherConfig { }
Student:

package org.hzgj.spring.study.student; import org.hzgj.spring.study.teacher.Teacher; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class Student { @Value("${jdbc.user}") private String name; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } private int age=20; public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } }
Teacher:

package org.hzgj.spring.study.teacher; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class Teacher { private String name = "张老师"; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
Main方法:

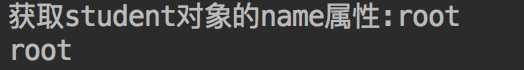
package org.hzgj.spring.study; import org.hzgj.spring.study.student.StudentConfig; import org.hzgj.spring.study.student.Student; import org.hzgj.spring.study.teacher.TeacherConfig; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; import javax.naming.NamingException; import java.io.IOException; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, NamingException { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext studentApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(StudentConfig.class); AnnotationConfigApplicationContext teacherApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(TeacherConfig.class); teacherApplicationContext.setParent(studentApplicationContext); Student student = teacherApplicationContext.getBean(Student.class); System.out.println("获取student对象的name属性:" + student.getName()); System.out.println(studentApplicationContext.getEnvironment().getProperty("jdbc.user")); } }
在这里我们将Teacher的父级上下文设置成student的,运行得到如下结果:
我在这里先贴出官方文档的一段描述:
一个Spring Cloud应用程序通过创建一个“引导”上下文来进行操作,这个上下文是主应用程序的父上下文。开箱即用,负责从外部源加载配置属性,还解密本地外部配置文件中的属性。这两个上下文共享一个Environment,这是任何Spring应用程序的外部属性的来源。Bootstrap属性的优先级高,因此默认情况下不能被本地配置覆盖。
引导上下文使用与主应用程序上下文不同的外部配置约定,因此使用bootstrap.yml application.yml(或.properties)代替引导和主上下文的外部配置。例:bootstrap.yml
spring:
application:
name: foo
cloud:
config:
uri: ${SPRING_CONFIG_URI:http://localhost:8888}
如果您的应用程序需要服务器上的特定于应用程序的配置,那么设置spring.application.name(在bootstrap.yml或application.yml)中是个好主意。
您可以通过设置spring.cloud.bootstrap.enabled=false(例如在系统属性中)来完全禁用引导过程。
初看这段话的朋友,可能会比较蒙圈,没关系我来解释几个关键点:
引导上下文,这个是什么意思呢?我们可以把这个理解为springcloud的"bios"。我们可以先看一下这个引导到底在哪里:
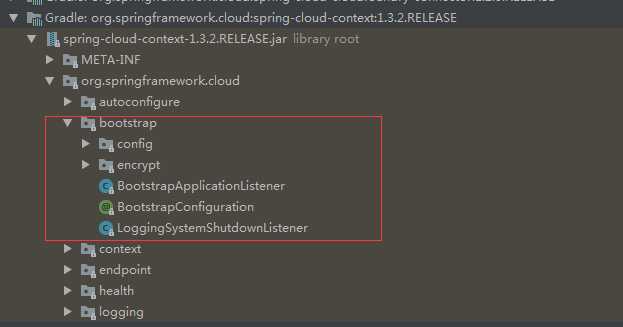
在这里我们可以发现几个关键的类,其中BootstrapApplicationListener是核心中的核心:我在这里贴一下源代码:

/* * Copyright 2013-2014 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Collection; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.LinkedHashMap; import java.util.LinkedHashSet; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Set; import org.springframework.beans.factory.ListableBeanFactory; import org.springframework.boot.Banner.Mode; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.builder.ParentContextApplicationContextInitializer; import org.springframework.boot.builder.SpringApplicationBuilder; import org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent; import org.springframework.boot.logging.LoggingApplicationListener; import org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.encrypt.EnvironmentDecryptApplicationInitializer; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener; import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext; import org.springframework.core.Ordered; import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationAwareOrderComparator; import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order; import org.springframework.core.env.CompositePropertySource; import org.springframework.core.env.ConfigurableEnvironment; import org.springframework.core.env.EnumerablePropertySource; import org.springframework.core.env.MapPropertySource; import org.springframework.core.env.MutablePropertySources; import org.springframework.core.env.PropertySource; import org.springframework.core.env.StandardEnvironment; import org.springframework.core.env.SystemEnvironmentPropertySource; import org.springframework.core.io.support.SpringFactoriesLoader; import org.springframework.util.ClassUtils; import org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils; import org.springframework.util.StringUtils; /** * A listener that prepares a SpringApplication (e.g. populating its Environment) by * delegating to {@link ApplicationContextInitializer} beans in a separate bootstrap * context. The bootstrap context is a SpringApplication created from sources defined in * spring.factories as {@link BootstrapConfiguration}, and initialized with external * config taken from "bootstrap.properties" (or yml), instead of the normal * "application.properties". * * @author Dave Syer * */ public class BootstrapApplicationListener implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent>, Ordered { public static final String BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "bootstrap"; public static final int DEFAULT_ORDER = Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 5; public static final String DEFAULT_PROPERTIES = "defaultProperties"; private int order = DEFAULT_ORDER; @Override public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event) { ConfigurableEnvironment environment = event.getEnvironment(); if (!environment.getProperty("spring.cloud.bootstrap.enabled", Boolean.class, true)) { return; } // don‘t listen to events in a bootstrap context if (environment.getPropertySources().contains(BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME)) { return; } ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null; String configName = environment .resolvePlaceholders("${spring.cloud.bootstrap.name:bootstrap}"); for (ApplicationContextInitializer<?> initializer : event.getSpringApplication() .getInitializers()) { if (initializer instanceof ParentContextApplicationContextInitializer) { context = findBootstrapContext( (ParentContextApplicationContextInitializer) initializer, configName); } } if (context == null) { context = bootstrapServiceContext(environment, event.getSpringApplication(), configName); } apply(context, event.getSpringApplication(), environment); } private ConfigurableApplicationContext findBootstrapContext( ParentContextApplicationContextInitializer initializer, String configName) { Field field = ReflectionUtils .findField(ParentContextApplicationContextInitializer.class, "parent"); ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field); ConfigurableApplicationContext parent = safeCast( ConfigurableApplicationContext.class, ReflectionUtils.getField(field, initializer)); if (parent != null && !configName.equals(parent.getId())) { parent = safeCast(ConfigurableApplicationContext.class, parent.getParent()); } return parent; } private <T> T safeCast(Class<T> type, Object object) { try { return type.cast(object); } catch (ClassCastException e) { return null; } } private ConfigurableApplicationContext bootstrapServiceContext( ConfigurableEnvironment environment, final SpringApplication application, String configName) { StandardEnvironment bootstrapEnvironment = new StandardEnvironment(); MutablePropertySources bootstrapProperties = bootstrapEnvironment .getPropertySources(); for (PropertySource<?> source : bootstrapProperties) { bootstrapProperties.remove(source.getName()); } String configLocation = environment .resolvePlaceholders("${spring.cloud.bootstrap.location:}"); Map<String, Object> bootstrapMap = new HashMap<>(); bootstrapMap.put("spring.config.name", configName); if (StringUtils.hasText(configLocation)) { bootstrapMap.put("spring.config.location", configLocation); } bootstrapProperties.addFirst( new MapPropertySource(BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, bootstrapMap)); for (PropertySource<?> source : environment.getPropertySources()) { bootstrapProperties.addLast(source); } ClassLoader classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(); // Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates List<String> names = SpringFactoriesLoader .loadFactoryNames(BootstrapConfiguration.class, classLoader); for (String name : StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray( environment.getProperty("spring.cloud.bootstrap.sources", ""))) { names.add(name); } // TODO: is it possible or sensible to share a ResourceLoader? SpringApplicationBuilder builder = new SpringApplicationBuilder() .profiles(environment.getActiveProfiles()).bannerMode(Mode.OFF) .environment(bootstrapEnvironment) .properties("spring.application.name:" + configName) .registerShutdownHook(false).logStartupInfo(false).web(false); if (environment.getPropertySources().contains("refreshArgs")) { // If we are doing a context refresh, really we only want to refresh the // Environment, and there are some toxic listeners (like the // LoggingApplicationListener) that affect global static state, so we need a // way to switch those off. builder.application() .setListeners(filterListeners(builder.application().getListeners())); } List<Class<?>> sources = new ArrayList<>(); for (String name : names) { Class<?> cls = ClassUtils.resolveClassName(name, null); try { cls.getDeclaredAnnotations(); } catch (Exception e) { continue; } sources.add(cls); } AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(sources); builder.sources(sources.toArray(new Class[sources.size()])); final ConfigurableApplicationContext context = builder.run(); // Make the bootstrap context a parent of the app context addAncestorInitializer(application, context); // It only has properties in it now that we don‘t want in the parent so remove // it (and it will be added back later) bootstrapProperties.remove(BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME); mergeDefaultProperties(environment.getPropertySources(), bootstrapProperties); return context; } private Collection<? extends ApplicationListener<?>> filterListeners( Set<ApplicationListener<?>> listeners) { Set<ApplicationListener<?>> result = new LinkedHashSet<>(); for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : listeners) { if (!(listener instanceof LoggingApplicationListener) && !(listener instanceof LoggingSystemShutdownListener)) { result.add(listener); } } return result; } private void mergeDefaultProperties(MutablePropertySources environment, MutablePropertySources bootstrap) { String name = DEFAULT_PROPERTIES; if (!bootstrap.contains(name)) { return; } PropertySource<?> source = bootstrap.get(name); if (source instanceof MapPropertySource) { Map<String, Object> map = ((MapPropertySource) source).getSource(); // The application name is "bootstrap" (by default) at this point and // we don‘t want that to appear in the parent context at all. map.remove("spring.application.name"); } if (!environment.contains(name)) { environment.addLast(source); } else { PropertySource<?> target = environment.get(name); if (target instanceof MapPropertySource) { Map<String, Object> targetMap = ((MapPropertySource) target).getSource(); if (target == source) { return; } if (source instanceof MapPropertySource) { Map<String, Object> map = ((MapPropertySource) source).getSource(); for (String key : map.keySet()) { if (!target.containsProperty(key)) { targetMap.put(key, map.get(key)); } } } } } mergeAdditionalPropertySources(environment, bootstrap); } private void mergeAdditionalPropertySources(MutablePropertySources environment, MutablePropertySources bootstrap) { PropertySource<?> defaultProperties = environment.get(DEFAULT_PROPERTIES); ExtendedDefaultPropertySource result = defaultProperties instanceof ExtendedDefaultPropertySource ? (ExtendedDefaultPropertySource) defaultProperties : new ExtendedDefaultPropertySource(defaultProperties.getName(), defaultProperties); for (PropertySource<?> source : bootstrap) { if (!environment.contains(source.getName())) { result.add(source); } } for (String name : result.getPropertySourceNames()) { bootstrap.remove(name); } environment.replace(DEFAULT_PROPERTIES, result); bootstrap.replace(DEFAULT_PROPERTIES, result); } private void addAncestorInitializer(SpringApplication application, ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { boolean installed = false; for (ApplicationContextInitializer<?> initializer : application .getInitializers()) { if (initializer instanceof AncestorInitializer) { installed = true; // New parent ((AncestorInitializer) initializer).setParent(context); } } if (!installed) { application.addInitializers(new AncestorInitializer(context)); } } private void apply(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, SpringApplication application, ConfigurableEnvironment environment) { @SuppressWarnings("rawtypes") List<ApplicationContextInitializer> initializers = getOrderedBeansOfType(context, ApplicationContextInitializer.class); application.addInitializers(initializers .toArray(new ApplicationContextInitializer[initializers.size()])); addBootstrapDecryptInitializer(application); } private void addBootstrapDecryptInitializer(SpringApplication application) { DelegatingEnvironmentDecryptApplicationInitializer decrypter = null; for (ApplicationContextInitializer<?> initializer : application .getInitializers()) { if (initializer instanceof EnvironmentDecryptApplicationInitializer) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext> delegate = (ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>) initializer; decrypter = new DelegatingEnvironmentDecryptApplicationInitializer( delegate); } } if (decrypter != null) { application.addInitializers(decrypter); } } private <T> List<T> getOrderedBeansOfType(ListableBeanFactory context, Class<T> type) { List<T> result = new ArrayList<T>(); for (String name : context.getBeanNamesForType(type)) { result.add(context.getBean(name, type)); } AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(result); return result; } public void setOrder(int order) { this.order = order; } @Override public int getOrder() { return this.order; } private static class AncestorInitializer implements ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>, Ordered { private ConfigurableApplicationContext parent; public AncestorInitializer(ConfigurableApplicationContext parent) { this.parent = parent; } public void setParent(ConfigurableApplicationContext parent) { this.parent = parent; } @Override public int getOrder() { // Need to run not too late (so not unordered), so that, for instance, the // ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer runs later and picks up the merged // Environment. Also needs to be quite early so that other initializers can // pick up the parent (especially the Environment). return Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 5; } @Override public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { while (context.getParent() != null && context.getParent() != context) { context = (ConfigurableApplicationContext) context.getParent(); } reorderSources(context.getEnvironment()); new ParentContextApplicationContextInitializer(this.parent) .initialize(context); } private void reorderSources(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) { PropertySource<?> removed = environment.getPropertySources() .remove(DEFAULT_PROPERTIES); if (removed instanceof ExtendedDefaultPropertySource) { ExtendedDefaultPropertySource defaultProperties = (ExtendedDefaultPropertySource) removed; environment.getPropertySources().addLast(new MapPropertySource( DEFAULT_PROPERTIES, defaultProperties.getSource())); for (PropertySource<?> source : defaultProperties.getPropertySources() .getPropertySources()) { if (!environment.getPropertySources().contains(source.getName())) { environment.getPropertySources().addBefore(DEFAULT_PROPERTIES, source); } } } } } /** * A special initializer designed to run before the property source bootstrap and * decrypt any properties needed there (e.g. URL of config server). */ @Order(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 9) private static class DelegatingEnvironmentDecryptApplicationInitializer implements ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext> { private ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext> delegate; public DelegatingEnvironmentDecryptApplicationInitializer( ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext> delegate) { this.delegate = delegate; } @Override public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) { this.delegate.initialize(applicationContext); } } private static class ExtendedDefaultPropertySource extends SystemEnvironmentPropertySource { private final CompositePropertySource sources; private final List<String> names = new ArrayList<>(); public ExtendedDefaultPropertySource(String name, PropertySource<?> propertySource) { super(name, findMap(propertySource)); this.sources = new CompositePropertySource(name); } public CompositePropertySource getPropertySources() { return this.sources; } public List<String> getPropertySourceNames() { return this.names; } public void add(PropertySource<?> source) { if (source instanceof EnumerablePropertySource && !this.names.contains(source.getName())) { this.sources.addPropertySource(source); this.names.add(source.getName()); } } @Override public Object getProperty(String name) { if (this.sources.containsProperty(name)) { return this.sources.getProperty(name); } return super.getProperty(name); } @Override public boolean containsProperty(String name) { if (this.sources.containsProperty(name)) { return true; } return super.containsProperty(name); } @Override public String[] getPropertyNames() { List<String> names = new ArrayList<>(); names.addAll(Arrays.asList(this.sources.getPropertyNames())); names.addAll(Arrays.asList(super.getPropertyNames())); return names.toArray(new String[0]); } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") private static Map<String, Object> findMap(PropertySource<?> propertySource) { if (propertySource instanceof MapPropertySource) { return (Map<String, Object>) propertySource.getSource(); } return new LinkedHashMap<String, Object>(); } } }
这个类是一个监听器,它用于监听ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件,而EventPublishingRunListener在SpringBoot启动时会触发该事件。如果不理解的这个类的朋友请务必先了解SpringBoot启动过程
这个工作主要分为两个层面:1.创建上下文引导 2.设置为其为当前程序的父级上下文
1) 我们先看看onApplicationEvent方法,该方法首先读取spring.cloud.bootstrap.enabled的属性值如果为false,那么就直接return。这也就是官方文档里的说明可以用此属性禁用引导的理由。
2)紧接着它会从当前应用程序SpringApplication试着在所有的ApplicationInitializer中获取ParentContextApplicationContextInitializer,如果找到的话就把该类下的parent做为引导上下文。
3)如果没有找到ParentContextApplicationContextInitializer,则通过 bootstrapServiceContext方法来创建引导上下文,其中如下代码请大家留意下:
List<String> names = SpringFactoriesLoader .loadFactoryNames(BootstrapConfiguration.class, classLoader);
看到SpringFactoriesLoader不用想一定会在META-INF/spring.factoies里找配置的BootstrapConfiguration的进行实例化
4)通过如下代码创建引导上下文对象:
SpringApplicationBuilder builder = new SpringApplicationBuilder() .profiles(environment.getActiveProfiles()).bannerMode(Mode.OFF) .environment(bootstrapEnvironment) .properties("spring.application.name:" + configName) .registerShutdownHook(false).logStartupInfo(false).web(false); if (environment.getPropertySources().contains("refreshArgs")) { // If we are doing a context refresh, really we only want to refresh the // Environment, and there are some toxic listeners (like the // LoggingApplicationListener) that affect global static state, so we need a // way to switch those off. builder.application() .setListeners(filterListeners(builder.application().getListeners())); } List<Class<?>> sources = new ArrayList<>(); for (String name : names) { Class<?> cls = ClassUtils.resolveClassName(name, null); try { cls.getDeclaredAnnotations(); } catch (Exception e) { continue; } sources.add(cls); } AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(sources); builder.sources(sources.toArray(new Class[sources.size()])); final ConfigurableApplicationContext context = builder.run();
5)最后通过如下方法设置引导上下文为当前应用程序的上下文:
// Make the bootstrap context a parent of the app context addAncestorInitializer(application, context);
开箱即用,理解起来很简单。通过2.2分析,引导程序在SpringBoot的启动前就帮我们创建好了,当然也就开箱即用了。
下面我们看一下spring-cloud-context.jar下的META-INF/spring.factoies文件:

# AutoConfiguration org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=org.springframework.cloud.autoconfigure.ConfigurationPropertiesRebinderAutoConfiguration,org.springframework.cloud.autoconfigure.RefreshAutoConfiguration,org.springframework.cloud.autoconfigure.RefreshEndpointAutoConfiguration,org.springframework.cloud.autoconfigure.LifecycleMvcEndpointAutoConfiguration # Application Listeners org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapApplicationListener,org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.LoggingSystemShutdownListener,org.springframework.cloud.context.restart.RestartListener # Bootstrap components org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapConfiguration=org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.config.PropertySourceBootstrapConfiguration,org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.encrypt.EncryptionBootstrapConfiguration,org.springframework.cloud.autoconfigure.ConfigurationPropertiesRebinderAutoConfiguration,org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration
我们来看一下 BootstrapConfiguration下面配置的引导程序类:
org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.config.PropertySourceBootstrapConfiguration:这个类主要解析加载外部化配置属性
org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.encrypt.EncryptionBootstrapConfiguration:主要配置文件中前缀为{cipher}的相关解密,熟悉spring-boot-starter-security在springcloud应用的朋友一定不陌生
org.springframework.cloud.autoconfigure.ConfigurationPropertiesRebinderAutoConfiguration:主要是监听EnvironmentChangeEvent事件用于刷新@ConfigurationProperties标记的配置
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration:主要解析配置文件中的${}占位符
Environment,这是任何Spring应用程序的外部属性的来源。既然引导上下文为当前主程序的父级上下文,那么就可以确定他们共享Environment,至于为什么请阅读文章第一部分
要解释这个我们必须用代码来演示了,结构图:
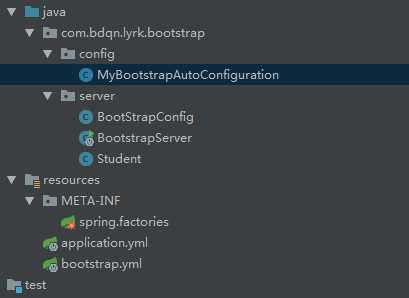
注意:MyBootstrapAutoConfiguration是我们自定义的引导类,该类一定不能被@SpringBootApplication注解ComponentScan到,否则引导必然就会被主程序所覆盖。因此我用包把他们区分开来
MyBootstrapAutoConfiguration代码:

package com.bdqn.lyrk.bootstrap.config; import com.bdqn.lyrk.bootstrap.server.BootStrapConfig; import com.bdqn.lyrk.bootstrap.server.Student; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration @EnableConfigurationProperties(BootStrapConfig.class) public class MyBootstrapAutoConfiguration { @Bean public Student student(BootStrapConfig bootStrapConfig){ Student student = new Student(); student.setName(bootStrapConfig.getName()); return student; } }
BootstrapConfig:

package com.bdqn.lyrk.bootstrap.server; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; @ConfigurationProperties("student") public class BootStrapConfig { private String name; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
Student:

package com.bdqn.lyrk.bootstrap.server; public class Student { private String name; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
application.yml:
student:
name: application
bootstrap.yml:
student:
name: bootstrap
spring.factories:
org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapConfiguration= com.bdqn.lyrk.bootstrap.config.MyBootstrapAutoConfiguration
启动类代码:

package com.bdqn.lyrk.bootstrap.server; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext; @SpringBootApplication() public class BootstrapServer { public static void main(String[] args) { ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext = SpringApplication.run(BootstrapServer.class, args); Student student = applicationContext.getBean(Student.class); System.out.println(student.getName()); } }
运行后得到结果:
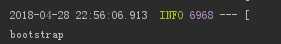
因此我们可以看到对于引导程序bootstrap.yml比application.yml优先级更高,更不可能被application.yml文件里的所覆盖
1)引导程序上下文在prepareEnvironment的阶段就会被创建,创建时会读取bootstrap.properties|yml 在内容作为引导配置, 因此bootstrap优先于application加载。引导程序非常类似于bios,而bootstrap.application就相当于设置bios的相关参数
2)boostrap的属性文件在以下情景下会使用:
配置中心:config-server里请用bootstrap属性文件
解密属性文件时,最好使用bootstrap属性文件
需要自定义引导程序时使用bootstrap属性文件,主要一定不要被我们主程序扫描到
3)application会覆盖bootstrap中的非引导配置,因此不建议两种类型配置文件同时存在。简单粗暴的做法是在springcloud应用中用bootstrap属性文件代替application一统江湖嘛,毕竟Envrionment是共享的。
4) 在阅读官方文档时,一定要结合源代码深入分析,才能更好的理解其用意
标签:classname foo 禁用 结果 ebean lte shu ref close
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/niechen/p/8968204.html