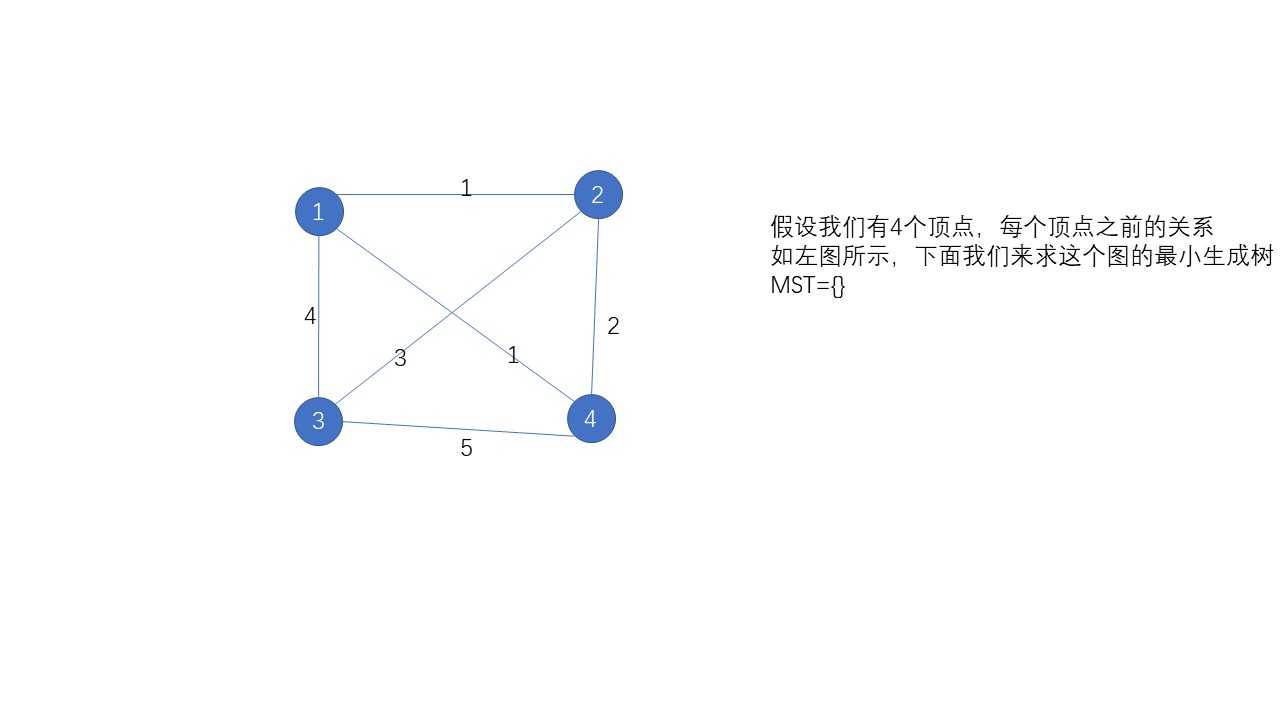
标签:read multiset 输出 nes 图解 with 例题 break min
在解决这个问题之前,我觉得有必要先解释一下什么叫做生成树,什么叫做最小生成树。给定一个图,如果它的某个子图中任意两个顶点都互相联通并且是一棵树,那么这棵树就叫做生成树。如果边上有权值,那么使得权值和最小的树叫做最小生成树。
安全边:当一条边(u,v)加入T时,必须保证T∪{(u,v)}仍是MST的子集,我们将这样的边称为T的安全边。
求MST(minimum spanning tree)的一般算法可描述为:针对图G,从空树T开始,往集合T中逐条选择并加入n-1条安全边(u,v),最终生成一棵含n-1条边的MST。求解最小生成树的方法主要有以下两种:
一、Prim算法:
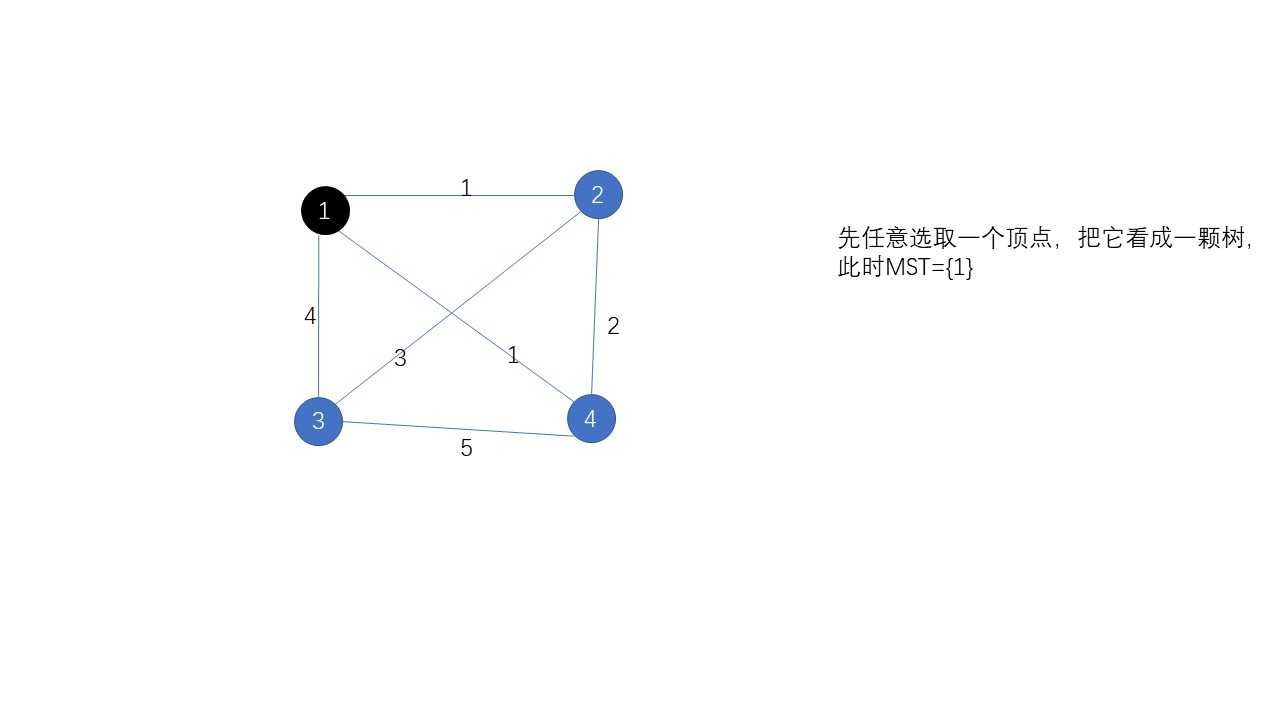
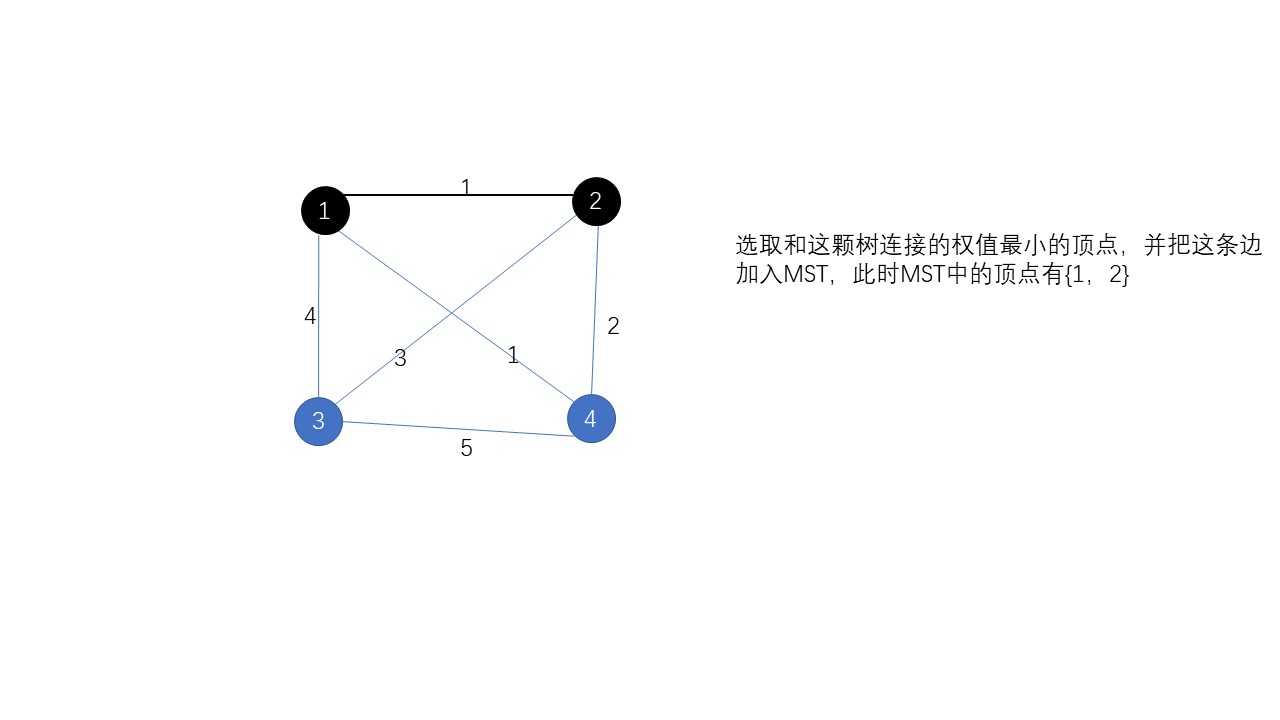
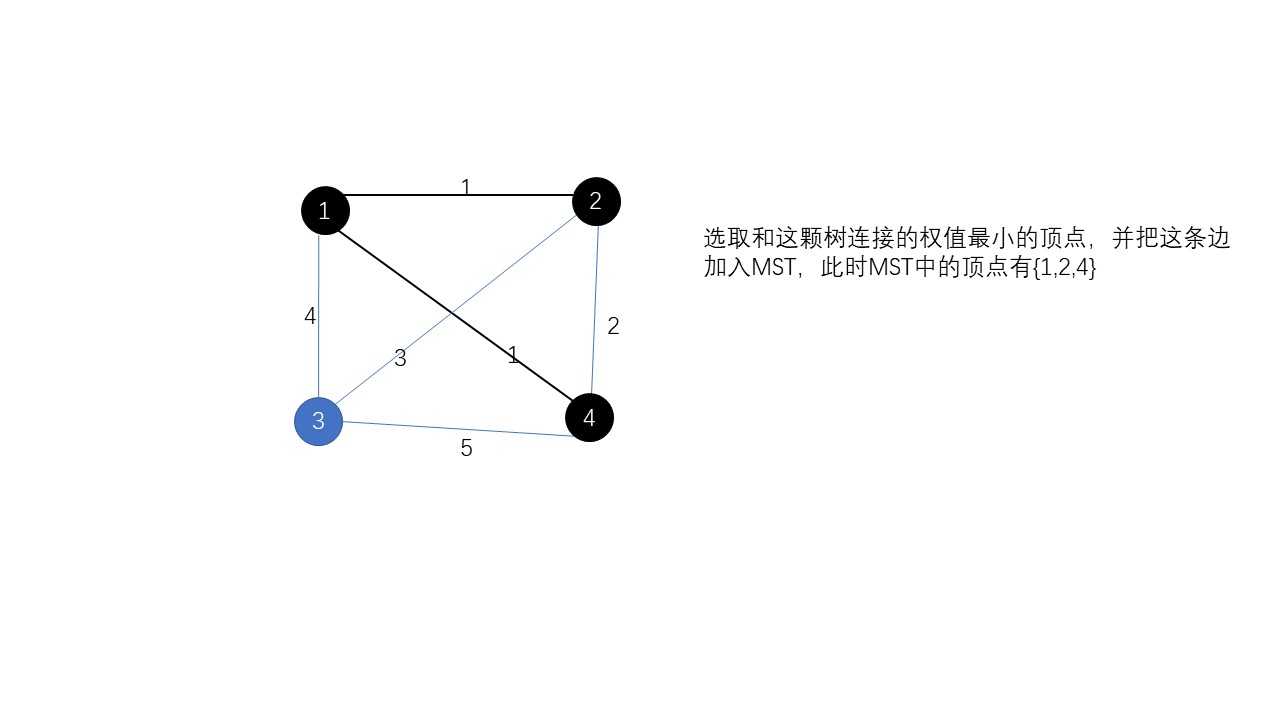
贪心的将MST和其他顶点相连的最小权值的边加入MST,重复操作,直到MST中有n条边。如果我们要高效地使用Prim算法,我们可以使用最小堆。下面看一下这个算法的图解:
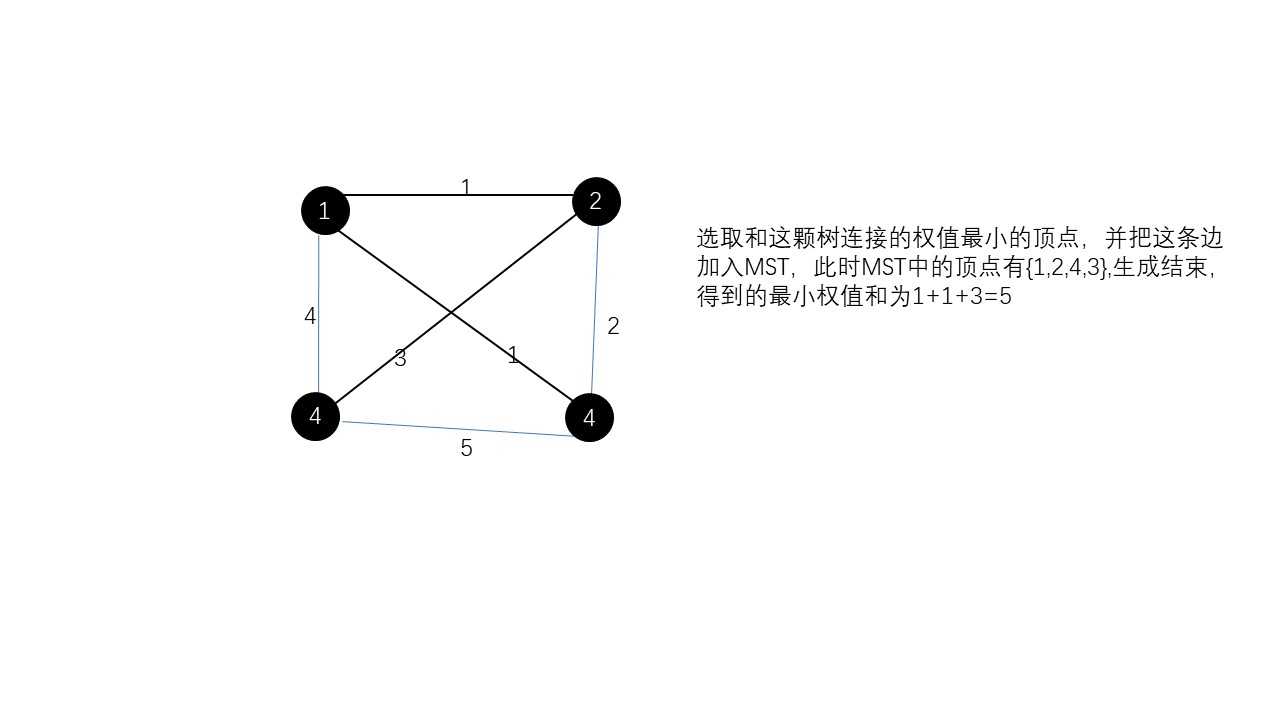
二、kruskal算法
kuskal的贪心策略更加容易理解:每次都选取最小权值的安全边,然后加入MST,直到MST中有n-1条边。当然,高效的查找需要用到并查集,比如下面的第二道例题,而且也需要使用最小堆。下面看kruskal的图解:
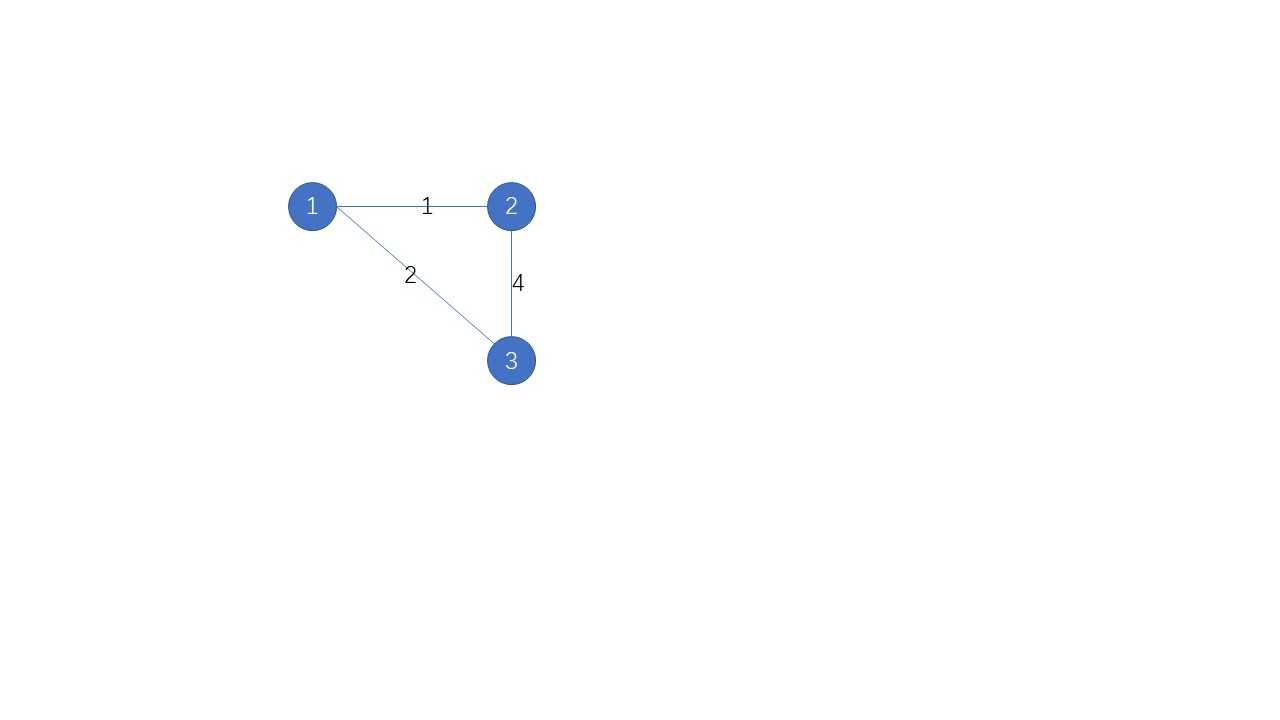
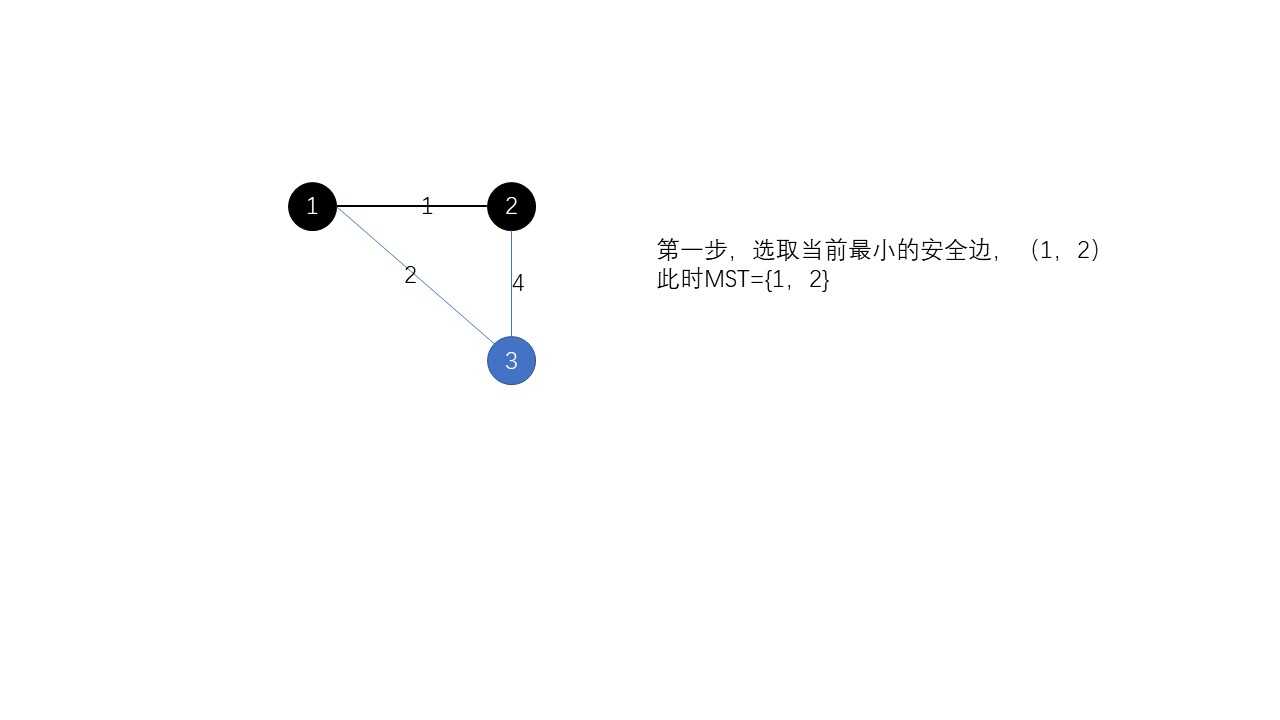
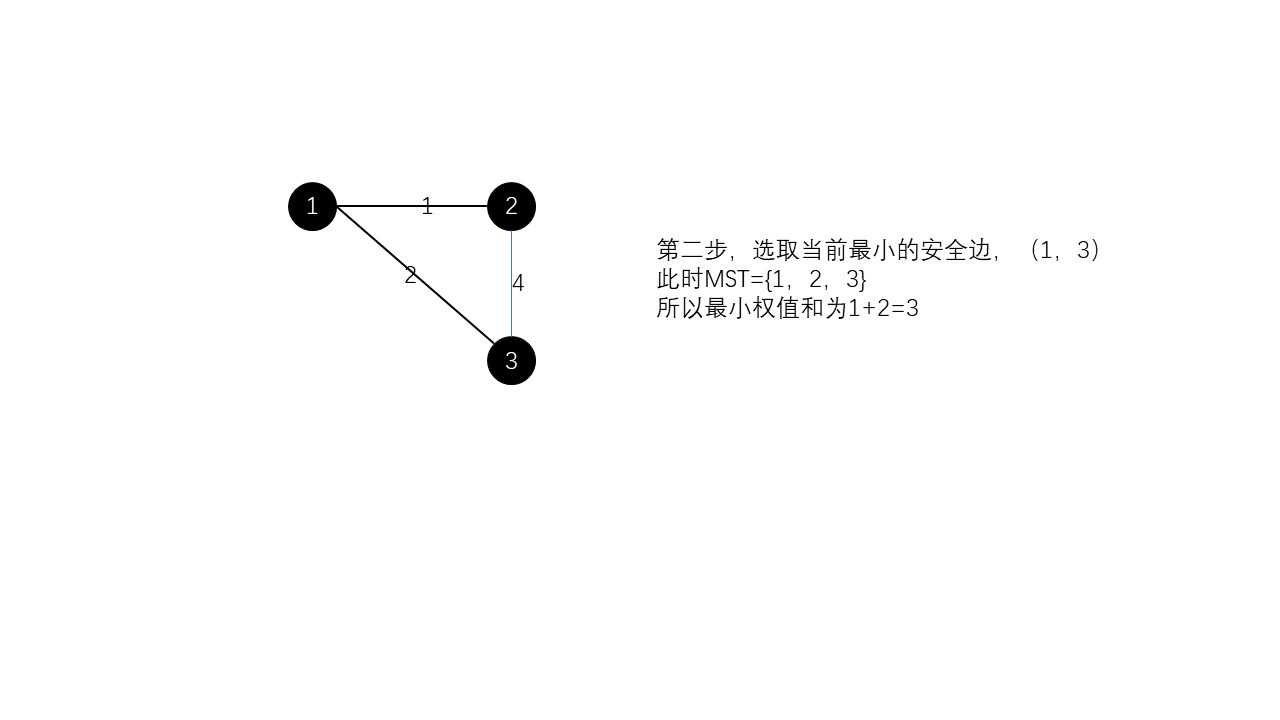
三、经典题目:
1.HDU 1233
还是畅通工程
描述
Input
测试输入包含若干测试用例。每个测试用例的第1行给出村庄数目N ( < 100 );随后的N(N-1)/2行对应村庄间的距离,每行给出一对正整数,分别是两个村庄的编号,以及此两村庄间的距离。为简单起见,村庄从1到N编号。
当N为0时,输入结束,该用例不被处理。
Output
对每个测试用例,在1行里输出最小的公路总长度。
Sample Input
3 1 2 1 1 3 2 2 3 4 4 1 2 1 1 3 4 1 4 1 2 3 3 2 4 2 3 4 5 0
Sample Output
3 5

#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> using namespace std; const int maxn=105; const int INF=0x3fffffff; int graph[maxn][maxn]; int n; int Prim() { int min_cost[maxn]; bool used[maxn]; for(int i=0;i<maxn;i++) { min_cost[i]=INF; used[i]=false; } min_cost[1]=0; int res=0; while(1) { int v=-1; for(int u=1;u<=n;u++) { if(!used[u]&&(v==-1||min_cost[u]<min_cost[v])) v=u; } if(v==-1) break; used[v]=true; res+=min_cost[v]; for(int u=1;u<=n;u++) { min_cost[u]=min(min_cost[u],graph[v][u]); } } return res; } int main() { while(~scanf("%d",&n)&&n) { for(int i=0;i<=n;i++) for(int j=0;j<maxn;j++) graph[i][j]=INF; int vertex1,vertex2,weight; for(int i=1;i<=n*(n-1)/2;i++) { scanf("%d%d%d",&vertex1,&vertex2,&weight); graph[vertex1][vertex2]=weight; graph[vertex2][vertex1]=weight; } printf("%d\n",Prim()); } }
2.Constructing Roads (HDU 1102)
InputThe first line is an integer N (3 <= N <= 100), which is the number of villages. Then come N lines, the i-th of which contains N integers, and the j-th of these N integers is the distance (the distance should be an integer within [1, 1000]) between village i and village j.
Then there is an integer Q (0 <= Q <= N * (N + 1) / 2). Then come Q lines, each line contains two integers a and b (1 <= a < b <= N), which means the road between village a and village b has been built.
OutputYou should output a line contains an integer, which is the length of all the roads to be built such that all the villages are connected, and this value is minimum.
Sample Input
3 0 990 692 990 0 179 692 179 0 1 1 2
Sample Output
179

#include<set> #include<cstdio> using namespace std; struct Node { int x,y,cost; Node() {} Node(int xx,int yy,int cc):x(xx),y(yy),cost(cc){} friend bool operator<(Node a,Node b); }; const int maxn=10000; int fa[maxn]; void init() { for(int i=0;i<maxn;i++) fa[i]=i; } int GetRoot(int x) { if(x!=fa[x]) { return fa[x]=GetRoot(fa[x]); } return fa[x]; } void Unite(int x,int y) { int fx=GetRoot(x); int fy=GetRoot(y); fa[fx]=fy; } int main() { int n; multiset<Node> s; while(~scanf("%d",&n)) { init(); s.clear(); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { for(int j=1;j<=n;j++) { int num; scanf("%d",&num); if(i!=j) { s.insert(Node(i,j,num)); } } } int q,ans=0,counter=0; //counter表示已经连接的边数 scanf("%d",&q); while(q--) { int xx,yy; scanf("%d%d",&xx,&yy); if(GetRoot(xx)!=GetRoot(yy)) counter++; Unite(xx,yy); } multiset<Node>::iterator it=s.begin(); while(counter<n-1) { Node node=(*it); int rx=GetRoot(node.x); int ry=GetRoot(node.y); if(rx!=ry) { Unite(rx,ry); ans+=it->cost; counter++; } it++; } printf("%d\n",ans); } } bool operator<(Node a,Node b) { return a.cost<b.cost; }
标签:read multiset 输出 nes 图解 with 例题 break min
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/Lewin671/p/8976910.html